Fibonotci sequence is an integer recursive sequence defined by the recurrence relation Fn = sn - 1·Fn - 1 + sn - 2·Fn - 2 with F0 = 0, F1 = 1
Sequence s is an infinite and almost cyclic sequence with a cycle of length N. A sequence s is called almost cyclic with a cycle of length N if 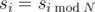 , for i ≥ N, except for a finite number of values s i, for which
, for i ≥ N, except for a finite number of values s i, for which 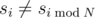 ( i ≥ N).
( i ≥ N).
Following is an example of an almost cyclic sequence with a cycle of length 4:s = (5,3,8,11,5,3,7,11,5,3,8,11,…)
Notice that the only value of s for which the equality 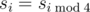 does not hold is s 6 ( s 6 = 7 and s 2 = 8). You are given s 0, s 1, …s N - 1 and all the values of sequence s for which
does not hold is s 6 ( s 6 = 7 and s 2 = 8). You are given s 0, s 1, …s N - 1 and all the values of sequence s for which 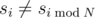 ( i ≥ N).
( i ≥ N).
Find 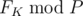 .
.
Input
The first line contains two numbers K and P. The second line contains a single number N. The third line contains N numbers separated by spaces, that represent the first N numbers of the sequence s. The fourth line contains a single number M, the number of values of sequence s for which 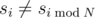 . Each of the following M lines contains two numbers j and v, indicating that
. Each of the following M lines contains two numbers j and v, indicating that 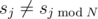 and s j = v. All j-s are distinct.
and s j = v. All j-s are distinct.
- 1 ≤ N, M ≤ 50000
- 0 ≤ K ≤ 1018
- 1 ≤ P ≤ 109
- 1 ≤ s i ≤ 109, for all i = 0, 1, …N - 1
- N ≤ j ≤ 1018
- 1 ≤ v ≤ 109
- All values are integers
Output
Output should contain a single integer equal to 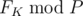 .
.
Examples
input
10 8
3
1 2 1
2
7 3
5 4
output
4
Solution:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 400010;
int n;
int md;
inline void add(int &a, int b) {
a += b;
if (a >= md) {
a -= md;
}
}
inline int mul(int a, int b) {
return (long long) a * b % md;
}
struct Matrix {
int a[2][2];
Matrix(int diag = 1) {
a[0][0] = diag;
a[0][1] = 0;
a[1][0] = 0;
a[1][1] = diag;
}
};
inline Matrix mul(Matrix &a, Matrix b) {
Matrix c(0);
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) {
c.a[i][j] = ((long long)a.a[i][0] * b.a[0][j] + (long long)a.a[i][1] * b.a[1][j]) % md;
}
}
return c;
}
inline Matrix power(Matrix a, long long b) {
Matrix res(1);
while (b > 0) {
if (b & 1) {
res = mul(res, a);
}
a = mul(a, a);
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
int s[N], value[N];
long long pos[N];
Matrix tree[N];
void build(int x, int l, int r) {
if (l < r) {
int y = (l + r) >> 1;
build(x + x, l, y);
build(x + x + 1, y + 1, r);
tree[x] = mul(tree[x + x], tree[x + x + 1]);
} else {
tree[x] = Matrix(0);
tree[x].a[1][0] = 1;
tree[x].a[0][1] = s[(l + n - 2) % n];
tree[x].a[1][1] = s[(l + n - 1) % n];
}
}
Matrix get(int x, int l, int r, int ll, int rr) {
if (r < ll || rr < l || ll > rr) {
return Matrix(1);
}
if (ll <= l && r <= rr) {
return tree[x];
}
int y = (l + r) >> 1;
Matrix res(1);
if (ll <= y) {
res = get(x + x, l, y, ll, rr);
}
if (rr > y) {
res = mul(res, get(x + x + 1, y + 1, r, ll, rr));
}
return res;
}
map <long long, int> mp;
inline void proceed(Matrix &res, long long pos) {
Matrix other(0);
other.a[1][0] = 1;
if (mp.find(pos - 2) == mp.end()) {
other.a[0][1] = s[(pos - 2 + n) % n];
} else {
other.a[0][1] = mp[pos - 2];
}
if (mp.find(pos - 1) == mp.end()) {
other.a[1][1] = s[(pos - 1 + n) % n];
} else {
other.a[1][1] = mp[pos - 1];
}
res = mul(res, other);
}
int main() {
long long k;
scanf("%I64d %d", &k, &md);
if (md == 1) {
printf("%d\n", 0);
return 0;
}
if (k == 0) {
printf("%d\n", 0 % md);
return 0;
}
if (k == 1) {
printf("%d\n", 1 % md);
return 0;
}
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%d", s + i);
s[i] %= md;
}
build(1, 0, n - 1);
Matrix all = tree[1];
vector <long long> special;
int m;
scanf("%d", &m);
mp.clear();
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
scanf("%I64d %d", pos + i, value + i);
value[i] %= md;
special.push_back(pos[i] + 1);
special.push_back(pos[i] + 2);
mp[pos[i]] = value[i];
}
special.push_back(k);
sort(special.begin(), special.end());
special.resize(unique(special.begin(), special.end()) - special.begin());
while (!special.empty() && special.back() > k) {
special.pop_back();
}
Matrix res(1);
long long cur = 1;
for (int id = 0; id < (int)special.size(); id++) {
long long nxt = special[id];
long long from = cur + 1;
long long to = nxt - 1;
if (from <= to) {
if (from / n == to / n) {
res = mul(res, get(1, 0, n - 1, from % n, to % n));
} else {
res = mul(res, get(1, 0, n - 1, from % n, n - 1));
res = mul(res, power(all, to / n - from / n - 1));
res = mul(res, get(1, 0, n - 1, 0, to % n));
}
}
proceed(res, nxt);
cur = nxt;
}
printf("%d\n", res.a[1][1]);
return 0;
}

