By the age of three Smart Beaver mastered all arithmetic operations and got this summer homework from the amazed teacher:
You are given a sequence of integers a 1, a 2, …, a n. Your task is to perform on it m consecutive operations of the following type:
- For given numbers x i and v i assign value v i to element a x i.
- For given numbers l i and r i you’ve got to calculate sum
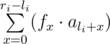 , where f 0 = f 1 = 1 and at i ≥ 2: f i = f i - 1 + f i - 2.
, where f 0 = f 1 = 1 and at i ≥ 2: f i = f i - 1 + f i - 2. - For a group of three numbers l i r i d i you should increase value a x by d i for all x (l i ≤ x ≤ r i).
Smart Beaver planned a tour around great Canadian lakes, so he asked you to help him solve the given problem.
Input
The first line contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 2·105) — the number of integers in the sequence and the number of operations, correspondingly. The second line contains n integers a 1, a 2, …, a n (0 ≤ a i ≤ 105). Then follow m lines, each describes an operation. Each line starts with an integer t i (1 ≤ t i ≤ 3) — the operation type:
- if t i = 1, then next follow two integers x i v i (1 ≤ x i ≤ n, 0 ≤ v i ≤ 105);
- if t i = 2, then next follow two integers l i r i (1 ≤ l i ≤ r i ≤ n);
- if t i = 3, then next follow three integers l i r i d i (1 ≤ l i ≤ r i ≤ n, 0 ≤ d i ≤ 105).
The input limits for scoring 30 points are (subproblem E1):
- It is guaranteed that n does not exceed 100, m does not exceed 10000 and there will be no queries of the 3-rd type.
The input limits for scoring 70 points are (subproblems E1+E2):
- It is guaranteed that there will be queries of the 1-st and 2-nd type only.
The input limits for scoring 100 points are (subproblems E1+E2+E3):
- No extra limitations.
Output
For each query print the calculated sum modulo 1000000000 (109).
Examples
input
5 5
1 3 1 2 4
2 1 4
2 1 5
2 2 4
1 3 10
2 1 5
output
12
32
8
50
input
5 4
1 3 1 2 4
3 1 4 1
2 2 4
1 2 10
2 1 5
output
12
45
Solution:
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <memory.h>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
const int md = 1000000000;
const int N = 222222;
long long a[N], f[N], sf[N];
long long s1[8*N], s2[8*N], push[8*N];
int added, ans;
int get(int first, int second, int id) {
int res = (f[id-1] * first + f[id] * second) % md;
return res;
}
void build(int x, int l, int r) {
push[x] = 0;
if (l == r) {
s1[x] = a[l];
s2[x] = a[l];
return;
}
int y = (l+r) >> 1;
build(x+x, l, y);
build(x+x+1, y+1, r);
s1[x] = s1[x+x] + get(s1[x+x+1], s2[x+x+1], y-l+2);
if (s1[x] >= md) s1[x] -= md;
s2[x] = s2[x+x] + get(s1[x+x+1], s2[x+x+1], y-l+3);
if (s2[x] >= md) s2[x] -= md;
}
void relax(int x, int l, int r) {
if (push[x]) {
s1[x] = (s1[x] + sf[r-l+2] * push[x]) % md;
s2[x] = (s2[x] + (sf[r-l+3] - 1) * push[x]) % md;
push[x+x] += push[x];
if (push[x+x] >= md) push[x+x] -= md;
push[x+x+1] += push[x];
if (push[x+x+1] >= md) push[x+x+1] -= md;
push[x] = 0;
}
}
void gather(int x, int l, int y) {
s1[x] = s1[x+x] + get(s1[x+x+1], s2[x+x+1], y-l+2);
if (s1[x] >= md) s1[x] -= md;
s2[x] = s2[x+x] + get(s1[x+x+1], s2[x+x+1], y-l+3);
if (s2[x] >= md) s2[x] -= md;
}
void modify(int x, int l, int r, int p, int v) {
relax(x, l, r);
if (p < l || p > r) return;
if (l == r) {
s1[x] = v;
s2[x] = v;
return;
}
int y = (l+r) >> 1;
modify(x+x, l, y, p, v);
modify(x+x+1, y+1, r, p, v);
gather(x, l, y);
}
void add(int x, int l, int r, int ll, int rr, int v) {
if (l >= ll && r <= rr) {
push[x] += v;
if (push[x] >= md) push[x] -= md;
}
relax(x, l, r);
if (l > rr || ll > r) return;
if (l >= ll && r <= rr) {
return;
}
int y = (l+r) >> 1;
add(x+x, l, y, ll, rr, v);
add(x+x+1, y+1, r, ll, rr, v);
gather(x, l, y);
}
void sum(int x, int l, int r, int ll, int rr) {
relax(x, l, r);
if (l > rr || ll > r) return;
if (l >= ll && r <= rr) {
ans += get(s1[x], s2[x], added+1);
if (ans >= md) ans -= md;
added += r-l+1;
return;
}
int y = (l+r) >> 1;
sum(x+x, l, y, ll, rr);
sum(x+x+1, y+1, r, ll, rr);
gather(x, l, y);
}
int main() {
int n, m;
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) scanf("%d", a+i);
f[0] = 1; f[1] = 0;
for (int i=2;i<=n+3;i++) f[i] = (f[i-1] + f[i-2]) % md;
sf[0] = 0;
for (int i=1;i<=n+3;i++) sf[i] = (sf[i-1] + f[i]) % md;
build(1, 1, n);
for (int i=1;i<=m;i++) {
int com;
scanf("%d", &com);
if (com == 1) {
int q, w;
scanf("%d %d", &q, &w);
modify(1, 1, n, q, w);
} else
if (com == 2) {
int l, r;
scanf("%d %d", &l, &r);
added = 0;
ans = 0;
sum(1, 1, n, l, r);
printf("%d\n", ans);
} else {
int l, r, v;
scanf("%d %d %d", &l, &r, &v);
add(1, 1, n, l, r, v);
}
// for (int ii=1;ii<=7;ii++) printf("%d %d %d %d\n", ii, (int)s1[ii], (int)s2[ii], (int)push[ii]);
}
return 0;
}

