There is a square grid of size $n \times n$. Some cells are colored in black, all others are colored in white. In one operation you can select some rectangle and color all its cells in white. It costs $\min(h, w)$ to color a rectangle of size $h \times w$. You are to make all cells white for minimum total cost.
The square is large, so we give it to you in a compressed way. The set of black cells is the union of $m$ rectangles.
Input
The first line contains two integers $n$ and $m$ ($1 \le n \le 10^{9}$, $0 \le m \le 50$) — the size of the square grid and the number of black rectangles.
Each of the next $m$ lines contains 4 integers $x_{i1}$ $y_{i1}$ $x_{i2}$ $y_{i2}$ ($1 \le x_{i1} \le x_{i2} \le n$, $1 \le y_{i1} \le y_{i2} \le n$) — the coordinates of the bottom-left and the top-right corner cells of the $i$-th black rectangle.
The rectangles may intersect.
Output
Print a single integer — the minimum total cost of painting the whole square in white.
Examples
input
10 2 4 1 5 10 1 4 10 5
output
4
input
7 6 2 1 2 1 4 2 4 3 2 5 2 5 2 3 5 3 1 2 1 2 3 2 5 3
output
3
Note
The examples and some of optimal solutions are shown on the pictures below.
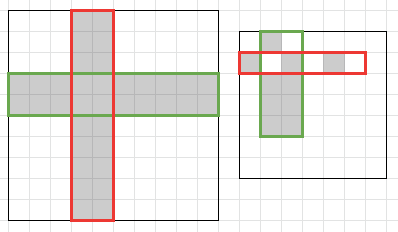
Solution:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
template <typename T>
class flow_graph {
public:
static constexpr T eps = (T) 1e-9;
struct edge {
int from;
int to;
T c;
T f;
};
vector<vector<int>> g;
vector<edge> edges;
int n;
int st;
int fin;
T flow;
flow_graph(int _n, int _st, int _fin) : n(_n), st(_st), fin(_fin) {
assert(0 <= st && st < n && 0 <= fin && fin < n && st != fin);
g.resize(n);
flow = 0;
}
void clear_flow() {
for (const edge &e : edges) {
e.f = 0;
}
flow = 0;
}
int add(int from, int to, T forward_cap, T backward_cap) {
assert(0 <= from && from < n && 0 <= to && to < n);
int id = (int) edges.size();
g[from].push_back(id);
edges.push_back({from, to, forward_cap, 0});
g[to].push_back(id + 1);
edges.push_back({to, from, backward_cap, 0});
return id;
}
};
template <typename T>
class dinic {
public:
flow_graph<T> &g;
vector<int> ptr;
vector<int> d;
vector<int> q;
dinic(flow_graph<T> &_g) : g(_g) {
ptr.resize(g.n);
d.resize(g.n);
q.resize(g.n);
}
bool expath() {
fill(d.begin(), d.end(), -1);
q[0] = g.fin;
d[g.fin] = 0;
int beg = 0, end = 1;
while (beg < end) {
int i = q[beg++];
for (int id : g.g[i]) {
const auto &e = g.edges[id];
const auto &back = g.edges[id ^ 1];
if (back.c - back.f > g.eps && d[e.to] == -1) {
d[e.to] = d[i] + 1;
if (e.to == g.st) {
return true;
}
q[end++] = e.to;
}
}
}
return false;
}
T dfs(int v, T w) {
if (v == g.fin) {
return w;
}
int &j = ptr[v];
while (j >= 0) {
int id = g.g[v][j];
const auto &e = g.edges[id];
if (e.c - e.f > g.eps && d[e.to] == d[v] - 1) {
T t = dfs(e.to, min(e.c - e.f, w));
if (t > g.eps) {
g.edges[id].f += t;
g.edges[id ^ 1].f -= t;
return t;
}
}
j--;
}
return 0;
}
T max_flow() {
while (expath()) {
for (int i = 0; i < g.n; i++) {
ptr[i] = (int) g.g[i].size() - 1;
}
T big_add = 0;
while (true) {
T add = dfs(g.st, numeric_limits<T>::max());
if (add <= g.eps) {
break;
}
big_add += add;
}
if (big_add <= g.eps) {
break;
}
g.flow += big_add;
}
return g.flow;
}
vector<bool> min_cut() {
max_flow();
vector<bool> ret(g.n);
for (int i = 0; i < g.n; i++) {
ret[i] = (d[i] != -1);
}
return ret;
}
};
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<int> xa(m), ya(m), xb(m), yb(m);
vector<int> xs = {0, n};
vector<int> ys = {0, n};
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
cin >> xa[i] >> ya[i] >> xb[i] >> yb[i];
--xa[i]; --ya[i];
xs.push_back(xa[i]);
ys.push_back(ya[i]);
xs.push_back(xb[i]);
ys.push_back(yb[i]);
}
sort(xs.begin(), xs.end());
xs.resize(unique(xs.begin(), xs.end()) - xs.begin());
sort(ys.begin(), ys.end());
ys.resize(unique(ys.begin(), ys.end()) - ys.begin());
int nx = (int) xs.size() - 1;
int ny = (int) ys.size() - 1;
const long long inf = (long long) 2e18;
flow_graph<long long> g(nx + ny + 2, nx + ny, nx + ny + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < nx; i++) {
g.add(nx + ny, i, xs[i + 1] - xs[i], 0);
}
for (int i = 0; i < ny; i++) {
g.add(nx + i, nx + ny + 1, ys[i + 1] - ys[i], 0);
}
for (int i = 0; i < nx; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < ny; j++) {
int ok = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < m; k++) {
if (xa[k] <= xs[i] && xs[i + 1] <= xb[k] && ya[k] <= ys[j] && ys[j + 1] <= yb[k]) {
ok = 1;
break;
}
}
if (ok) {
g.add(i, nx + j, inf, 0);
}
}
}
dinic<long long> d(g);
cout << d.max_flow() << '\n';
return 0;
}

