Whoa! You did a great job helping Team Rocket who managed to capture all the Pokemons sent by Bash. Meowth, part of Team Rocket, having already mastered the human language, now wants to become a master in programming as well. He agrees to free the Pokemons if Bash can answer his questions.
Initially, Meowth gives Bash a weighted tree containing n nodes and a sequence a 1, a 2…, a n which is a permutation of 1, 2, …, n. Now, Mewoth makes q queries of one of the following forms:
- 1 l r v: meaning Bash should report
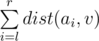 , where dist(a, b) is the length of the shortest path from node a to node b in the given tree.
, where dist(a, b) is the length of the shortest path from node a to node b in the given tree. - 2 x: meaning Bash should swap a x and a x + 1 in the given sequence. This new sequence is used for later queries.
Help Bash to answer the questions!
Input
The first line contains two integers n and q (1 ≤ n ≤ 2·105, 1 ≤ q ≤ 2·105) — the number of nodes in the tree and the number of queries, respectively.
The next line contains n space-separated integers — the sequence a 1, a 2, …, a n which is a permutation of 1, 2, …, n.
Each of the next n - 1 lines contain three space-separated integers u, v, and w denoting that there exists an undirected edge between node u and node v of weight w, (1 ≤ u, v ≤ n, u ≠ v, 1 ≤ w ≤ 106). It is guaranteed that the given graph is a tree.
Each query consists of two lines. First line contains single integer t, indicating the type of the query. Next line contains the description of the query:
- t = 1: Second line contains three integers a, b and c (1 ≤ a, b, c < 230) using which l, r and v can be generated using the formula given below:
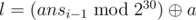 ,
,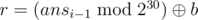 ,
,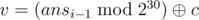 .
.
- t = 2: Second line contains single integer a (1 ≤ a < 230) using which x can be generated using the formula given below:
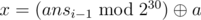 .
.
The ans i is the answer for the i-th query, assume that ans 0 = 0. If the i-th query is of type 2 then ans i = ans i - 1. It is guaranteed that:
- for each query of type 1: 1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n, 1 ≤ v ≤ n,
- for each query of type 2: 1 ≤ x ≤ n - 1.
The  operation means bitwise exclusive OR.
operation means bitwise exclusive OR.
Output
For each query of type 1, output a single integer in a separate line, denoting the answer to the query.
Example
input
5 5
4 5 1 3 2
4 2 4
1 3 9
4 1 4
4 5 2
1
1 5 4
1
22 20 20
2
38
2
39
1
36 38 38
output
23
37
28
Note
In the sample, the actual queries are the following:
- 1 1 5 4
- 1 1 3 3
- 2 3
- 2 2
- 1 1 3 3
Solution:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const long long inf = (long long) 1e18;
const int N = 400010;
vector < pair <int, long long> > forc[N];
vector < pair <int, long long> > centroid[N];
long long dist[N];
long long last_dist[N];
int sub[N];
bool alive[N];
vector < pair <int, int> > g[N];
int perm[N], pos[N];
int v_goes_to[N];
vector <int> all;
vector <int> in_forc[N];
void dfs(int v, int pr) {
all.push_back(v);
sub[v] = 1;
int sz = g[v].size();
for (int j = 0; j < sz; j++) {
int u = g[v][j].first;
if (!alive[u] || u == pr) {
continue;
}
int len = g[v][j].second;
dist[u] = dist[v] + len;
dfs(u, v);
sub[v] += sub[u];
}
}
void build(int v) {
all.clear();
dfs(v, -1);
{
// changing the root
int old_v = v;
int total = sub[v];
int pr = -1;
while (true) {
bool found = false;
int sz = g[v].size();
for (int j = 0; j < sz; j++) {
int u = g[v][j].first;
if (!alive[u] || u == pr) {
continue;
}
if (2 * sub[u] >= total) {
pr = v;
v = u;
found = true;
break;
}
}
if (!found) {
break;
}
}
v_goes_to[old_v] = v;
}
all.clear();
dist[v] = 0;
dfs(v, -1);
int cnt = all.size();
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++) {
int u = all[i];
centroid[u].push_back(make_pair(v, dist[u]));
}
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++) {
int u = all[i];
forc[v].push_back(make_pair(pos[u], dist[u] - last_dist[u]));
last_dist[u] = dist[u];
}
sort(forc[v].begin(), forc[v].end());
for (int j = 1; j < cnt; j++) {
forc[v][j].second += forc[v][j - 1].second;
}
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++) {
int u = perm[forc[v][i].first];
in_forc[u].push_back(i);
}
vector <int> children;
for (int i = 0; i < (int) g[v].size(); i++) {
int u = g[v][i].first;
if (alive[u]) {
children.push_back(u);
}
}
alive[v] = false;
for (int i = 0; i < (int) children.size(); i++) {
build(children[i]);
}
}
int main() {
int n, tt;
scanf("%d %d", &n, &tt);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%d", perm + i);
perm[i]--;
pos[perm[i]] = i;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
int x, y, z;
scanf("%d %d %d", &x, &y, &z);
x--; y--;
g[x].push_back(make_pair(y, z));
g[y].push_back(make_pair(x, z));
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
alive[i] = true;
}
build(0);
int last = 0;
while (tt--) {
int com;
scanf("%d", &com);
if (com == 1) {
int from, to, ver;
scanf("%d %d %d", &from, &to, &ver);
from ^= last;
to ^= last;
ver ^= last;
from--; to--; ver--;
long long ans = 0;
long long prev_d = 0;
for (pair <int, long long> p : centroid[ver]) {
int v = p.first;
long long d = p.second;
long long sumd = 0;
int cnt = 0;
{
int pf = lower_bound(forc[v].begin(), forc[v].end(), make_pair(from, -inf)) - forc[v].begin();
int pt = lower_bound(forc[v].begin(), forc[v].end(), make_pair(to + 1, -inf)) - forc[v].begin();
if (pf < pt) {
sumd += forc[v][pt - 1].second;
if (pf > 0) {
sumd -= forc[v][pf - 1].second;
}
cnt += pt - pf;
}
}
ans += sumd + cnt * (d - prev_d);
prev_d = d;
}
printf("%I64d\n", ans);
last = ans & ((1 << 30) - 1);
} else {
int x;
scanf("%d", &x);
x ^= last;
x--;
int v1 = perm[x];
int v2 = perm[x + 1];
int c1 = centroid[v1].size();
int c2 = centroid[v2].size();
int i1 = 0;
int i2 = 0;
long long prev_d2 = 0;
while (i1 < c1 && i2 < c2 && centroid[v1][i1].first == centroid[v2][i2].first) {
int v = centroid[v1][i1].first;
long long d2 = centroid[v2][i2].second;
{
int at = in_forc[v1][i1];
forc[v][at].second = (at == 0 ? 0LL : forc[v][at - 1].second) + d2 - prev_d2;
swap(in_forc[v1][i1], in_forc[v2][i2]);
}
prev_d2 = d2;
i1++; i2++;
}
for (int rot = 0; rot < 2; rot++) {
while (i1 < c1) {
int v = centroid[v1][i1].first;
{
int at = in_forc[v1][i1];
forc[v][at].first = pos[v2];
}
i1++;
}
swap(v1, v2);
swap(c1, c2);
swap(i1, i2);
}
swap(perm[x], perm[x + 1]);
pos[perm[x]] = x;
pos[perm[x + 1]] = x + 1;
}
}
return 0;
}

