Dima and Anya love playing different games. Now Dima has imagined a new game that he wants to play with Anya.
Dima writes n pairs of integers on a piece of paper (l i, r i) (1 ≤ l i < r i ≤ p). Then players take turns. On his turn the player can do the following actions:
- choose the number of the pair i (1 ≤ i ≤ n), such that r i - l i > 2;
- replace pair number i by pair
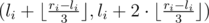 or by pair
or by pair 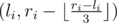 . Notation ⌊x⌋ means rounding down to the closest integer.
. Notation ⌊x⌋ means rounding down to the closest integer.
The player who can’t make a move loses.
Of course, Dima wants Anya, who will move first, to win. That’s why Dima should write out such n pairs of integers (l i, r i) (1 ≤ l i < r i ≤ p), that if both players play optimally well, the first one wins. Count the number of ways in which Dima can do it. Print the remainder after dividing the answer by number 1000000007 (109 + 7).
Two ways are considered distinct, if the ordered sequences of the written pairs are distinct.
Input
The first line contains two integers n, p (1 ≤ n ≤ 1000, 1 ≤ p ≤ 109). The numbers are separated by a single space.
Output
In a single line print the remainder after dividing the answer to the problem by number 1000000007 (109 + 7).
Examples
input
2 2
output
0
input
4 4
output
520
input
100 1000
output
269568947
Solution:
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <memory.h>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
const int md = 1000000007;
int f[1111][7];
int n, p, j, k;
int a[111111], b[111111], g[111111], was[7];
long long sum(int from, int to) {
return (long long)(from+to)*(to-from+1)/2;
}
int main() {
scanf("%d %d", &n, &p);
a[1] = 0;
b[1] = 2;
g[1] = 0;
int i = 1, sx = 1, sy = 1;
while (b[i] < p) {
int v = b[i]+1;
while (b[sx] < v/3) sx++;
while (b[sy] < v-v/3) sy++;
was[0] = was[1] = was[2] = 0;
was[g[sx]] = 1;
was[g[sy]] = 1;
int gr = 0;
while (was[gr]) gr++;
if (gr == g[i]) b[i]++; else {
i++;
a[i] = b[i-1]+1;
b[i] = a[i];
g[i] = gr;
}
if (b[i] == 780)
b[i] = b[i];
int len = (b[sx]-v/3)*3;
int other = (b[sy]-(v-v/3))*3/2;
if (other < len) len = other;
len -= 7;
if (len > 0) b[i] += len;
}
long long cnt[7];
cnt[0] = cnt[1] = cnt[2] = 0;
int q = i;
for (i=1;i<=q;i++) {
if (b[i] > p) b[i] = p;
if (a[i] < 1) a[i] = 1;
if (a[i] <= b[i]) cnt[g[i]] += sum(p-b[i], p-a[i]);
}
cnt[0] %= md;
cnt[1] %= md;
cnt[2] %= md;
memset(f, 0, sizeof(f));
f[0][0] = 1;
for (i=0;i<n;i++)
for (j=0;j<=3;j++)
for (k=0;k<=2;k++) f[i+1][j ^ k] = (f[i+1][j ^ k]+(long long)f[i][j]*cnt[k]) % md;
printf("%d\n", ((long long)f[n][1]+f[n][2]+f[n][3]) % md);
return 0;
}

