Table of Contents
Loops are used in programming to repeat a specific block of code. In this article, you will learn to create a while loop in Python.
1. What is while loop in Python?
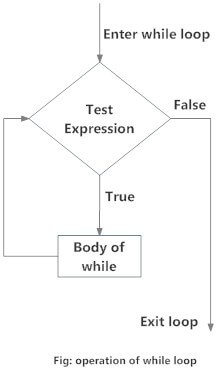
The while loop in Python is used to iterate over a block of code as long as the test expression (condition) is true.
We generally use this loop when we don’t know the number of times to iterate beforehand.
1.1. Syntax of while Loop in Python
while test_expression:
Body of while
In the while loop, test expression is checked first. The body of the loop is entered only if the test_expression evaluates to True. After one iteration, the test expression is checked again. This process continues until the test_expression evaluates to False.
In Python, the body of the while loop is determined through indentation.
The body starts with indentation and the first unindented line marks the end.
Python interprets any non-zero value as True. None and 0 are interpreted as False.
1.2. Flowchart of while Loop
1.3. Example: Python while Loop
# Program to add natural
# numbers up to
# sum = 1+2+3+...+n
# To take input from the user,
# n = int(input("Enter n: "))
n = 10
# initialize sum and counter
sum = 0
i = 1
while i <= n:
sum = sum + i
i = i+1 # update counter
# print the sum
print("The sum is", sum)
When you run the program, the output will be:
Enter n: 10 The sum is 55
In the above program, the test expression will be True as long as our counter variable i is less than or equal to n (10 in our program).
We need to increase the value of the counter variable in the body of the loop. This is very important (and mostly forgotten). Failing to do so will result in an infinite loop (never-ending loop).
Finally, the result is displayed.
2. While loop with else
Same as with for loops, while loops can also have an optional else block.
The else part is executed if the condition in the while loop evaluates to False.
The while loop can be terminated with a break statement. In such cases, the else part is ignored. Hence, a while loop’s else part runs if no break occurs and the condition is false.
Here is an example to illustrate this.
'''Example to illustrate
the use of else statement
with the while loop'''
counter = 0
while counter < 3:
print("Inside loop")
counter = counter + 1
else:
print("Inside else")
Output
Inside loop Inside loop Inside loop Inside else
Here, we use a counter variable to print the string Inside loop three times.
On the fourth iteration, the condition in while becomes False. Hence, the else part is executed.

