Let’s define the Eulerian traversal of a tree (a connected undirected graph without cycles) as follows: consider a depth-first search algorithm which traverses vertices of the tree and enumerates them in the order of visiting (only the first visit of each vertex counts). This function starts from the vertex number $1$ and then recursively runs from all vertices which are connected with an edge with the current vertex and are not yet visited in increasing numbers order. Formally, you can describe this function using the following pseudocode:
next_id = 1
id = array of length n filled with -1
visited = array of length n filled with false
function dfs(v):
visited[v] = true
id[v] = next_id
next_id += 1
for to in neighbors of v in increasing order:
if not visited[to]:
dfs(to)
You are given a weighted tree, the vertices of which were enumerated with integers from $1$ to $n$ using the algorithm described above.
A leaf is a vertex of the tree which is connected with only one other vertex. In the tree given to you, the vertex $1$ is not a leaf. The distance between two vertices in the tree is the sum of weights of the edges on the simple path between them.
You have to answer $q$ queries of the following type: given integers $v$, $l$ and $r$, find the shortest distance from vertex $v$ to one of the leaves with indices from $l$ to $r$ inclusive.
Input
The first line contains two integers $n$ and $q$ ($3 \leq n \leq 500\,000, 1 \leq q \leq 500\,000$) — the number of vertices in the tree and the number of queries, respectively.
The $(i – 1)$-th of the following $n – 1$ lines contains two integers $p_i$ and $w_i$ ($1 \leq p_i < i, 1 \leq w_i \leq 10^9$), denoting an edge between vertices $p_i$ and $i$ with the weight $w_i$.
It’s guaranteed that the given edges form a tree and the vertices are enumerated in the Eulerian traversal order and that the vertex with index $1$ is not a leaf.
The next $q$ lines describe the queries. Each of them contains three integers $v_i$, $l_i$, $r_i$ ($1 \leq v_i \leq n, 1 \leq l_i \leq r_i \leq n$), describing the parameters of the query. It is guaranteed that there is at least one leaf with index $x$ such that $l_i \leq x \leq r_i$.
Output
Output $q$ integers — the answers for the queries in the order they are given in the input.
Examples
input
5 3 1 10 1 1 3 2 3 3 1 1 5 5 4 5 4 1 2
output
3 0 13
input
5 3 1 1000000000 2 1000000000 1 1000000000 1 1000000000 3 4 5 2 1 5 2 4 5
output
3000000000 1000000000 2000000000
input
11 8 1 7 2 1 1 20 1 2 5 6 6 2 6 3 5 1 9 10 9 11 5 1 11 1 1 4 9 4 8 6 1 4 9 7 11 9 10 11 8 1 11 11 4 5
output
8 8 9 16 9 10 0 34
Note
In the first example, the tree looks like this:
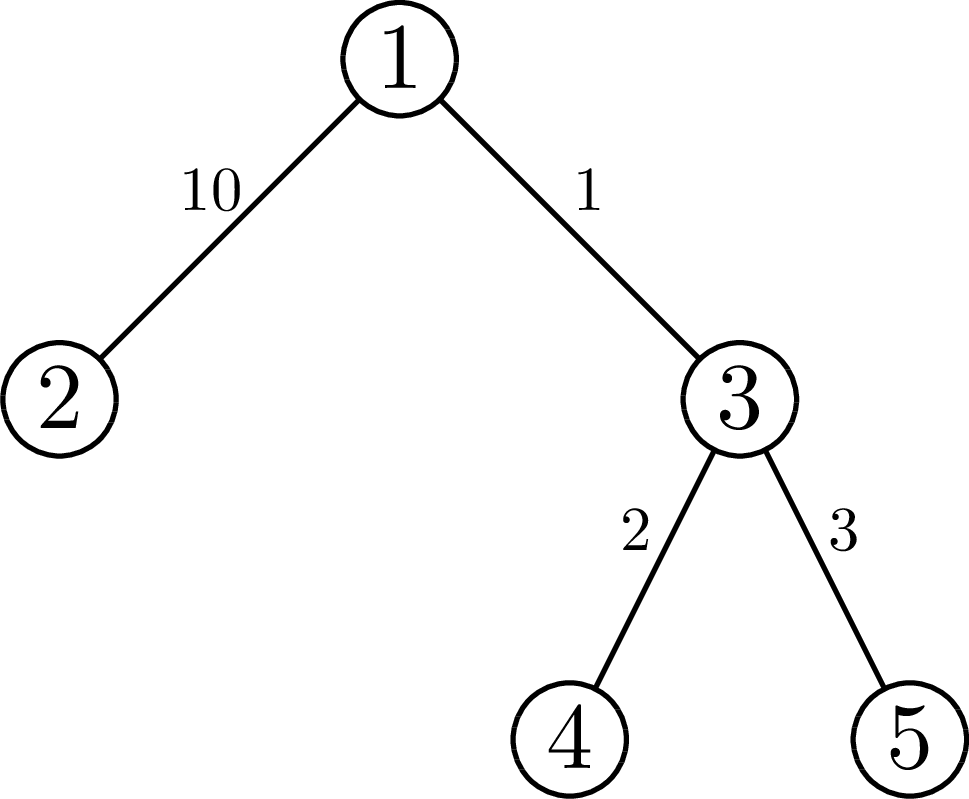
In the first query, the nearest leaf for the vertex $1$ is vertex $4$ with distance $3$. In the second query, the nearest leaf for vertex $5$ is vertex $5$ with distance $0$. In the third query the nearest leaf for vertex $4$ is vertex $4$; however, it is not inside interval $[1, 2]$ of the query. The only leaf in interval $[1, 2]$ is vertex $2$ with distance $13$ from vertex $4$.
Solution:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
string to_string(string s) {
return '"' + s + '"';
}
string to_string(const char* s) {
return to_string((string) s);
}
string to_string(bool b) {
return (b ? "true" : "false");
}
template <typename A, typename B>
string to_string(pair<A, B> p) {
return "(" + to_string(p.first) + ", " + to_string(p.second) + ")";
}
template <typename A>
string to_string(A v) {
bool first = true;
string res = "{";
for (const auto &x : v) {
if (!first) {
res += ", ";
}
first = false;
res += to_string(x);
}
res += "}";
return res;
}
void debug_out() { cerr << endl; }
template <typename Head, typename... Tail>
void debug_out(Head H, Tail... T) {
cerr << " " << to_string(H);
debug_out(T...);
}
#ifdef LOCAL
#define debug(...) cerr << "[" << #__VA_ARGS__ << "]:", debug_out(__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define debug(...) 42
#endif
class segtree {
public:
struct node {
// don't forget to set default value (used for leaves)
// not necessarily neutral element!
long long mn = 0;
long long add = 0;
void apply(int l, int r, long long v) {
mn += v;
add += v;
}
};
node unite(const node &a, const node &b) const {
node res;
res.mn = min(a.mn, b.mn);
return res;
}
inline void push(int x, int l, int r) {
int y = (l + r) >> 1;
int z = x + ((y - l + 1) << 1);
// push from x into (x + 1) and z
if (tree[x].add != 0) {
tree[x + 1].apply(l, y, tree[x].add);
tree[z].apply(y + 1, r, tree[x].add);
tree[x].add = 0;
}
}
inline void pull(int x, int z) {
tree[x] = unite(tree[x + 1], tree[z]);
}
int n;
vector<node> tree;
void build(int x, int l, int r) {
if (l == r) {
return;
}
int y = (l + r) >> 1;
int z = x + ((y - l + 1) << 1);
build(x + 1, l, y);
build(z, y + 1, r);
pull(x, z);
}
template <typename M>
void build(int x, int l, int r, const vector<M> &v) {
if (l == r) {
tree[x].apply(l, r, v[l]);
return;
}
int y = (l + r) >> 1;
int z = x + ((y - l + 1) << 1);
build(x + 1, l, y, v);
build(z, y + 1, r, v);
pull(x, z);
}
node get(int x, int l, int r, int ll, int rr) {
if (ll <= l && r <= rr) {
return tree[x];
}
int y = (l + r) >> 1;
int z = x + ((y - l + 1) << 1);
push(x, l, r);
node res{};
if (rr <= y) {
res = get(x + 1, l, y, ll, rr);
} else {
if (ll > y) {
res = get(z, y + 1, r, ll, rr);
} else {
res = unite(get(x + 1, l, y, ll, rr), get(z, y + 1, r, ll, rr));
}
}
pull(x, z);
return res;
}
template <typename... M>
void modify(int x, int l, int r, int ll, int rr, const M&... v) {
if (ll <= l && r <= rr) {
tree[x].apply(l, r, v...);
return;
}
int y = (l + r) >> 1;
int z = x + ((y - l + 1) << 1);
push(x, l, r);
if (ll <= y) {
modify(x + 1, l, y, ll, rr, v...);
}
if (rr > y) {
modify(z, y + 1, r, ll, rr, v...);
}
pull(x, z);
}
int find_first_knowingly(int x, int l, int r, const function<bool(const node&)> &f) {
if (l == r) {
return l;
}
push(x, l, r);
int y = (l + r) >> 1;
int z = x + ((y - l + 1) << 1);
int res;
if (f(tree[x + 1])) {
res = find_first_knowingly(x + 1, l, y, f);
} else {
res = find_first_knowingly(z, y + 1, r, f);
}
pull(x, z);
return res;
}
int find_first(int x, int l, int r, int ll, int rr, const function<bool(const node&)> &f) {
if (ll <= l && r <= rr) {
if (!f(tree[x])) {
return -1;
}
return find_first_knowingly(x, l, r, f);
}
push(x, l, r);
int y = (l + r) >> 1;
int z = x + ((y - l + 1) << 1);
int res = -1;
if (ll <= y) {
res = find_first(x + 1, l, y, ll, rr, f);
}
if (rr > y && res == -1) {
res = find_first(z, y + 1, r, ll, rr, f);
}
pull(x, z);
return res;
}
int find_last_knowingly(int x, int l, int r, const function<bool(const node&)> &f) {
if (l == r) {
return l;
}
push(x, l, r);
int y = (l + r) >> 1;
int z = x + ((y - l + 1) << 1);
int res;
if (f(tree[z])) {
res = find_last_knowingly(z, y + 1, r, f);
} else {
res = find_last_knowingly(x + 1, l, y, f);
}
pull(x, z);
return res;
}
int find_last(int x, int l, int r, int ll, int rr, const function<bool(const node&)> &f) {
if (ll <= l && r <= rr) {
if (!f(tree[x])) {
return -1;
}
return find_last_knowingly(x, l, r, f);
}
push(x, l, r);
int y = (l + r) >> 1;
int z = x + ((y - l + 1) << 1);
int res = -1;
if (rr > y) {
res = find_last(z, y + 1, r, ll, rr, f);
}
if (ll <= y && res == -1) {
res = find_last(x + 1, l, y, ll, rr, f);
}
pull(x, z);
return res;
}
segtree(int _n) : n(_n) {
assert(n > 0);
tree.resize(2 * n - 1);
build(0, 0, n - 1);
}
template <typename M>
segtree(const vector<M> &v) {
n = v.size();
assert(n > 0);
tree.resize(2 * n - 1);
build(0, 0, n - 1, v);
}
node get(int ll, int rr) {
assert(0 <= ll && ll <= rr && rr <= n - 1);
return get(0, 0, n - 1, ll, rr);
}
node get(int p) {
assert(0 <= p && p <= n - 1);
return get(0, 0, n - 1, p, p);
}
template <typename... M>
void modify(int ll, int rr, const M&... v) {
assert(0 <= ll && ll <= rr && rr <= n - 1);
modify(0, 0, n - 1, ll, rr, v...);
}
// find_first and find_last call all FALSE elements
// to the left (right) of the sought position exactly once
int find_first(int ll, int rr, const function<bool(const node&)> &f) {
assert(0 <= ll && ll <= rr && rr <= n - 1);
return find_first(0, 0, n - 1, ll, rr, f);
}
int find_last(int ll, int rr, const function<bool(const node&)> &f) {
assert(0 <= ll && ll <= rr && rr <= n - 1);
return find_last(0, 0, n - 1, ll, rr, f);
}
};
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int n, tt;
cin >> n >> tt;
vector<int> p(n);
vector<int> w(n);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
cin >> p[i] >> w[i];
p[i]--;
}
vector<vector<int>> qs(n);
vector<int> L(tt), R(tt), v(tt);
vector<long long> res(tt, -1);
for (int i = 0; i < tt; i++) {
cin >> v[i] >> L[i] >> R[i];
v[i]--; L[i]--; R[i]--;
qs[v[i]].push_back(i);
}
vector<long long> dst(n);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
dst[i] = dst[p[i]] + w[i];
}
vector<int> is_leaf(n, 1);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
is_leaf[p[i]] = 0;
}
const long long inf = (long long) 1e18;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!is_leaf[i]) {
dst[i] = inf;
}
}
segtree st(dst);
vector<int> stk;
vector<int> to(n, n - 1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
while (!stk.empty() && stk.back() != p[i]) {
int u = stk.back();
to[u] = i - 1;
stk.pop_back();
}
stk.push_back(i);
}
debug(to);
stk.clear();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
while (!stk.empty() && stk.back() != p[i]) {
int u = stk.back();
st.modify(0, n - 1, -w[u]);
st.modify(u, to[u], 2 * w[u]);
stk.pop_back();
}
stk.push_back(i);
st.modify(0, n - 1, w[i]);
st.modify(i, to[i], -2 * w[i]);
for (int id : qs[i]) {
res[id] = st.get(L[id], R[id]).mn;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < tt; i++) {
cout << res[i] << '\n';
}
return 0;
}

