Table of Contents
1. Giới thiệu
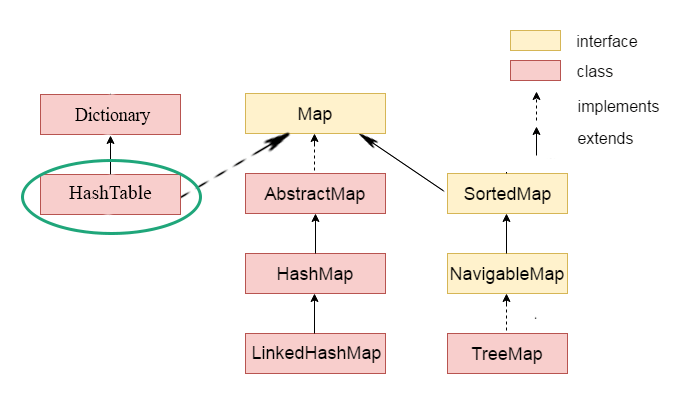
Lớp Java Hashtable cài đặt (implement) một bảng hashtable để map khóa và giá trị. Hashtable kế thừa lớp Dictionary và cài đặt (implement) Map Interface.
Các đặc điểm quan trọng về lớp Hashtable trong java là:
- Hashtable là một mảng của list. Mỗi list được biết đến như một bucket (vùng chứa) các phần tử. Ví trí của một bucket được xác định bằng việc gọi phương thức hashcode(). Hashtable cũng lưu trữ dữ liệu dưới dạng cặp key và value.
- Hashtable chứa các key duy nhất.
- Hashtable KHÔNG thể có bất kỳ key hoặc giá trị nào là null.
- Hashtable được đồng bộ (synchronized).
2. Hierarchy của lớp Hashtable
Lớp java.util.Hashtable được định nghĩa như sau:
public class Hashtable<K,V>
extends Dictionary<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {
}
Trong đó:
- K: đây là kiểu key để lưu trữ.
- V: đây là kiểu giá trị được ánh xạ.
3. Các phương thức khởi tạo (constructor) của lớp Hashtable
- Hashtable(): khởi tạo một hashtable trống, sức chứa (capacity) ban đầu mặc định là 11.
- Hashtable(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> t): khởi tạo một hashtable với các phần tử của map t.
- Hashtable(int initialCapacity): khởi tạo một hashtable trống, với sức chứa (capacity) ban đầu được xác định.
4. Các phương thức (method) của lớp Hashtable
Xem thêm các phương thức của Map ở bài viết Map Interface trong java.
5. Ví dụ minh họa
5.1. Ví dụ sử dụng Hashtable với kiểu dữ liệu cơ bản (Wrapper)
package com.maixuanviet.collection.map.hashtable;
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
public class HashTableExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// init Hashtable
Hashtable<Integer, String> hashTable = new Hashtable<Integer, String>();
hashTable.put(1, "Basic java");
hashTable.put(2, "OOP");
hashTable.put(3, "Collection");
// show Hashtable using method keySet()
for (Integer key : hashTable.keySet()) {
String value = hashTable.get(key);
System.out.println(key + " = " + value);
}
System.out.println("---");
// show map using method keySet()
for (Entry<Integer, String> entry : hashTable.entrySet()) {
Integer key = entry.getKey();
String value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key + " = " + value);
}
}
}
Kết quả thực thi chương trình trên:
3 = Collection 2 = OOP 1 = Basic java --- 3 = Collection 2 = OOP 1 = Basic java
5.2. Ví dụ sử dụng Hashtable với kiểu do người dùng tự định nghĩa (Object)
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
class Student {
private int id;
private String name;
public Student(int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + "]";
}
}
public class HashTableExample2 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// Student's data
Student student1 = new Student(1, "Student 1");
Student student2 = new Student(2, "Student 2");
Student student3 = new Student(3, "Student 3");
// init Hashtable
Hashtable<Integer, Student> hashTable = new Hashtable<Integer, Student>();
hashTable.put(student1.getId(), student1);
hashTable.put(student2.getId(), student2);
hashTable.put(student3.getId(), student3);
// show Hashtable using method keySet()
for (Integer key : hashTable.keySet()) {
Student value = hashTable.get(key);
System.out.println(key + " = " + value);
}
System.out.println("---");
// show Hashtable using method keySet()
for (Entry<Integer, Student> entry : hashTable.entrySet()) {
Integer key = entry.getKey();
Student value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key + " = " + value);
}
}
}
Kết quả thực thi chương trình trên:
3 = Student [id=3, name=Student 3] 2 = Student [id=2, name=Student 2] 1 = Student [id=1, name=Student 1] --- 3 = Student [id=3, name=Student 3] 2 = Student [id=2, name=Student 2] 1 = Student [id=1, name=Student 1] <span data-mce-type="bookmark" style="display: inline-block; width: 0px; overflow: hidden; line-height: 0;" class="mce_SELRES_start"></span>
Related posts:
Template Engines for Spring
Java Program to find the peak element of an array using Binary Search approach
Lớp LinkedHashMap trong Java
Spring Cloud – Securing Services
Java Program to Check whether Undirected Graph is Connected using BFS
Java Program to Implement Bit Array
Java Program to Implement Aho-Corasick Algorithm for String Matching
Refactoring Design Pattern với tính năng mới trong Java 8
Java Program to Perform Naive String Matching
Rest Web service: Filter và Interceptor với Jersey 2.x (P1)
Java Program to Implement LinkedList API
Java Program to Implement Hash Tables
Serverless Functions with Spring Cloud Function
Java Program to Implement Floyd Cycle Algorithm
New Features in Java 14
Guide to @ConfigurationProperties in Spring Boot
Java Program to Implement Binary Heap
Spring Boot - Enabling HTTPS
Java Program to Implement Queue using Two Stacks
Adding Parameters to HttpClient Requests
Java Program to Implement the String Search Algorithm for Short Text Sizes
Java Program to Perform Right Rotation on a Binary Search Tree
Reactive WebSockets with Spring 5
Java Program to Generate Random Partition out of a Given Set of Numbers or Characters
Set Interface trong Java
Spring Boot: Customize the Jackson ObjectMapper
Custom Thread Pools In Java 8 Parallel Streams
Java Program to Perform Cryptography Using Transposition Technique
Spring Boot - Interceptor
Spring’s RequestBody and ResponseBody Annotations
Wrapper Classes in Java
Java Program to Generate All Pairs of Subsets Whose Union Make the Set