Nagini, being a horcrux You-know-who created with the murder of Bertha Jorkins, has accumulated its army of snakes and is launching an attack on Hogwarts school.
Hogwarts’ entrance can be imagined as a straight line (x-axis) from 1 to 105. Nagini is launching various snakes at the Hogwarts entrance. Each snake lands parallel to the entrance, covering a segment at a distance k from x = l to x = r. Formally, each snake can be imagined as being a line segment between points (l, k) and (r, k). Note that k can be both positive and negative, but not 0.
Let, at some x-coordinate x = i, there be snakes at point (i, y 1) and point (i, y 2), such that y 1 > 0 and y 2 < 0. Then, if for any point (i, y 3) containing a snake such that y 3 > 0, y 1 ≤ y 3 holds and for any point (i, y 4) containing a snake such that y 4 < 0, |y 2| ≤ |y 4| holds, then the danger value at coordinate x = i is y 1 + |y 2|. If no such y 1 and y 2 exist, danger value is 0.
Harry wants to calculate the danger value of various segments of the Hogwarts entrance. Danger value for a segment [l, r) of the entrance can be calculated by taking the sum of danger values for each integer x-coordinate present in the segment.
Formally, you have to implement two types of queries:
- 1 l r k: a snake is added parallel to entrance from x = l to x = r at y-coordinate y = k ( l inclusive, r exclusive).
- 2 l r: you have to calculate the danger value of segment l to r ( l inclusive, r exclusive).
Input
First line of input contains a single integer q (1 ≤ q ≤ 5·104) denoting the number of queries.
Next q lines each describe a query. Each query description first contains the query type type i (1 ≤ type i ≤ 2). This is followed by further description of the query. In case of the type being 1, it is followed by integers l i, r i and k i (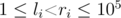 , - 109 ≤ k i ≤ 109, k ≠ 0). Otherwise, it just contains two integers, l i and r i (1 ≤ l i < r i ≤ 105).
, - 109 ≤ k i ≤ 109, k ≠ 0). Otherwise, it just contains two integers, l i and r i (1 ≤ l i < r i ≤ 105).
Output
Output the answer for each query of type 2 in a separate line.
Examples
input
3
1 1 10 10
1 2 4 -7
2 1 10
output
34
input
7
1 2 3 5
1 1 10 10
1 4 5 -5
2 4 8
1 1 10 -10
2 4 8
2 1 10
output
15
75
170
Note
In the first sample case, the danger value for x-coordinates 1 is 0 as there is no y 2 satisfying the above condition for x = 1.
Danger values for x-coordinates 2 and 3 is 10 + | - 7| = 17.
Danger values for x-coordinates 4 to 9 is again 0 as there is no y 2 satisfying the above condition for these coordinates.
Thus, total danger value is 17 + 17 = 34.
Solution:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int BLOCK = 301;
const int CNT = (100010 + BLOCK - 1) / BLOCK;
const int n = CNT * BLOCK;
const int N = n + 10;
inline void upd(int &a, int b) {
a = ((a == 0 || b == 0) ? a + b : min(a, b));
}
int a[2][N];
int b[2][CNT];
bool zeros[2][CNT];
vector<int> c[2][CNT];
int sz[2][CNT];
long long sum[CNT];
inline void push(int id) {
for (int p = 0; p < 2; p++) {
if (b[p][id] != 0) {
for (int i = id * BLOCK; i < (id + 1) * BLOCK; i++) {
upd(a[p][i], b[p][id]);
}
b[p][id] = 0;
}
}
}
inline void pull(int id) {
for (int p = 0; p < 2; p++) {
zeros[p][id] = false;
for (int i = id * BLOCK; i < (id + 1) * BLOCK; i++) {
if (a[p][i] == 0) {
zeros[p][id] = true;
break;
}
}
if (zeros[p][id]) {
continue;
}
c[p][id].clear();
for (int i = id * BLOCK; i < (id + 1) * BLOCK; i++) {
if (a[1 - p][i] != 0) {
c[p][id].push_back(a[p][i]);
}
}
sz[p][id] = c[p][id].size();
sort(c[p][id].begin(), c[p][id].end());
}
sum[id] = 0;
for (int i = id * BLOCK; i < (id + 1) * BLOCK; i++) {
if (a[0][i] > 0 && a[1][i] > 0) {
sum[id] += a[0][i] + a[1][i];
}
}
}
inline void update_block(int id, int p, int k) {
int old = b[p][id];
upd(b[p][id], k);
if (zeros[p][id]) {
push(id);
pull(id);
} else {
int extra = sz[p][id] - (int) c[p][id].size();
if (extra > 0 && k < old) {
sum[id] -= extra * 1LL * (old - k);
}
while (!c[p][id].empty() && c[p][id].back() > k) {
sum[id] -= c[p][id].back() - k;
c[p][id].pop_back();
}
}
}
inline long long get_block(int id) {
return sum[id];
}
int main() {
int tt;
scanf("%d", &tt);
for (int p = 0; p < 2; p++) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
a[p][i] = 0;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n / BLOCK; i++) {
pull(i);
}
while (tt--) {
int type, from, to;
scanf("%d %d %d", &type, &from, &to);
to--;
if (type == 1) {
int k;
scanf("%d", &k);
int p;
if (k > 0) {
p = 0;
} else {
p = 1;
k = -k;
}
int fid = from / BLOCK;
int tid = to / BLOCK;
push(fid);
if (fid != tid) {
push(tid);
}
while (from <= to && from / BLOCK == fid) {
upd(a[p][from], k);
from++;
}
while (from <= to && to / BLOCK == tid) {
upd(a[p][to], k);
to--;
}
pull(fid);
if (fid != tid) {
pull(tid);
}
for (int id = fid + 1; id <= tid - 1; id++) {
update_block(id, p, k);
}
} else {
long long ans = 0;
int fid = from / BLOCK;
int tid = to / BLOCK;
push(fid);
if (fid != tid) {
push(tid);
}
while (from <= to && from / BLOCK == fid) {
if (a[0][from] > 0 && a[1][from] > 0) {
ans += a[0][from] + a[1][from];
}
from++;
}
while (from <= to && to / BLOCK == tid) {
if (a[0][to] > 0 && a[1][to] > 0) {
ans += a[0][to] + a[1][to];
}
to--;
}
pull(fid);
if (fid != tid) {
pull(tid);
}
for (int id = fid + 1; id <= tid - 1; id++) {
ans += get_block(id);
}
printf("%I64d\n", ans);
}
}
cerr << "time = " << clock() << " ms" << endl;
return 0;
}

