Table of Contents
Trong bài trước, chúng ta đã tìm hiểu Vòng lặp trong Java. Giả sử trong một vòng lặp tại một điều kiện cụ thể nào đó, bạn muốn dừng thực thi hoặc tiếp tục thực thi vòng lặp đó, thì bạn sử dụng cách nào. Java hỗ trợ 2 lệnh break và continue giúp bạn điều khiển và kiểm soát vòng lặp.
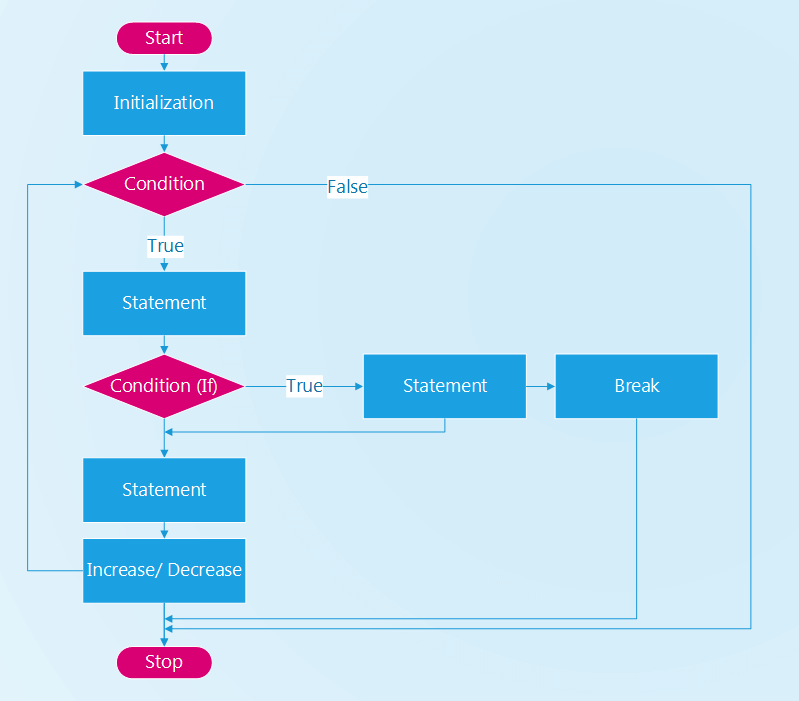
1. break
Từ khóa break trong java được sử dụng để dừng thực thi lệnh trong vòng lặp hoặc trong mệnh đề switch tại điều kiện đã được chỉ định. Đối với vòng lặp bên trong vòng lặp khác, thì nó chỉ dừng vòng lặp bên trong đó.
Ví dụ sử dụng break với vòng lặp for:
package com.maixuanviet;
public class ForSample3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
if (i == 4) {
break;
}
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
}
}
Kết quả:
1 2 3
Ví dụ sử dụng break với vòng lặp bên trong vòng lặp for khác:
package com.maixuanviet;
public class ForSample4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
System.out.print(i + ": ");
for (int j = 1; j <= 5; j++) {
if (j == 4) {
break;
}
System.out.print(j + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Kết quả:
1: 1 2 3 2: 1 2 3 3: 1 2 3 4: 1 2 3 5: 1 2 3
2. continue
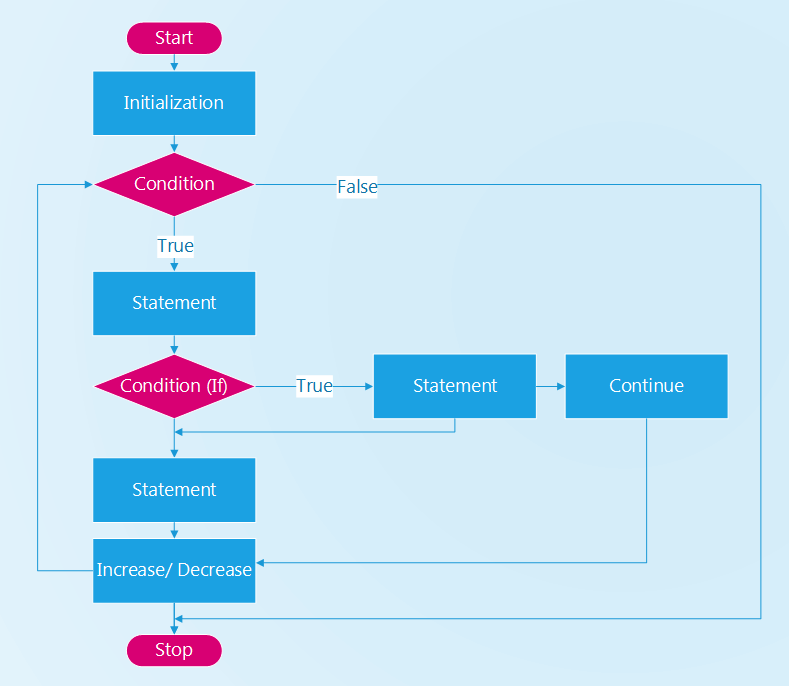
Từ khóa continue trong java được sử dụng để tiếp tục vòng lặp tại điều kiện đã được xác định, với điều kiện đó khối lệnh phía sau từ khóa continue sẽ không được thực thi. Đối với vòng lặp bên trong một vòng lặp khác, continue chỉ có tác dụng với vọng lặp bên trong đó.
Ví dụ sử dụng Continue trong java với vòng lặp for:
package com.maixuanviet;
public class ForSample5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
if (i == 4) {
continue;
}
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
}
}
Kết quả:
1 2 3 5
Ví dụ sử dụng Continue với vòng lặp bên trong vòng lặp for khác:
package com.maixuanviet;
public class ForSample6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
System.out.print(i + ": ");
for (int j = 1; j <= 5; j++) {
if (j == 4) {
continue;
}
System.out.print(j + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Kết quả:
1: 1 2 3 5 2: 1 2 3 5 3: 1 2 3 5 4: 1 2 3 5 5: 1 2 3 5