Table of Contents
1. Giới thiệu
Lớp HashSet trong Java kế thừa AbstractSet và triển khai Set Interface. Nó tạo một collection mà sử dụng một hash table để lưu giữ.
Một hash table lưu giữ thông tin bởi sử dụng một kỹ thuật được gọi là hashing (băm). Trong hashing, nội dung mang tính thông tin của một key được sử dụng để quyết định một value duy nhất, được gọi là hash code của nó.
Hash code sau đó được sử dụng như là index, tại đó dữ liệu mà liên kết với key được lưu giữ. Phép biến đổi của key vào trong hash code của nó được thực hiện tự động.
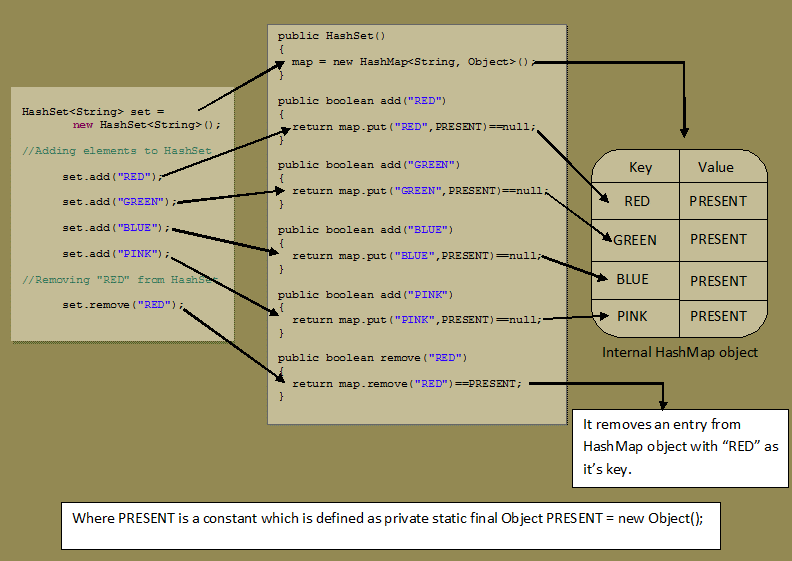
Các điểm quan trọng về lớp HashSet trong java là:
- HashSet chỉ chứa các phần tử duy nhất, không chấp nhận 2 phần tử trùng nhau.
- HashSet lưu trữ các phần tử bằng cách sử dụng một cơ chế được gọi là hashing (băm).
- HashSet không đảm bảo thứ tự được thêm vào.
- HashSet cho phép chứa phần tử NULL.
2. Hierarchy của lớp HashSet
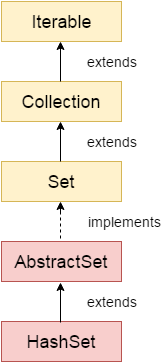
Lớp java.util.HashSet được định nghĩa như sau:
public class HashSet<E> extends AbstractSet<E>
implements Set<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {
static final long serialVersionUID = -5024744406713321676L;
private transient HashMap<E,Object> map;
private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();
public HashSet() {
map = new HashMap<>();
}
}
3. Các phương thức khởi tạo (constructor) của lớp HashSet
- HashSet(): khởi tạo một danh sách mảng trống.
- HashSet(Collection c): khởi tạo một danh sách với các phần tử của collection c.
4. Các phương thức (method) của lớp HashSet
Xem thêm các phương thức của Set ở bài viết Set Interface trong java.
5. Ví dụ minh họa
5.1. Ví dụ sử dụng HashSet với kiểu dữ liệu cơ bản (Wrapper)
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class HashSetExample2 {
public static final int NUM_OF_ELEMENT = 5;
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create set
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add("Item01");
set.add("Item02");
set.add("Item03");
set.add("Item04");
set.add("Item05");
set.add("Item02");
set.add("Item03");
// Show set through for-each
for (String item : set) {
System.out.print(item + " ");
}
}
}
Kết quả thực thi chương trình trên:
Item04 Item03 Item02 Item01 Item05
5.2. Ví dụ sử dụng LinkedList với kiểu do người dùng tự định nghĩa (Object)
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
class Student {
private int id;
private String name;
public Student(int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + "]";
}
}
public class HashSetExample {
public static final int NUM_OF_ELEMENT = 5;
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create list
Set<Student> students = new HashSet<>();
Student student1 = new Student(1, "myname1");
Student student2 = new Student(2, "myname2");
Student student3 = new Student(3, "myname3");
Student student4 = new Student(4, "myname4");
Student student5 = new Student(5, "myname5");
students.add(student1);
students.add(student2);
students.add(student3);
students.add(student4);
students.add(student5);
students.add(student2);
students.add(student3);
// Show set student
for (Student student : students) {
System.out.println(student);
}
}
}
Kết quả thực thi chương trình trên:
Student [id=1, name=myname1] Student [id=4, name=myname4] Student [id=5, name=myname5] Student [id=3, name=myname3] Student [id=2, name=myname2]

