Arkady words in a large company. There are n employees working in a system of a strict hierarchy. Namely, each employee, with an exception of the CEO, has exactly one immediate manager. The CEO is a manager (through a chain of immediate managers) of all employees.
Each employee has an integer rank. The CEO has rank equal to 1, each other employee has rank equal to the rank of his immediate manager plus 1.
Arkady has a good post in the company, however, he feels that he is nobody in the company’s structure, and there are a lot of people who can replace him. He introduced the value of replaceability. Consider an employee a and an employee b, the latter being manager of a (not necessarily immediate). Then the replaceability r(a, b) of a with respect to b is the number of subordinates (not necessarily immediate) of the manager b, whose rank is not greater than the rank of a. Apart from replaceability, Arkady introduced the value of negligibility. The negligibility z a of employee a equals the sum of his replaceabilities with respect to all his managers, i.e. 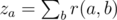 , where the sum is taken over all his managers b.
, where the sum is taken over all his managers b.
Arkady is interested not only in negligibility of himself, but also in negligibility of all employees in the company. Find the negligibility of each employee for Arkady.
Input
The first line contains single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 5·105) — the number of employees in the company.
The second line contains n integers p 1, p 2, …, p n (0 ≤ p i ≤ n), where p i = 0 if the i-th employee is the CEO, otherwise p i equals the id of the immediate manager of the employee with id i. The employees are numbered from 1 to n. It is guaranteed that there is exactly one 0 among these values, and also that the CEO is a manager (not necessarily immediate) for all the other employees.
Output
Print n integers — the negligibilities of all employees in the order of their ids: z 1, z 2, …, z n.
Examples
input
4
0 1 2 1
output
0 2 4 2
input
5
2 3 4 5 0
output
10 6 3 1 0
input
5
0 1 1 1 3
output
0 3 3 3 5
Note
Consider the first example:
- The CEO has no managers, thus z 1 = 0.
- r(2, 1) = 2 (employees 2 and 4 suit the conditions, employee 3 has too large rank). Thus z 2 = r(2, 1) = 2.
- Similarly, z 4 = r(4, 1) = 2.
- r(3, 2) = 1 (employee 3 is a subordinate of 2 and has suitable rank). r(3, 1) = 3 (employees 2, 3, 4 suit the conditions). Thus z 3 = r(3, 2) + r(3, 1) = 4.
Solution:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
template <typename T>
class graph {
public:
struct edge {
int from;
int to;
T cost;
};
vector<edge> edges;
vector< vector<int> > g;
int n;
graph(int n) : n(n) {
g.resize(n);
}
virtual int add(int from, int to, T cost) = 0;
};
template <typename T>
class forest : public graph<T> {
public:
using graph<T>::edges;
using graph<T>::g;
using graph<T>::n;
forest(int n) : graph<T>(n) {
}
int add(int from, int to, T cost = 1) {
assert(0 <= from && from < n && 0 <= to && to < n);
int id = edges.size();
g[from].push_back(id);
g[to].push_back(id);
edges.push_back({from, to, cost});
return id;
}
};
template <typename T>
class dfs_forest : public forest<T> {
public:
using forest<T>::edges;
using forest<T>::g;
using forest<T>::n;
vector<int> pv;
vector<int> pe;
vector<int> order;
vector<int> pos;
vector<int> end;
vector<int> sz;
vector<int> root;
vector<int> depth;
vector<T> dist;
vector<bool> alive_vertex;
vector<bool> alive_edge;
dfs_forest(int n) : forest<T>(n) {
alive_vertex = vector<bool>(n, true);
alive_edge = vector<bool>(edges.size(), true);
}
void clear() {
pv.clear();
pe.clear();
order.clear();
pos.clear();
end.clear();
sz.clear();
root.clear();
depth.clear();
dist.clear();
}
void init() {
pv = vector<int>(n, -1);
pe = vector<int>(n, -1);
order.clear();
pos = vector<int>(n, -1);
end = vector<int>(n, -1);
sz = vector<int>(n, 0);
root = vector<int>(n, -1);
depth = vector<int>(n, -1);
dist.clear();
dist.resize(n);
}
private:
void do_dfs(int v) {
pos[v] = order.size();
order.push_back(v);
sz[v] = 1;
for (int id : g[v]) {
if (id == pe[v]) {
continue;
}
auto &e = edges[id];
int to = e.from ^ e.to ^ v;
// since this is a forest...
assert(depth[to] == -1);
depth[to] = depth[v] + 1;
dist[to] = dist[v] + e.cost;
pv[to] = v;
pe[to] = id;
root[to] = root[v];
do_dfs(to);
sz[v] += sz[to];
}
end[v] = order.size() - 1;
}
void do_dfs_from(int v) {
depth[v] = 0;
dist[v] = T{};
root[v] = v;
pv[v] = pe[v] = -1;
do_dfs(v);
}
public:
int dfs_one_unsafe(int v) {
// run init() before this
// then run this with the required v's
do_dfs_from(v);
return v;
}
int dfs(int v) {
init();
do_dfs_from(v);
assert((int) order.size() == n);
return v;
}
vector<int> dfs_all() {
init();
vector<int> roots;
for (int v = 0; v < n; v++) {
if (depth[v] == -1) {
roots.push_back(v);
do_dfs_from(v);
}
}
assert((int) order.size() == n);
return roots;
}
};
template <typename T>
class lca_forest : public dfs_forest<T> {
public:
using dfs_forest<T>::edges;
using dfs_forest<T>::g;
using dfs_forest<T>::n;
using dfs_forest<T>::pv;
using dfs_forest<T>::pos;
using dfs_forest<T>::end;
using dfs_forest<T>::depth;
int h;
vector< vector<int> > pr;
lca_forest(int n) : dfs_forest<T>(n) {
}
inline void build_lca() {
assert(!pv.empty());
int max_depth = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
max_depth = max(max_depth, depth[i]);
}
h = 1;
while ((1 << h) <= max_depth) {
h++;
}
pr.resize(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
pr[i].resize(h);
pr[i][0] = pv[i];
}
for (int j = 1; j < h; j++) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
pr[i][j] = (pr[i][j - 1] == -1 ? -1 : pr[pr[i][j - 1]][j - 1]);
}
}
}
inline bool anc(int x, int y) {
return (pos[x] <= pos[y] && end[y] <= end[x]);
}
inline int lca(int x, int y) {
// maybe optimize?
// if depth[x] > depth[y], swap
// then go from j = log(depth[x])?
assert(!pr.empty());
if (anc(x, y)) {
return x;
}
if (anc(y, x)) {
return y;
}
for (int j = h - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
if (pr[x][j] != -1 && !anc(pr[x][j], y)) {
x = pr[x][j];
}
}
return pr[x][0];
}
};
template <typename T>
class hld_forest : public lca_forest<T> {
public:
using lca_forest<T>::edges;
using lca_forest<T>::g;
using lca_forest<T>::n;
using lca_forest<T>::pv;
using lca_forest<T>::pr;
using lca_forest<T>::sz;
using lca_forest<T>::pos;
using lca_forest<T>::order;
using lca_forest<T>::depth;
using lca_forest<T>::dfs;
using lca_forest<T>::dfs_all;
using lca_forest<T>::lca;
using lca_forest<T>::build_lca;
vector<int> head;
hld_forest(int n) : lca_forest<T>(n) {
}
void build_hld(int v) {
if (v == -1) {
dfs_all();
} else {
dfs(v);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (g[i].empty()) {
continue;
}
int best = -1, bid = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < (int) g[i].size(); j++) {
int id = g[i][j];
int v = edges[id].from ^ edges[id].to ^ i;
if (pv[v] != i) {
continue;
}
if (sz[v] > best) {
best = sz[v];
bid = j;
}
}
swap(g[i][0], g[i][bid]);
}
if (v == -1) {
dfs_all();
} else {
dfs(v);
}
// build_lca();
head.resize(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
head[i] = i;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
int x = order[i];
int y = order[i + 1];
if (pv[y] == x) {
head[y] = head[x];
}
}
}
void build_hld_all() {
build_hld(-1);
}
/*
vector< pair<int, int> > get_path(int x, int y) {
vector< pair<int, int> > path[2];
int z = lca(x, y);
for (int id = 0; id < 2; id++) {
int v = (id == 0 ? x : y);
while (v != z) {
if (depth[head[v]] <= depth[z]) {
path[id].emplace_back(pos[z] + 1, pos[v]);
break;
}
path[id].emplace_back(pos[head[v]], pos[v]);
v = pv[head[v]];
}
}
vector< pair<int, int> > ret;
for (int i = 0; i < (int) path[0].size(); i++) {
ret.emplace_back(path[0][i].second, path[0][i].first);
}
ret.emplace_back(-1, pos[z]);
for (int i = (int) path[1].size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
ret.push_back(path[1][i]);
}
return ret;
// returns segments of the path:
// first from x to lca, reversed segments
// then (-1, pos[lca])
// then from lca to y, direct segments
// but in most cases, apply_on_path should be enough
}
*/
void apply_on_path(int x, int y, bool with_lca, function<void(int,int,bool)> f) {
// f(x, y, up): up -- whether this part of the path goes up
int z = x;//lca(x, y);
for (int id = 0; id < 2; id++) {
int v = (id == 0 ? x : y);
while (v != z) {
if (depth[head[v]] <= depth[z]) {
f(pos[z] + 1, pos[v], id == 0);
break;
}
f(pos[head[v]], pos[v], id == 0);
v = pv[head[v]];
}
if (id == 0 && with_lca) {
f(pos[z], pos[z], false);
}
}
}
};
template <typename T>
class fenwick {
public:
vector<T> fenw;
int n;
fenwick(int n) : n (n) {
fenw.resize(n);
}
void modify(int x, T v) {
while (x < n) {
fenw[x] += v;
x |= (x + 1);
}
}
T get(int x) {
T v{};
while (x >= 0) {
v += fenw[x];
x = (x & (x + 1)) - 1;
}
return v;
}
};
// in_reader and out_writer by cdkrot
template <size_t buf_sz>
struct in_reader {
in_reader(FILE* f): f(f) {}
void set_err() {
err = true;
#ifdef LOCAL
assert(false);
#endif
}
int peekch() {
if (term)
return EOF;
else if (l == r and r == buf_sz) {
l = 0;
r = fread(buf, 1, buf_sz, f);
}
if (l != r)
return buf[l];
else {
term = true;
if (ferror(f))
set_err();
return EOF;
}
}
int getch() {
int res = peekch();
if (res != EOF)
++l;
return res;
}
void seek_token() {
while (peekch() != EOF and std::isspace(peekch()))
getch();
}
template <typename T>
T input_int() {
seek_token();
if (peekch() == EOF)
set_err();
char ch = peekch();
bool positive = true;
if (ch == '+')
getch();
else if (ch == '-')
getch(), positive = false;
else if (not ('0' <= ch and ch <= '9')) {
set_err();
return 0;
}
int num_read = 0;
T res = 0;
while ('0' <= peekch() and peekch() <= '9')
res = 10 * res + getch() - '0', ++num_read;
if (num_read == 0)
set_err();
if (positive == false and res > 0 and not std::numeric_limits<T>::is_signed)
set_err();
if (positive == false)
res = -res;
return res;
}
std::string input_string() {
seek_token();
std::string res;
while (peekch() != EOF and not std::isspace(peekch()))
res += getch();
return res;
}
template <typename T>
T input_float() {
seek_token();
size_t tmp_sz = 0;
if (peekch() == '+' or peekch() == '-')
tmp[tmp_sz++] = getch();
while ('0' <= peekch() and peekch() <= '9' and tmp_sz != 60)
tmp[tmp_sz++] = getch();
if (peekch() == '.' and tmp_sz != 60) {
tmp[tmp_sz++] = getch();
while ('0' <= peekch() and peekch() <= '9' and tmp_sz != 60)
tmp[tmp_sz++] = getch();
}
if (tmp_sz == 60 or tmp_sz == 0) {
set_err();
return 0;
}
tmp[tmp_sz] = 0;
if (std::is_same<T, float>::value)
return strtof(tmp, NULL);
else if (std::is_same<T, double>::value)
return strtod(tmp, NULL);
else if (std::is_same<T, long double>::value)
return strtold(tmp, NULL);
else {
set_err();
return 0;
}
}
void input_string_to(char* out, size_t mx) {
seek_token();
mx -= 1;
while (peekch() != EOF and not std::isspace(peekch()) and mx != 0)
*(out++) = getch(), --mx;
*out = 0;
}
char tmp[60];
char buf[buf_sz];
FILE* f;
size_t l = buf_sz;
size_t r = buf_sz;
bool term = false;
bool err = false;
};
in_reader<4096> in(stdin);
template <typename T>
typename std::enable_if<std::is_integral<T>::value, T>::type input() {
return in.input_int<T>();
}
template <size_t buf_sz>
struct out_writer {
out_writer(FILE* f): f(f) {}
~out_writer() {flush();}
void set_err() {
err = true;
#ifdef LOCAL
assert(false);
#endif
}
void flush() {
if (pos == 0)
return;
if (fwrite(buf, 1, pos, f) != pos)
set_err();
pos = 0;
}
void putch(char ch) {
if (pos == buf_sz)
flush();
buf[pos++] = ch;
}
template <typename T>
void write_int(T elem) {
if (elem < 0) {
putch('-');
elem = -elem;
}
size_t tmp_sz = 0;
while (elem != 0)
tmp[tmp_sz++] = '0' + elem % 10, elem /= 10;
if (tmp_sz == 0)
putch('0');
else
while (tmp_sz != 0)
putch(tmp[--tmp_sz]);
}
void write_string(const std::string& str) {
write_string_raw(str.data());
}
template <typename T>
void write_float(T v) {
if (std::is_same<T, float>::value)
snprintf(tmp, 60, "%.7f", v);
else if (std::is_same<T, double>::value)
snprintf(tmp, 60, "%.7lf", v);
else if (std::is_same<T, long double>::value)
snprintf(tmp, 60, "%.7Lf", v);
else {
set_err();
}
write_string_raw(tmp);
}
void write_string_raw(const char* out) {
while (*out != 0)
putch(*(out++));
}
char tmp[60];
char buf[buf_sz];
FILE* f;
size_t pos = 0;
bool err = false;
};
out_writer<4096> out(stdout);
#define OUTI(EXPR) out.write_int(EXPR)
int main() {
srand(8753);
int n = input<int>();
hld_forest<int> g(n);
int root = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int p = input<int>();
p--;
if (p == -1) {
root = i;
} else {
g.add(p, i);
}
}
g.build_hld(root);
vector< vector<int> > layers(n);
for (int i : g.order) {
layers[g.depth[i]].push_back(i);
}
fenwick<long long> f0(n);
fenwick<int> f1(n);
vector<long long> res(n, 0);
for (int id = 1; id < n; id++) {
auto &layer = layers[id];
for (int i : layer) {
g.apply_on_path(root, g.pv[i], true, [&](int x, int y, bool up) {
f1.modify(x, 1);
f1.modify(y + 1, -1);
f0.modify(x, -x + 1);
f0.modify(y + 1, y);
});
}
for (int i : layer) {
g.apply_on_path(root, g.pv[i], true, [&](int x, int y, bool up) {
res[i] += (long long) f1.get(y) * y + f0.get(y);
res[i] -= (long long) f1.get(x - 1) * (x - 1) + f0.get(x - 1);
});
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (i > 0) {
out.putch(' ');
}
OUTI(res[i]);
// printf("%lld", res[i]);
}
out.putch('\n');
cerr << "time = " << clock() << " ms" << endl;
return 0;
}

