You are given $n$ pairwise non-collinear two-dimensional vectors. You can make shapes in the two-dimensional plane with these vectors in the following fashion:
- Start at the origin $(0, 0)$.
- Choose a vector and add the segment of the vector to the current point. For example, if your current point is at $(x, y)$ and you choose the vector $(u, v)$, draw a segment from your current point to the point at $(x + u, y + v)$ and set your current point to $(x + u, y + v)$.
- Repeat step 2 until you reach the origin again.
You can reuse a vector as many times as you want.
Count the number of different, non-degenerate (with an area greater than $0$) and convex shapes made from applying the steps, such that the shape can be contained within a $m \times m$ square, and the vectors building the shape are in counter-clockwise fashion. Since this number can be too large, you should calculate it by modulo $998244353$.
Two shapes are considered the same if there exists some parallel translation of the first shape to another.
A shape can be contained within a $m \times m$ square if there exists some parallel translation of this shape so that every point $(u, v)$ inside or on the border of the shape satisfies $0 \leq u, v \leq m$.Input
The first line contains two integers $n$ and $m$ — the number of vectors and the size of the square ($1 \leq n \leq 5$, $1 \leq m \leq 10^9$).
Each of the next $n$ lines contains two integers $x_i$ and $y_i$ — the $x$-coordinate and $y$-coordinate of the $i$-th vector ($|x_i|, |y_i| \leq 4$, $(x_i, y_i) \neq (0, 0)$).
It is guaranteed, that no two vectors are parallel, so for any two indices $i$ and $j$ such that $1 \leq i < j \leq n$, there is no real value $k$ such that $x_i \cdot k = x_j$ and $y_i \cdot k = y_j$.Output
Output a single integer — the number of satisfiable shapes by modulo $998244353$.Examplesinput
3 3 -1 0 1 1 0 -1
output
3
input
3 3 -1 0 2 2 0 -1
output
1
input
3 1776966 -1 0 3 3 0 -2
output
296161
input
4 15 -4 -4 -1 1 -1 -4 4 3
output
1
input
5 10 3 -4 4 -3 1 -3 2 -3 -3 -4
output
0
input
5 1000000000 -2 4 2 -3 0 -4 2 4 -1 -3
output
9248783
Note
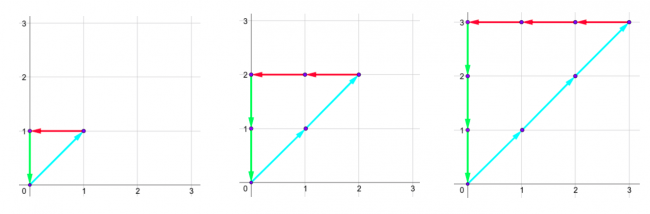
The shapes for the first sample are:
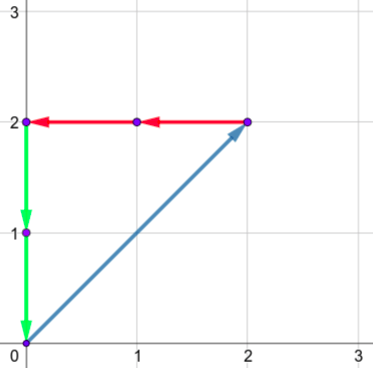
The only shape for the second sample is:
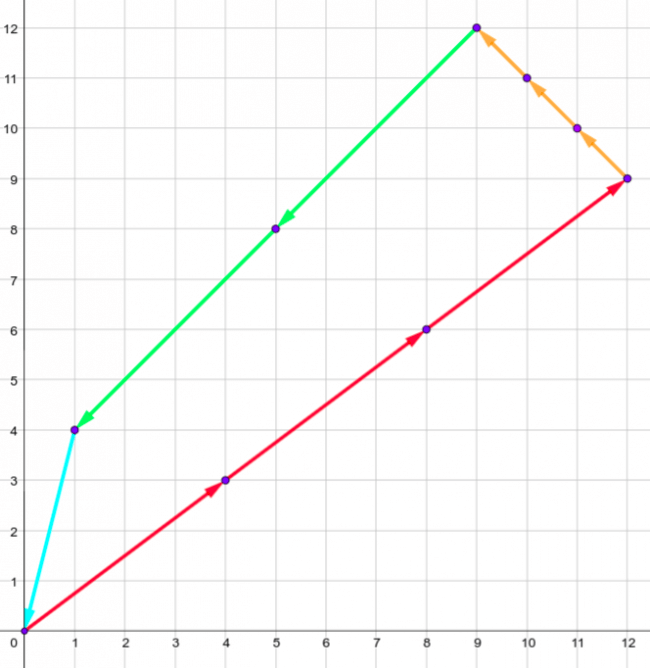
The only shape for the fourth sample is:
Solution:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
template <typename T>
T inverse(T a, T m) {
T u = 0, v = 1;
while (a != 0) {
T t = m / a;
m -= t * a; swap(a, m);
u -= t * v; swap(u, v);
}
assert(m == 1);
return u;
}
template <typename T>
class Modular {
public:
using Type = typename decay<decltype(T::value)>::type;
constexpr Modular() : value() {}
template <typename U>
Modular(const U& x) {
value = normalize(x);
}
template <typename U>
static Type normalize(const U& x) {
Type v;
if (-mod() <= x && x < mod()) v = static_cast<Type>(x);
else v = static_cast<Type>(x % mod());
if (v < 0) v += mod();
return v;
}
const Type& operator()() const { return value; }
template <typename U>
explicit operator U() const { return static_cast<U>(value); }
constexpr static Type mod() { return T::value; }
Modular& operator+=(const Modular& other) { if ((value += other.value) >= mod()) value -= mod(); return *this; }
Modular& operator-=(const Modular& other) { if ((value -= other.value) < 0) value += mod(); return *this; }
template <typename U> Modular& operator+=(const U& other) { return *this += Modular(other); }
template <typename U> Modular& operator-=(const U& other) { return *this -= Modular(other); }
Modular& operator++() { return *this += 1; }
Modular& operator--() { return *this -= 1; }
Modular operator++(int) { Modular result(*this); *this += 1; return result; }
Modular operator--(int) { Modular result(*this); *this -= 1; return result; }
Modular operator-() const { return Modular(-value); }
template <typename U = T>
typename enable_if<is_same<typename Modular<U>::Type, int>::value, Modular>::type& operator*=(const Modular& rhs) {
#ifdef _WIN32
uint64_t x = static_cast<int64_t>(value) * static_cast<int64_t>(rhs.value);
uint32_t xh = static_cast<uint32_t>(x >> 32), xl = static_cast<uint32_t>(x), d, m;
asm(
"divl %4; \n\t"
: "=a" (d), "=d" (m)
: "d" (xh), "a" (xl), "r" (mod())
);
value = m;
#else
value = normalize(static_cast<int64_t>(value) * static_cast<int64_t>(rhs.value));
#endif
return *this;
}
template <typename U = T>
typename enable_if<is_same<typename Modular<U>::Type, int64_t>::value, Modular>::type& operator*=(const Modular& rhs) {
int64_t q = static_cast<int64_t>(static_cast<long double>(value) * rhs.value / mod());
value = normalize(value * rhs.value - q * mod());
return *this;
}
template <typename U = T>
typename enable_if<!is_integral<typename Modular<U>::Type>::value, Modular>::type& operator*=(const Modular& rhs) {
value = normalize(value * rhs.value);
return *this;
}
Modular& operator/=(const Modular& other) { return *this *= Modular(inverse(other.value, mod())); }
template <typename U>
friend const Modular<U>& abs(const Modular<U>& v) { return v; }
template <typename U>
friend bool operator==(const Modular<U>& lhs, const Modular<U>& rhs);
template <typename U>
friend bool operator<(const Modular<U>& lhs, const Modular<U>& rhs);
template <typename U>
friend std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& stream, Modular<U>& number);
private:
Type value;
};
template <typename T> bool operator==(const Modular<T>& lhs, const Modular<T>& rhs) { return lhs.value == rhs.value; }
template <typename T, typename U> bool operator==(const Modular<T>& lhs, U rhs) { return lhs == Modular<T>(rhs); }
template <typename T, typename U> bool operator==(U lhs, const Modular<T>& rhs) { return Modular<T>(lhs) == rhs; }
template <typename T> bool operator!=(const Modular<T>& lhs, const Modular<T>& rhs) { return !(lhs == rhs); }
template <typename T, typename U> bool operator!=(const Modular<T>& lhs, U rhs) { return !(lhs == rhs); }
template <typename T, typename U> bool operator!=(U lhs, const Modular<T>& rhs) { return !(lhs == rhs); }
template <typename T> bool operator<(const Modular<T>& lhs, const Modular<T>& rhs) { return lhs.value < rhs.value; }
template <typename T> Modular<T> operator+(const Modular<T>& lhs, const Modular<T>& rhs) { return Modular<T>(lhs) += rhs; }
template <typename T, typename U> Modular<T> operator+(const Modular<T>& lhs, U rhs) { return Modular<T>(lhs) += rhs; }
template <typename T, typename U> Modular<T> operator+(U lhs, const Modular<T>& rhs) { return Modular<T>(lhs) += rhs; }
template <typename T> Modular<T> operator-(const Modular<T>& lhs, const Modular<T>& rhs) { return Modular<T>(lhs) -= rhs; }
template <typename T, typename U> Modular<T> operator-(const Modular<T>& lhs, U rhs) { return Modular<T>(lhs) -= rhs; }
template <typename T, typename U> Modular<T> operator-(U lhs, const Modular<T>& rhs) { return Modular<T>(lhs) -= rhs; }
template <typename T> Modular<T> operator*(const Modular<T>& lhs, const Modular<T>& rhs) { return Modular<T>(lhs) *= rhs; }
template <typename T, typename U> Modular<T> operator*(const Modular<T>& lhs, U rhs) { return Modular<T>(lhs) *= rhs; }
template <typename T, typename U> Modular<T> operator*(U lhs, const Modular<T>& rhs) { return Modular<T>(lhs) *= rhs; }
template <typename T> Modular<T> operator/(const Modular<T>& lhs, const Modular<T>& rhs) { return Modular<T>(lhs) /= rhs; }
template <typename T, typename U> Modular<T> operator/(const Modular<T>& lhs, U rhs) { return Modular<T>(lhs) /= rhs; }
template <typename T, typename U> Modular<T> operator/(U lhs, const Modular<T>& rhs) { return Modular<T>(lhs) /= rhs; }
template<typename T, typename U>
Modular<T> power(const Modular<T>& a, const U& b) {
assert(b >= 0);
Modular<T> x = a, res = 1;
U p = b;
while (p > 0) {
if (p & 1) res *= x;
x *= x;
p >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
template <typename T>
bool IsZero(const Modular<T>& number) {
return number() == 0;
}
template <typename T>
string to_string(const Modular<T>& number) {
return to_string(number());
}
template <typename T>
std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& stream, const Modular<T>& number) {
return stream << number();
}
template <typename T>
std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& stream, Modular<T>& number) {
typename common_type<typename Modular<T>::Type, int64_t>::type x;
stream >> x;
number.value = Modular<T>::normalize(x);
return stream;
}
/*
using ModType = int;
struct VarMod { static ModType value; };
ModType VarMod::value;
ModType& md = VarMod::value;
using Mint = Modular<VarMod>;
*/
constexpr int md = 998244353;
using Mint = Modular<std::integral_constant<decay<decltype(md)>::type, md>>;
const int MAX = 20;
Mint dp[MAX][MAX][MAX][MAX][2][2];
Mint new_dp[MAX][MAX][MAX][MAX][2][2];
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<int> x(n), y(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> x[i] >> y[i];
}
memset(dp, 0, sizeof(dp));
dp[0][0][0][0][0][0] = 1;
while (m > 0) {
int bit = m & 1;
memset(new_dp, 0, sizeof(new_dp));
for (int cpx = 0; cpx < MAX; cpx++) {
for (int cmx = 0; cmx < MAX; cmx++) {
for (int cpy = 0; cpy < MAX; cpy++) {
for (int cmy = 0; cmy < MAX; cmy++) {
for (int fx = 0; fx < 2; fx++) {
for (int fy = 0; fy < 2; fy++) {
Mint ft = dp[cpx][cmx][cpy][cmy][fx][fy];
if (ft == 0) {
continue;
}
for (int mask = 0; mask < (1 << n); mask++) {
int dpx = cpx;
int dpy = cpy;
int dmx = cmx;
int dmy = cmy;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (mask & (1 << i)) {
dpx += max(x[i], 0);
dmx -= min(x[i], 0);
dpy += max(y[i], 0);
dmy -= min(y[i], 0);
}
}
if ((dpx & 1) != (dmx & 1)) {
continue;
}
if ((dpy & 1) != (dmy & 1)) {
continue;
}
int new_fx = ((dpx & 1) > bit ? 1 : ((dpx & 1) < bit ? 0 : fx));
int new_fy = ((dpy & 1) > bit ? 1 : ((dpy & 1) < bit ? 0 : fy));
dpx >>= 1;
dmx >>= 1;
dpy >>= 1;
dmy >>= 1;
assert(dpx < MAX && dpy < MAX && dmx < MAX && dmy < MAX);
new_dp[dpx][dmx][dpy][dmy][new_fx][new_fy] += ft;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
swap(dp, new_dp);
m >>= 1;
}
cout << dp[0][0][0][0][0][0] - 1 << '\n';
return 0;
}

