Consider an array A with N elements, all being the same integer a.
Define the product transformation as a simultaneous update A i = A i·A i + 1, that is multiplying each element to the element right to it for 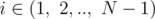 , with the last number A N remaining the same. For example, if we start with an array A with a = 2 and N = 4, then after one product transformation A = [4, 4, 4, 2], and after two product transformations A = [16, 16, 8, 2].
, with the last number A N remaining the same. For example, if we start with an array A with a = 2 and N = 4, then after one product transformation A = [4, 4, 4, 2], and after two product transformations A = [16, 16, 8, 2].
Your simple task is to calculate the array A after M product transformations. Since the numbers can get quite big you should output them modulo Q.
Input
The first and only line of input contains four integers N, M, a, Q (7 ≤ Q ≤ 109 + 123, 2 ≤ a ≤ 106 + 123, 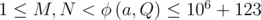 ,
, 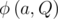 is prime), where
is prime), where 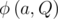 is the multiplicative order of the integer a modulo Q, see notes for definition.
is the multiplicative order of the integer a modulo Q, see notes for definition.
Output
You should output the array A from left to right.
Example
input
2 2 2 7
output
1 2
Note
The multiplicative order of a number a modulo Q 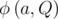 , is the smallest natural number x such that a x mod Q = 1. For example,
, is the smallest natural number x such that a x mod Q = 1. For example, 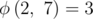 .
.
Solution:
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class F {
int mod;
long pow(long a, long b, long mod) {
long res = 1 % mod;
while (b > 0) {
if ((b & 1) == 1) {
res = res * a % mod;
}
a = a * a % mod;
b >>>= 1;
}
return res;
}
long inv(long a, long mod) {
return pow(a, mod - 2, mod);
}
void solve() {
int n = in.nextInt(), m = in.nextInt();
long a = in.nextInt(), q = in.nextInt();
a %= q;
mod = 1;
long cur = a;
while (cur != 1) {
mod++;
cur = cur * a % q;
}
long[] choose = new long[n];
choose[0] = 1 % mod;
for (int i = 1; i < n && i <= m; i++) {
choose[i] = choose[i - 1] * (m - i + 1) % mod;
choose[i] = choose[i] * inv(i, mod) % mod;
}
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
choose[i] += choose[i - 1];
choose[i] %= mod;
}
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
out.print(pow(a, choose[i], q) + " ");
}
out.println();
}
FastScanner in;
PrintWriter out;
void run() {
in = new FastScanner();
out = new PrintWriter(System.out);
solve();
out.close();
}
class FastScanner {
BufferedReader br;
StringTokenizer st;
public FastScanner() {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
public FastScanner(String s) {
try {
br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(s));
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public String nextToken() {
while (st == null || !st.hasMoreTokens()) {
try {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
return st.nextToken();
}
public int nextInt() {
return Integer.parseInt(nextToken());
}
public long nextLong() {
return Long.parseLong(nextToken());
}
public double nextDouble() {
return Double.parseDouble(nextToken());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new F().run();
}
}

