You are given two rectangles on a plane. The centers of both rectangles are located in the origin of coordinates (meaning the center of the rectangle’s symmetry). The first rectangle’s sides are parallel to the coordinate axes: the length of the side that is parallel to the Ox axis, equals w, the length of the side that is parallel to the Oy axis, equals h. The second rectangle can be obtained by rotating the first rectangle relative to the origin of coordinates by angle α.
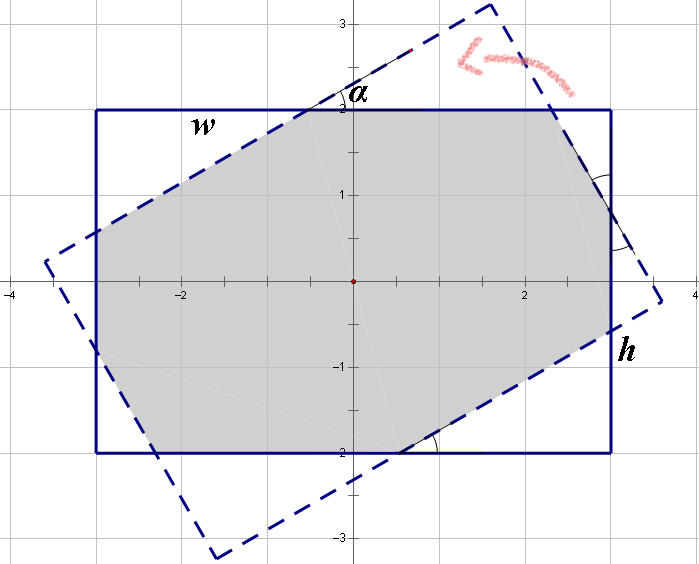
Your task is to find the area of the region which belongs to both given rectangles. This region is shaded in the picture.
Input
The first line contains three integers w, h, α (1 ≤ w, h ≤ 106; 0 ≤ α ≤ 180). Angle α is given in degrees.
Output
In a single line print a real number — the area of the region which belongs to both given rectangles.
The answer will be considered correct if its relative or absolute error doesn’t exceed 10 - 6.
Examples
input
1 1 45
output
0.828427125
input
6 4 30
output
19.668384925
Note
The second sample has been drawn on the picture above.
Solution:
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <memory.h>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
const long double pi = 3.1415926535897932384626433832795;
long double x[42], y[42];
int n;
void add(int qx, int qy, long double ang) {
x[n] = cos(ang)*qx-sin(ang)*qy;
y[n] = sin(ang)*qx+cos(ang)*qy;
n++;
}
void cut(long double xa, long double ya, long double xb, long double yb) {
long double a = yb-ya, b = xa-xb;
long double c = -a*xa-b*ya;
long double eps = (1e-10)*1.00042;
int nn = 0;
long double xx[42], yy[42];
x[n] = x[0]; y[n] = y[0];
for (int i=0;i<n;i++) {
long double z1 = a*x[i]+b*y[i]+c;
if (z1 < eps) {
xx[nn] = x[i];
yy[nn] = y[i];
nn++;
}
long double z2 = a*x[i+1]+b*y[i+1]+c;
if (z1 < eps && z2 > eps || z1 > eps && z2 < eps) {
long double aa = y[i+1]-y[i], bb = x[i]-x[i+1];
long double cc = -aa*x[i]-bb*y[i];
long double d = a*bb-b*aa;
xx[nn] = (b*cc-c*bb)/d;
yy[nn] = (c*aa-a*cc)/d;
nn++;
}
}
n = nn;
for (int i=0;i<n;i++) x[i] = xx[i], y[i] = yy[i];
}
int main() {
int w, h, iang;
scanf("%d %d %d", &w, &h, &iang);
long double ang = iang/180.0*pi;
n = 0;
add(w, h, ang);
add(-w, h, ang);
add(-w, -h, ang);
add(w, -h, ang);
cut(w, h, -w, h);
cut(-w, h, -w, -h);
cut(-w, -h, w, -h);
cut(w, -h, w, h);
x[n] = x[0]; y[n] = y[0];
long double area = 0;
for (int i=0;i<n;i++) area += (x[i]-x[i+1])*(y[i]+y[i+1]);
printf("%.17lf\n", (double)(0.125*area));
return 0;
}

