Ali is Hamed’s little brother and tomorrow is his birthday. Hamed wants his brother to earn his gift so he gave him a hard programming problem and told him if he can successfully solve it, he’ll get him a brand new laptop. Ali is not yet a very talented programmer like Hamed and although he usually doesn’t cheat but this time is an exception. It’s about a brand new laptop. So he decided to secretly seek help from you. Please solve this problem for Ali.
An n-vertex weighted rooted tree is given. Vertex number 1 is a root of the tree. We define d(u, v) as the sum of edges weights on the shortest path between vertices u and v. Specifically we define d(u, u) = 0. Also let’s define S(v) for each vertex v as a set containing all vertices u such that d(1, u) = d(1, v) + d(v, u). Function f(u, v) is then defined using the following formula:
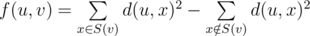
The goal is to calculate f(u, v) for each of the q given pair of vertices. As the answer can be rather large it’s enough to print it modulo 109 + 7.
Input
In the first line of input an integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105), number of vertices of the tree is given.
In each of the next n - 1 lines three space-separated integers a i, b i, c i (1 ≤ a i, b i ≤ n, 1 ≤ c i ≤ 109) are given indicating an edge between a i and b i with weight equal to c i.
In the next line an integer q (1 ≤ q ≤ 105), number of vertex pairs, is given.
In each of the next q lines two space-separated integers u i, v i (1 ≤ u i, v i ≤ n) are given meaning that you must calculate f(u i, v i).
It is guaranteed that the given edges form a tree.
Output
Output q lines. In the i-th line print the value of f(u i, v i) modulo 109 + 7.
Examples
input
5
1 2 1
4 3 1
3 5 1
1 3 1
5
1 1
1 5
2 4
2 1
3 5
output
10
1000000005
1000000002
23
1000000002
input
8
1 2 100
1 3 20
2 4 2
2 5 1
3 6 1
3 7 2
6 8 5
6
1 8
2 3
5 8
2 6
4 7
6 1
output
999968753
49796
999961271
999991235
999958569
45130
Solution:
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <deque>
#include <stack>
#include <bitset>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
#include <numeric>
#include <utility>
#include <sstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
#include <memory.h>
#include <cassert>
using namespace std;
const int md = 1000000007;
inline void add(int &a, int b) {
a += b;
if (a >= md) {
a -= md;
}
}
inline int mul(int a, int b) {
return (long long)a * b % md;
}
const int N = 400010;
vector < pair <int, int> > g[N];
int cnt[N], sum[N], sumsq[N];
int tin[N], tout[N], TIME = 0;
int depth[N];
int pv[N];
const int LOG = 20;
int pr[N][LOG];
void dfs(int v, int pr) {
tin[v] = ++TIME;
int sz = g[v].size();
cnt[v] = 1;
sum[v] = 0;
sumsq[v] = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < sz; j++) {
int u = g[v][j].first;
if (u == pr) {
continue;
}
pv[u] = v;
int len = g[v][j].second;
depth[u] = depth[v];
add(depth[u], len);
dfs(u, v);
add(cnt[v], cnt[u]);
add(sum[v], sum[u]);
add(sum[v], mul(cnt[u], len));
add(sumsq[v], sumsq[u]);
add(sumsq[v], mul(cnt[u], mul(len, len)));
add(sumsq[v], mul(mul(2, len), sum[u]));
}
tout[v] = ++TIME;
}
bool anc(int x, int y) {
return (tin[x] <= tin[y] && tout[y] <= tout[x]);
}
int lca(int x, int y) {
if (anc(x, y)) return x;
for (int j = LOG - 1; j >= 0; j--)
if (!anc(pr[x][j], y)) x = pr[x][j];
return pv[x];
}
int ups[N];
int up[N];
int n;
void get_up(int v, int pr) {
int sz = g[v].size();
for (int j = 0; j < sz; j++) {
int u = g[v][j].first;
if (u == pr) {
continue;
}
int len = g[v][j].second;
int no_s = sum[v];
add(no_s, md - sum[u]);
add(no_s, md - mul(cnt[u], len));
add(no_s, ups[v]);
int no_sq = sumsq[v];
add(no_sq, md - sumsq[u]);
add(no_sq, md - mul(cnt[u], mul(len, len)));
add(no_sq, md - mul(mul(2, len), sum[u]));
up[u] = up[v];
add(up[u], no_sq);
add(up[u], mul(n - cnt[u], mul(len, len)));
add(up[u], mul(mul(2, len), no_s));
ups[u] = ups[v];
int no_sss = sum[v];
add(no_sss, md - sum[u]);
add(no_sss, md - mul(cnt[u], len));
add(ups[u], no_sss);
add(ups[u], mul(n - cnt[u], len));
get_up(u, v);
}
}
int res[N];
int main() {
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
g[i].clear();
}
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
int foo, bar, len;
scanf("%d %d %d", &foo, &bar, &len);
foo--; bar--;
g[foo].push_back(make_pair(bar, len));
g[bar].push_back(make_pair(foo, len));
}
depth[0] = 0;
dfs(0, -1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) pr[i][0] = pv[i];
for (int j = 1; j < LOG; j++)
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) pr[i][j] = pr[pr[i][j - 1]][j - 1];
ups[0] = 0;
up[0] = 0;
get_up(0, -1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
res[i] = sumsq[i];
add(res[i], up[i]);
}
int tt;
scanf("%d", &tt);
while (tt--) {
int u, v;
scanf("%d %d", &u, &v);
u--; v--;
if (!anc(v, u)) {
int len = depth[v];
add(len, depth[u]);
int z = lca(v, u);
add(len, md - mul(2, depth[z]));
int good = sumsq[v];
add(good, mul(cnt[v], mul(len, len)));
add(good, mul(mul(2, len), sum[v]));
good = mul(good, 2);
add(good, md - res[u]);
printf("%d\n", good);
} else {
int len = depth[u];
add(len, md - depth[v]);
int good = up[v];
add(good, mul(n - cnt[v], mul(len, len)));
add(good, mul(mul(2, len), ups[v]));
good = (res[u] - good + md) % md;
good = mul(good, 2);
add(good, md - res[u]);
printf("%d\n", good);
}
}
return 0;
}

