Amr doesn’t like Maths as he finds it really boring, so he usually sleeps in Maths lectures. But one day the teacher suspected that Amr is sleeping and asked him a question to make sure he wasn’t.
First he gave Amr two positive integers n and k. Then he asked Amr, how many integer numbers x > 0 exist such that:
- Decimal representation of x (without leading zeroes) consists of exactly n digits;
- There exists some integer y > 0 such that:
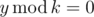 ;
;- decimal representation of y is a suffix of decimal representation of x.
As the answer to this question may be pretty huge the teacher asked Amr to output only its remainder modulo a number m.
Can you help Amr escape this embarrassing situation?
Input
Input consists of three integers n, k, m (1 ≤ n ≤ 1000, 1 ≤ k ≤ 100, 1 ≤ m ≤ 109).
Output
Print the required number modulo m.
Examples
input
1 2 1000
output
4
input
2 2 1000
output
45
input
5 3 1103
output
590
Note
A suffix of a string S is a non-empty string that can be obtained by removing some number (possibly, zero) of first characters from S.
Solution:
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <deque>
#include <stack>
#include <bitset>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
#include <numeric>
#include <utility>
#include <sstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
#include <memory.h>
#include <cassert>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2010;
int f[N][N][2][2];
int main() {
int n, k, m;
cin >> n >> k >> m;
memset(f, 0, sizeof(f));
f[n - 1][0][0][0] = 1 % m;
int z = 1 % k;
int ans = 0;
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int r = 0; r < k; r++) {
for (int w = 0; w < 2; w++) {
for (int q = 0; q < 2; q++) {
int ft = f[i][r][w][q];
if (ft == 0) {
continue;
}
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
int nr = (r + z * j) % k;
int nq = (q | (j != 0));
int nw = (w | (nr == 0 && nq == 1));
if (i == 0) {
if (n == 1 || j != 0) {
if (nw == 1) {
ans += ft;
if (ans >= m) ans -= m;
}
}
} else {
f[i - 1][nr][nw][nq] += ft;
if (f[i - 1][nr][nw][nq] >= m) f[i - 1][nr][nw][nq] -= m;
}
}
}
}
}
z = z * 10 % k;
}
printf("%d\n", ans % m);
return 0;
}

