Table of Contents
1. Đặc điểm
Những điểm quan trọng về lớp LinkedHashMap trong java cần nhớ là:
- LinkedHashMap lưu trữ dữ liệu dưới dạng cặp key và value.
- LinkedHashMap chỉ chứa các key duy nhất.
- LinkedHashMap có thể có 1 key là null và nhiều giá trị null.
- LinkedHashMap duy trì các phần tử theo thứ tự chèn.
2. Hierarchy của lớp LinkedHashMap
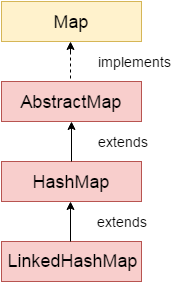
Lớp java.util.LinkedHashMap được định nghĩa như sau:
public class LinkedHashMap<K,V>
extends HashMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V> {
}
Trong đó:
- K: đây là kiểu key để lưu trữ.
- V: đây là kiểu giá trị được ánh xạ.
3. Các phương thức khởi tạo (constructor) của lớp LinkedHashMap
- LinkedHashMap(): khởi tạo một map trống.
- LinkedHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m): khởi tạo một map với các phần tử của map m.
4. Các phương thức (method) của lớp LinkedHashMap
Xem thêm các phương thức của Map ở bài viết Map Interface trong java.
5. Ví dụ minh họa
5.1. Ví dụ sử dụng LinkedHashMap với kiểu dữ liệu cơ bản (Wrapper)
package com.maixuanviet.collection.linkedhashmap;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
public class LinkedHashMapExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// init map
Map<Integer, String> map = new LinkedHashMap<Integer, String>();
map.put(1, "Basic java");
map.put(2, "OOP");
map.put(4, "Multi-Thread");
map.put(3, "Collection");
// show map using method keySet()
for (Integer key : map.keySet()) {
String value = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key + " = " + value);
}
System.out.println("---");
// show map using method keySet()
for (Entry<Integer, String> entry : map.entrySet()) {
Integer key = entry.getKey();
String value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key + " = " + value);
}
}
}
Kết quả thực thi chương trình trên:
1 = Basic java 2 = OOP 4 = Multi-Thread 3 = Collection --- 1 = Basic java 2 = OOP 4 = Multi-Thread 3 = Collection
5.2. Ví dụ sử dụng LinkedHashMap với key có kiểu String, value có kiểu Student
package com.maixuanviet.collection.map;
public class Student {
private int id;
private String name;
public Student(int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + "]";
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
package com.maixuanviet.collection.linkedhashmap;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
public class LinkedHashMapExample2 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// Student's data
Student student1 = new Student(1, "Student 1");
Student student2 = new Student(2, "Student 2");
Student student3 = new Student(3, "Student 3");
Student student4 = new Student(4, "Student 4");
// init map
Map<Integer, Student> map = new LinkedHashMap<Integer, Student>();
map.put(student1.getId(), student1);
map.put(student2.getId(), student2);
map.put(student4.getId(), student4);
map.put(student3.getId(), student3);
// show map using method keySet()
for (Integer key : map.keySet()) {
Student value = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key + " = " + value);
}
System.out.println("---");
// show map using method keySet()
for (Entry<Integer, Student> entry : map.entrySet()) {
Integer key = entry.getKey();
Student value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key + " = " + value);
}
}
}
Kết quả thực thi chương trình trên:
1 = Student [id=1, name=Student 1] 2 = Student [id=2, name=Student 2] 4 = Student [id=4, name=Student 4] 3 = Student [id=3, name=Student 3] --- 1 = Student [id=1, name=Student 1] 2 = Student [id=2, name=Student 2] 4 = Student [id=4, name=Student 4] 3 = Student [id=3, name=Student 3]
Related posts:
The Spring @Controller and @RestController Annotations
Implementing a Binary Tree in Java
So sánh HashMap và HashSet trong Java
Spring – Injecting Collections
Phân biệt JVM, JRE, JDK
Java Program to Implement the RSA Algorithm
Java Program to Implement the One Time Pad Algorithm
How to Get a Name of a Method Being Executed?
Java Program to Implement Hash Tables Chaining with Binary Trees
Transaction Propagation and Isolation in Spring @Transactional
Java Program to Use rand and srand Functions
The Modulo Operator in Java
Spring Security OAuth Login with WebFlux
Documenting a Spring REST API Using OpenAPI 3.0
Lớp Collections trong Java (Collections Utility Class)
Java 8 Predicate Chain
Model, ModelMap, and ModelAndView in Spring MVC
Java Program to Implement AA Tree
Converting a Stack Trace to a String in Java
Java Program to Perform Encoding of a Message Using Matrix Multiplication
Spring Boot Application as a Service
Lớp HashMap trong Java
Refactoring Design Pattern với tính năng mới trong Java 8
Recommended Package Structure of a Spring Boot Project
HandlerAdapters in Spring MVC
Guide to Spring Cloud Kubernetes
Spring Security Basic Authentication
ETags for REST with Spring
Tìm hiểu về xác thực và phân quyền trong ứng dụng
Java Program to do a Depth First Search/Traversal on a graph non-recursively
Java Program to Compute Cross Product of Two Vectors
Java Program to implement Circular Buffer

