Table of Contents
1. Overview
In this short tutorial, we’re going to learn about the Java XOR operator. We’ll go through a bit of theory about XOR operations, and then we’ll see how to implement them in Java.
2. The XOR Operator
Let’s begin with a little reminder of the semantics of the XOR operation. The XOR logical operation, or exclusive or, takes two boolean operands and returns true if and only if the operands are different. Thus, it returns false if the two operands have the same value.
So, the XOR operator can be used, for example, when we have to check for two conditions that can’t be true at the same time.
Let’s consider two conditions, A and B. Then the following table shows the possible values of A XOR B:
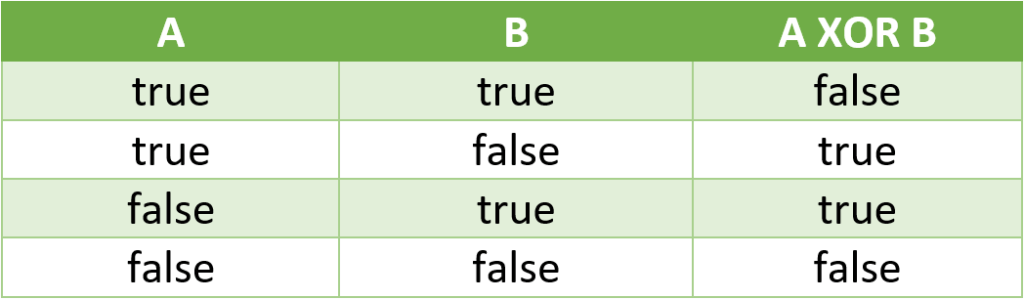
The A XOR B operation is equivalent to (A AND !B) OR (!A AND B). Parentheses have been included for clarity, but are optional, as the AND operator takes precedence over the OR operator.
3. How to Do It in Java?
Now, let’s see how to express the XOR operation in Java. Of course, we have the possibility to use the && and || operators, but this can be a bit wordy, as we’re going to see.
Imagine a Car class having two boolean attributes: diesel and manual. And now, let’s say we want to tell if the car is either diesel or manual, but not both.
Let’s check this using the && and || operators:
Car car = Car.dieselAndManualCar(); boolean dieselXorManual = (car.isDiesel() && !car.isManual()) || (!car.isDiesel() && car.isManual());
That’s a bit long, especially considering that we have an alternative — the Java XOR operator, represented by the ^ symbol. It’s a bitwise operator — that is, an operator comparing the matching bits of two values in order to return a result. In the XOR case, if two bits of the same position have the same value, the resulting bit will be 0. Otherwise, it’ll be 1.
So, instead of our cumbersome XOR implementation, we can directly use the ^ operator:
Car car = Car.dieselAndManualCar(); boolean dieselXorManual = car.isDiesel() ^ car.isManual();
As we can wee, the ^ operator allows us to be more concise in expressing XOR operations.
Finally, it’s worth mentioning that the XOR operator, like the other bitwise operators, works with every primitive type. For example, let’s consider two integers 1 and 3, whose binary representations are 00000001 and 000000011, respectively. Then, using the XOR operator between them will result in the integer 2:
assertThat(1 ^ 3).isEqualTo(2);
Only the second bit is different in those two numbers, therefore the result of the XOR operator on this bit will be 1. All other bits are identical, thus their bitwise XOR result is 0, giving us a final value of 00000010 — the binary representation of the integer 2.
4. Conclusion
In this article, we learned about the Java XOR operator. We saw that it offers a concise way to express XOR operations.
As usual, the full code of the article can be found over on GitHub.

