Table of Contents
1. Overview
Map is one of the most common data structures in Java, and String is one of the most common types for a map’s key. By default, a map of this sort has case-sensitive keys.
In this short tutorial, we’ll explore different Map implementations that accept all case variations of a String as the same key.
2. A Closer Look at Map with Case-Insensitive Keys
Let’s examine the problem we’re trying to solve in more detail.
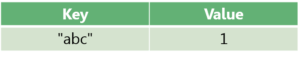
Suppose we have a Map<String, Integer> with one entry:
Let’s add the next entry:
map.put("ABC", 2);
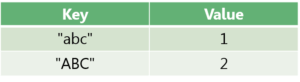
When working with a Map with case-sensitive keys, we’ll end up with two entries:
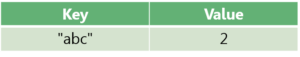
But when working with a Map with case-insensitive keys, the content will be:
In the next examples, we’ll dive into case-insensitive implementations of some popular Map implementations: TreeMap, HashMap, and LinkedHashMap.
3. TreeMap
TreeMap is an implementation of NavigableMap, which means that it always sorts the entries after inserting, based on a given Comparator. Also, TreeMap uses a Comparator to find if an inserted key is a duplicate or a new one.
Therefore, if we provide a case-insensitive String Comparator, we’ll get a case-insensitive TreeMap.
Luckily, String already supplies this static Comparator:
public static final Comparator <String> CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER
which we can supply in the constructor:
Map<String, Integer> treeMap = new TreeMap<>(String.CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER);
treeMap.put("abc", 1);
treeMap.put("ABC", 2);
And now, when we run tests, we can see that the size of the Map is one:
assertEquals(1, treeMap.size());
and the value is updated to 2:
assertEquals(2, treeMap.get("aBc").intValue());
assertEquals(2, treeMap.get("ABc").intValue());
Now let’s remove the entry, using the same String, but with another case:
treeMap.remove("aBC");
assertEquals(0, treeMap.size());
We should keep in mind that functions like put and get cost an average time of O(log n) for the TreeMap compared to a HashMap that provides O(1) insertion and lookup.
It is also worth noting that TreeMap doesn’t allow null keys.
4. Apache’s CaseInsensitiveMap
Apache’s Commons-Collections is a very popular Java library, providing a large number of useful classes with CaseInsensitiveMap among them.
CaseInsensitiveMap is a hash-based Map, which converts keys to lower case before they are being added or retrieved. Unlike TreeMap, CaseInsensitiveMap allows null key inserting.
First, we need to add the commons-collections4 dependency:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-collections4</artifactId>
<version>4.4</version>
</dependency>
Now, we can use CaseInsensitiveMap and add two entries:
Map<String, Integer> commonsHashMap = new CaseInsensitiveMap<>();
commonsHashMap.put("abc", 1);
commonsHashMap.put("ABC", 2);
When we test it, we expect the same results as we saw previously:
assertEquals(1, commonsHashMap.size());
assertEquals(2, commonsHashMap.get("aBc").intValue());
assertEquals(2, commonsHashMap.get("ABc").intValue());
commonsHashMap.remove("aBC");
assertEquals(0, commonsHashMap.size());
5. Spring’s LinkedCaseInsensitiveMap
Spring Core is a Spring Framework module that also provides utility classes, including LinkedCaseInsensitiveMap.
LinkedCaseInsensitiveMap wraps a LinkedHashMap, which is a Map based on a hash table and a linked list. Unlike LinkedHashMap, it doesn’t allow null key inserting. LinkedCaseInsensitiveMap preserves the original order as well as the original casing of keys while allowing calling functions like get and remove with any case.
First, let’s add the spring-core dependency:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
<version>5.2.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
Now, we can initialize a new LinkedCaseInsensitiveMap:
Map<String, Integer> linkedHashMap = new LinkedCaseInsensitiveMap<>();
linkedHashMap.put("abc", 1);
linkedHashMap.put("ABC", 2);
add test it:
assertEquals(1, linkedHashMap.size());
assertEquals(2, linkedHashMap.get("aBc").intValue());
assertEquals(2, linkedHashMap.get("ABc").intValue());
linkedHashMap.remove("aBC");
assertEquals(0, linkedHashMap.size());
6. Conclusion
In this tutorial, we’ve looked at different ways to create a Java Map with case-insensitive keys and used different classes to obtain this.
As always, the code is available over on GitHub.