Bill is a famous mathematician in BubbleLand. Thanks to his revolutionary math discoveries he was able to make enough money to build a beautiful house. Unfortunately, for not paying property tax on time, court decided to punish Bill by making him lose a part of his property.
Bill’s property can be observed as a convex regular 2n-sided polygon A 0 A 1… A 2n - 1 A 2n, A 2n = A 0, with sides of the exactly 1 meter in length.
Court rules for removing part of his property are as follows:
- Split every edge A k A k + 1, k = 0… 2n - 1 in n equal parts of size 1 / n with points P 0, P 1, …, P n - 1
- On every edge A 2k A 2k + 1, k = 0… n - 1 court will choose one point B 2k = P i for some i = 0, …, n - 1 such that
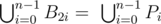
- On every edge A 2k + 1 A 2k + 2, k = 0…n - 1 Bill will choose one point B 2k + 1 = P i for some i = 0, …, n - 1 such that
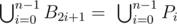
- Bill gets to keep property inside of 2n-sided polygon B 0 B 1… B 2n - 1
Luckily, Bill found out which B 2k points the court chose. Even though he is a great mathematician, his house is very big and he has a hard time calculating. Therefore, he is asking you to help him choose points so he maximizes area of property he can keep.
Input
The first line contains one integer number n (2 ≤ n ≤ 50000), representing number of edges of 2n-sided polygon.
The second line contains n distinct integer numbers B 2k (0 ≤ B 2k ≤ n - 1, k = 0… n - 1) separated by a single space, representing points the court chose. If B 2k = i, the court chose point P i on side A 2k A 2k + 1.
Output
Output contains n distinct integers separated by a single space representing points B 1, B 3, …, B 2n - 1 Bill should choose in order to maximize the property area. If there are multiple solutions that maximize the area, return any of them.
Example
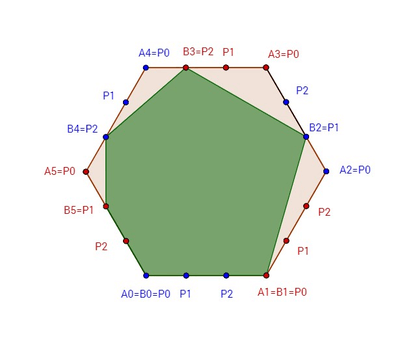
input
3
0 1 2
output
0 2 1
Note
To maximize area Bill should choose points: B 1 = P 0, B 3 = P 2, B 5 = P 1
Solution:
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class C {
class Pair implements Comparable<Pair> {
int a, b;
public Pair(int a, int b) {
super();
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Pair o) {
return Integer.compare(a, o.a);
}
}
void solve() {
int n = in.nextInt();
int[] a = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
a[i] = in.nextInt();
}
a[n] = a[0];
Pair[] b = new Pair[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
b[i] = new Pair(n - a[i] - a[i + 1], i);
}
Arrays.sort(b);
int[] ans = new int[n];
int tmp = 0;
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
ans[b[i].b] = tmp++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
out.print(ans[i] + " ");
}
out.println();
}
FastScanner in;
PrintWriter out;
void run() {
in = new FastScanner();
out = new PrintWriter(System.out);
solve();
out.close();
}
class FastScanner {
BufferedReader br;
StringTokenizer st;
public FastScanner() {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
public FastScanner(String s) {
try {
br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(s));
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public String nextToken() {
while (st == null || !st.hasMoreTokens()) {
try {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
return st.nextToken();
}
public int nextInt() {
return Integer.parseInt(nextToken());
}
public long nextLong() {
return Long.parseLong(nextToken());
}
public double nextDouble() {
return Double.parseDouble(nextToken());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new C().run();
}
}

