Some time ago Leonid have known about idempotent functions. Idempotent function defined on a set {1, 2, …, n} is such function 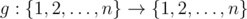 , that for any
, that for any 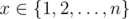 the formula g(g(x)) = g(x) holds.
the formula g(g(x)) = g(x) holds.
Let’s denote as f (k)(x) the function f applied k times to the value x. More formally, f (1)(x) = f(x), f (k)(x) = f(f (k - 1)(x)) for each k > 1.
You are given some function 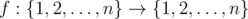 . Your task is to find minimum positive integer k such that function f (k)(x) is idempotent.
. Your task is to find minimum positive integer k such that function f (k)(x) is idempotent.
Input
In the first line of the input there is a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 200) — the size of function f domain.
In the second line follow f(1), f(2), …, f(n) (1 ≤ f(i) ≤ n for each 1 ≤ i ≤ n), the values of a function.
Output
Output minimum k such that function f (k)(x) is idempotent.
Examples
input
4
1 2 2 4
output
1
input
3
2 3 3
output
2
input
3
2 3 1
output
3
Note
In the first sample test function f(x) = f (1)(x) is already idempotent since f(f(1)) = f(1) = 1, f(f(2)) = f(2) = 2, f(f(3)) = f(3) = 2, f(f(4)) = f(4) = 4.
In the second sample test:
- function f(x) = f (1)(x) isn’t idempotent because f(f(1)) = 3 but f(1) = 2;
- function f(x) = f (2)(x) is idempotent since for any x it is true that f (2)(x) = 3, so it is also true that f (2)(f (2)(x)) = 3.
In the third sample test:
- function f(x) = f (1)(x) isn’t idempotent because f(f(1)) = 3 but f(1) = 2;
- function f(f(x)) = f (2)(x) isn’t idempotent because f (2)(f (2)(1)) = 2 but f (2)(1) = 3;
- function f(f(f(x))) = f (3)(x) is idempotent since it is identity function: f (3)(x) = x for any
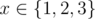 meaning that the formula f (3)(f (3)(x)) = f (3)(x) also holds.
meaning that the formula f (3)(f (3)(x)) = f (3)(x) also holds.
Solution:
import java.io.Reader;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.InputMismatchException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.io.Writer;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* Built using CHelper plug-in
* Actual solution is at the top
* @author Niyaz Nigmatullin
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InputStream inputStream = System.in;
OutputStream outputStream = System.out;
FastScanner in = new FastScanner(inputStream);
FastPrinter out = new FastPrinter(outputStream);
TaskC solver = new TaskC();
solver.solve(1, in, out);
out.close();
}
}
class TaskC {
public void solve(int testNumber, FastScanner in, FastPrinter out) {
int n = in.nextInt();
int[] f = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) f[i] = in.nextInt() - 1;
int[] was = new int[n];
int[] d = new int[n];
BigInteger ans = BigInteger.ONE;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Arrays.fill(was, 0);
int p = i;
int c = 0;
while (was[p] == 0) {
d[p] = c++;
was[p] = 1;
p = f[p];
}
BigInteger cycle = BigInteger.valueOf(c - d[p]);
ans = ans.divide(ans.gcd(cycle)).multiply(cycle);
}
for (int q = 1; q <= 2 * n; q++) {
boolean bad = false;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int v = i;
for (int j = 0; j < q; j++) v = f[v];
int u = v;
for (int j = 0; j < q; j++) u = f[u];
if (v != u) {
bad = true;
}
}
if (!bad) {
out.println(q);
return;
}
}
out.println(ans);
}
}
class FastScanner extends BufferedReader {
public FastScanner(InputStream is) {
super(new InputStreamReader(is));
}
public int read() {
try {
int ret = super.read();
// if (isEOF && ret < 0) {
// throw new InputMismatchException();
// }
// isEOF = ret == -1;
return ret;
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new InputMismatchException();
}
}
static boolean isWhiteSpace(int c) {
return c >= 0 && c <= 32;
}
public int nextInt() {
int c = read();
while (isWhiteSpace(c)) {
c = read();
}
int sgn = 1;
if (c == '-') {
sgn = -1;
c = read();
}
int ret = 0;
while (c >= 0 && !isWhiteSpace(c)) {
if (c < '0' || c > '9') {
throw new NumberFormatException("digit expected " + (char) c
+ " found");
}
ret = ret * 10 + c - '0';
c = read();
}
return ret * sgn;
}
public String readLine() {
try {
return super.readLine();
} catch (IOException e) {
return null;
}
}
}
class FastPrinter extends PrintWriter {
public FastPrinter(OutputStream out) {
super(out);
}
}

