Piegirl got bored with binary, decimal and other integer based counting systems. Recently she discovered some interesting properties about number 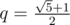 , in particular that q 2 = q + 1, and she thinks it would make a good base for her new unique system. She called it “golden system”. In golden system the number is a non-empty string containing 0’s and 1’s as digits. The decimal value of expression a 0 a 1…a n equals to
, in particular that q 2 = q + 1, and she thinks it would make a good base for her new unique system. She called it “golden system”. In golden system the number is a non-empty string containing 0’s and 1’s as digits. The decimal value of expression a 0 a 1…a n equals to 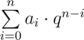 .
.
Soon Piegirl found out that this system doesn’t have same properties that integer base systems do and some operations can not be performed on it. She wasn’t able to come up with a fast way of comparing two numbers. She is asking for your help.
Given two numbers written in golden system notation, determine which of them has larger decimal value.
Input
Input consists of two lines — one for each number. Each line contains non-empty string consisting of ‘0’ and ‘1’ characters. The length of each string does not exceed 100000.
Output
Print “>” if the first number is larger, “<” if it is smaller and “=” if they are equal.
Examples
input
1000
111
output
<
input
00100
11
output
=
input
110
101
output
>
Note
In the first example first number equals to 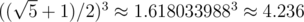 , while second number is approximately 1.6180339882 + 1.618033988 + 1 ≈ 5.236, which is clearly a bigger number.
, while second number is approximately 1.6180339882 + 1.618033988 + 1 ≈ 5.236, which is clearly a bigger number.
In the second example numbers are equal. Each of them is ≈ 2.618.
Solution:
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <deque>
#include <stack>
#include <bitset>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
#include <numeric>
#include <utility>
#include <sstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
#include <memory.h>
#include <cassert>
using namespace std;
void wr(char c) {
printf("%c\n", c);
exit(0);
}
const int N = 1000010;
int a[N];
char foo[N];
int main() {
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
a[i] = 0;
}
for (int r = 1; r >= -1; r -= 2) {
scanf("%s", foo);
int n = strlen(foo);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (foo[i] == '1') {
a[n - i - 1] += r;
}
}
}
for (int i = N - 1; i >= 2; i--) {
if (a[i] != 0) {
if (a[i] >= 2) {
wr('>');
}
if (a[i] <= -2) {
wr('<');
}
a[i - 1] += a[i];
a[i - 2] += a[i];
a[i] = 0;
}
}
long double q = 1.6180339887498948482045868343656;
long double x = a[1] * q + a[0];
if (x > 1e-9) {
wr('>');
}
if (x < -1e-9) {
wr('<');
}
wr('=');
return 0;
}

