Hongcow’s teacher heard that Hongcow had learned about the cyclic shift, and decided to set the following problem for him.
You are given a list of n strings s 1, s 2, …, s n contained in the list A.
A list X of strings is called stable if the following condition holds.
First, a message is defined as a concatenation of some elements of the list X. You can use an arbitrary element as many times as you want, and you may concatenate these elements in any arbitrary order. Let S X denote the set of of all messages you can construct from the list. Of course, this set has infinite size if your list is nonempty.
Call a single message good if the following conditions hold:
- Suppose the message is the concatenation of k strings w 1, w 2, …, w k, where each w i is an element of X.
- Consider the |w 1| + |w 2| + … + |w k| cyclic shifts of the string. Let m be the number of these cyclic shifts of the string that are elements of S X.
- A message is good if and only if m is exactly equal to k.
The list X is called stable if and only if every element of S X is good.
Let f(L) be 1 if L is a stable list, and 0 otherwise.
Find the sum of f(L) where L is a nonempty contiguous sublist of A (there are 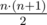 contiguous sublists in total).
contiguous sublists in total).
Input
The first line of input will contain a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 30), denoting the number of strings in the list.
The next n lines will each contain a string s i (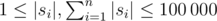 ).
).
Output
Print a single integer, the number of nonempty contiguous sublists that are stable.
Examples
input
4
a
ab
b
bba
output
7
input
5
hh
ee
ll
ll
oo
output
0
input
6
aab
ab
bba
b
ab
c
output
13
Note
For the first sample, there are 10 sublists to consider. Sublists [“a”, “ab”, “b”], [“ab”, “b”, “bba”], and [“a”, “ab”, “b”, “bba”] are not stable. The other seven sublists are stable.
For example, X = [“a”, “ab”, “b”] is not stable, since the message “ab” + “ab” = “abab” has four cyclic shifts [“abab”, “baba”, “abab”, “baba”], which are all elements of S X.
Solution:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1234567;
char foo[42][N];
int z[N];
char s[N];
void build_z(int n) {
int l = 0, r = 0;
z[0] = n;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
z[i] = (i > r ? 0 : min(r - i + 1, z[i - l]));
while (i + z[i] < n && s[z[i]] == s[i + z[i]]) {
z[i]++;
}
if (i + z[i] - 1 > r) {
l = i;
r = i + z[i] - 1;
}
}
}
vector < pair <int, int> > edges[N];
vector <int> g[N], gr[N];
void add(int x, int y, int z) {
// cerr << "adding " << x << " " << y << " " << z << endl;
edges[x].push_back(make_pair(y, z));
}
bool was[N];
int w[N], kw;
void dfs1(int v) {
was[v] = true;
for (int j = 0; j < (int) g[v].size(); j++) {
int u = g[v][j];
if (!was[u]) {
dfs1(u);
}
}
w[kw++] = v;
}
int c[N];
int of_c[N];
void dfs2(int v) {
for (int j = 0; j < (int) gr[v].size(); j++) {
int u = gr[v][j];
if (c[u] == -1) {
c[u] = c[v];
of_c]++;
dfs2(u);
}
}
}
bool loop[N];
int start[N], finish[N];
int flen[N];
int vers;
bool test(int from, int to) {
if (from > to) {
return true;
}
for (int i = 0; i < vers; i++) {
g[i].clear();
gr[i].clear();
}
for (int i = 0; i < vers; i++) {
was[i] = true;
loop[i] = false;
}
was[0] = false;
for (int j = 0; j < (int) edges[0].size(); j++) {
g[0].push_back(edges[0][j].first);
gr[edges[0][j].first].push_back(0);
}
for (int id = from; id <= to; id++) {
for (int i = start[id]; i < finish[id]; i++) {
was[i] = false;
for (int j = 0; j < (int) edges[i].size(); j++) {
int helper = edges[i][j].second;
if (helper < from || helper > to) {
continue;
}
if (i == edges[i][j].first) {
loop[i] = true;
}
g[i].push_back(edges[i][j].first);
gr[edges[i][j].first].push_back(i);
}
}
}
kw = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < vers; i++) {
if (was[i]) {
continue;
}
dfs1(i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < vers; i++) {
c[i] = -1;
}
int nc = 0;
for (int id = kw - 1; id >= 0; id--) {
int i = w[id];
if (c[i] == -1) {
of_c[nc] = 1;
c[i] = nc++;
dfs2(i);
}
}
for (int id = from; id <= to; id++) {
for (int i = start[id] + 1; i < finish[id]; i++) {
if (of_c] > 1 || loop[i]) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
int main() {
int cnt;
scanf("%d", &cnt);
vers = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++) {
scanf("%s", foo[i]);
flen[i] = strlen(foo[i]);
start[i] = vers;
vers += flen[i];
finish[i] = vers;
add(0, start[i], -1);
}
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++) {
int n = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < flen[i]; j++) {
s[n++] = foo[i][j];
}
s[n++] = '#';
int from = n;
for (int q = 0; q < cnt; q++) {
n = from;
for (int j = 0; j < flen[q]; j++) {
s[n++] = foo[q][j];
}
build_z(n);
for (int j = 0; j < flen[q]; j++) {
int x = flen[i];
int y = flen[q] - j;
if (z[from + j] != min(x, y)) {
continue;
}
// cerr << "hi! " << i << " " << q << " " << j << " " << x << " " << y << " " << z[from + j] << endl;
if (x == y) {
add(start[q] + j, 0, i);
} else {
if (x < y) {
add(start[q] + j, start[q] + j + x, i);
} else {
add(start[q] + j, start[i] + y, i);
}
}
}
}
}
int j = -1;
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++) {
while (j + 1 < cnt) {
if (!test(i, j + 1)) {
break;
}
j++;
}
if (i <= j) {
ans += j - i + 1;
}
// cerr << i << " -> " << j << endl;
}
printf("%d\n", ans);
return 0;
}

