Hamed has recently found a string t and suddenly became quite fond of it. He spent several days trying to find all occurrences of t in other strings he had. Finally he became tired and started thinking about the following problem. Given a string s how many ways are there to extract k ≥ 1 non-overlapping substrings from it such that each of them contains string t as a substring? More formally, you need to calculate the number of ways to choose two sequences a 1, a 2, …, a k and b 1, b 2, …, b k satisfying the following requirements:
- k ≥ 1
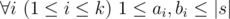
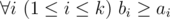
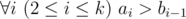
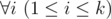 t is a substring of string s a i s a i + 1… s b i (string s is considered as 1-indexed).
t is a substring of string s a i s a i + 1… s b i (string s is considered as 1-indexed).
As the number of ways can be rather large print it modulo 109 + 7.
Input
Input consists of two lines containing strings s and t (1 ≤ |s|, |t| ≤ 105). Each string consists of lowercase Latin letters.
Output
Print the answer in a single line.
Examples
input
ababa
aba
output
5
input
welcometoroundtwohundredandeightytwo
d
output
274201
input
ddd
d
output
12
Solution:
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <deque>
#include <stack>
#include <bitset>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
#include <numeric>
#include <utility>
#include <sstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
#include <memory.h>
#include <cassert>
using namespace std;
const int md = 1000000007;
inline void add(int &a, int b) {
a += b;
if (a >= md) {
a -= md;
}
}
inline int mul(int a, int b) {
return (long long)a * b % md;
}
const int N = 500010;
char s[N], t[N];
int f[N], value[N];
bool into[N];
int p[N];
int jump[N];
int main() {
scanf("%s", s + 1);
scanf("%s", t + 1);
int n = strlen(s + 1);
int m = strlen(t + 1);
int k = 0;
p[1] = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= m; i++) {
while (k > 0 && t[i] != t[k + 1]) k = p[k];
if (t[i] == t[k + 1]) k++;
p[i] = k;
}
k = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
while (k > 0 && s[i] != t[k + 1]) k = p[k];
if (s[i] == t[k + 1]) k++;
into[i] = (k == m);
}
jump[n] = n + 1;
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
jump[i] = jump[i + 1];
if (i + m <= n && into[i + m]) {
jump[i] = i + m;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
value[i] = 0;
f[i] = 0;
}
f[0] = 1;
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
add(sum, value[i]);
add(f[i], sum);
add(f[i + 1], f[i]);
add(value[jump[i]], f[i]);
}
add(f[n], md - 1);
printf("%d\n", f[n]);
return 0;
}

