Sherlock found a piece of encrypted data which he thinks will be useful to catch Moriarty. The encrypted data consists of two integer l and r. He noticed that these integers were in hexadecimal form.
He takes each of the integers from l to r, and performs the following operations:
- He lists the distinct digits present in the given number. For example: for 101416, he lists the digits as 1, 0, 4.
- Then he sums respective powers of two for each digit listed in the step above. Like in the above example sum = 21 + 20 + 24 = 1910.
- He changes the initial number by applying bitwise xor of the initial number and the sum. Example:
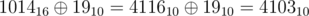 . Note that xor is done in binary notation.
. Note that xor is done in binary notation.
One more example: for integer 1e the sum is sum = 21 + 214. Letters a, b, c, d, e, f denote hexadecimal digits 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, respertively.
Sherlock wants to count the numbers in the range from l to r (both inclusive) which decrease on application of the above four steps. He wants you to answer his q queries for different l and r.
Input
First line contains the integer q (1 ≤ q ≤ 10000).
Each of the next q lines contain two hexadecimal integers l and r (0 ≤ l ≤ r < 1615).
The hexadecimal integers are written using digits from 0 to 9 and/or lowercase English letters a, b, c, d, e, f.
The hexadecimal integers do not contain extra leading zeros.
Output
Output q lines, i-th line contains answer to the i-th query (in decimal notation).
Examples
input
1
1014 1014
output
1
input
2
1 1e
1 f
output
1
0
input
2
1 abc
d0e fe23
output
412
28464
Note
For the second input,
1416 = 2010
sum = 21 + 24 = 18
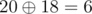
Thus, it reduces. And, we can verify that it is the only number in range 1 to 1e that reduces.
Solution:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
inline int decode(char c) {
if ('0' <= c && c <= '9') {
return c - '0';
}
return (c - 'a') + 10;
}
const int N = 77;
char foo[N], bar[N];
int a[N];
long long f[N][N][N];
int main() {
int tt;
scanf("%d", &tt);
while (tt--) {
scanf("%s %s", foo, bar);
long long ans = 0;
for (int rot = 0; rot < 2; rot++) {
int n;
if (rot == 0) {
n = strlen(bar);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
a[i] = decode(bar[n - i - 1]);
}
} else {
n = strlen(foo);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
a[i] = decode(foo[n - i - 1]);
}
ans = -ans;
}
for (int max_d = 0; max_d < 16; max_d++) {
int pos = max_d / 4;
int bit = (1 << (max_d % 4));
if (pos >= n) {
continue;
}
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
for (int eq = 0; eq < 2; eq++) {
for (int was = 0; was < 2; was++) {
f[i][eq][was] = 0;
}
}
}
f[n][1][0] = 1;
for (int i = n; i > 0; i--) {
for (int eq = 0; eq < 2; eq++) {
for (int was = 0; was < 2; was++) {
long long ft = f[i][eq][was];
if (ft == 0) {
continue;
}
int up = min(max_d, (eq == 0 ? 15 : a[i - 1]));
for (int d = 0; d <= up; d++) {
if (i - 1 == pos && !(d & bit)) {
continue;
}
int new_eq = (eq && (d == a[i - 1]));
int new_was = (was || (d == max_d));
f[i - 1][new_eq][new_was] += ft;
}
}
}
}
int max_eq = (rot == 0 ? 1 : 0);
for (int eq = 0; eq <= max_eq; eq++) {
ans += f[0][eq][1];
}
}
if (rot == 1) {
ans = -ans;
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
return 0;
}

