You’ve got an array consisting of n integers: a[1], a[2], …, a[n]. Moreover, there are m queries, each query can be described by three integers l i, r i, k i. Query l i, r i, k i means that we should add 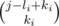 to each element a[j], where l i ≤ j ≤ r i.
to each element a[j], where l i ≤ j ≤ r i.
Record  means the binomial coefficient, or the number of combinations from y elements into groups of x elements.
means the binomial coefficient, or the number of combinations from y elements into groups of x elements.
You need to fulfil consecutively all queries and then print the final array.
Input
The first line contains integers n, m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 105).
The second line contains n integers a[1], a[2], …, a[n] (0 ≤ a i ≤ 109) — the initial array.
Next m lines contain queries in the format l i, r i, k i — to all elements of the segment l i… r i add number 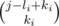 (1 ≤ l i ≤ r i ≤ n; 0 ≤ k ≤ 100).
(1 ≤ l i ≤ r i ≤ n; 0 ≤ k ≤ 100).
Output
Print n integers: the i-th number is the value of element a[i] after all the queries. As the values can be rather large, print them modulo 1000000007 (109 + 7).
Examples
input
5 1
0 0 0 0 0
1 5 0
output
1 1 1 1 1
input
10 2
1 2 3 4 5 0 0 0 0 0
1 6 1
6 10 2
output
2 4 6 8 10 7 3 6 10 15
Solution:
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <cstdio>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <memory.h>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <sstream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
#include <cassert>
using namespace std;
const int md = 1000000007;
const int N = 100010;
const int K = 100;
const int K10 = K + 10;
int inv[K10];
int ans[K10][N];
void init() {
for (int k = 0; k <= K; k++) {
inv[k] = 1;
int step = 1 << 30;
while (step > 0) {
inv[k] = (long long)inv[k] * inv[k] % md;
if (step & (md - 2)) inv[k] = (long long)inv[k] * k % md;
step >>= 1;
}
}
}
inline void add(int &x, int y) {
x += y;
if (x >= md) x -= md;
}
int nouse[N];
int main() {
init();
int n, tt;
scanf("%d %d", &n, &tt);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) scanf("%d", nouse + i);
for (int i = 0; i <= K; i++)
for (int j = 0; j <= n + 1; j++) ans[i][j] = 0;
while (tt--) {
int ll, rr, k;
scanf("%d %d %d", &ll, &rr, &k);
add(ans[K - k][ll], 1);
add(ans[K - k][rr + 1], md - 1);
int u = 1;
for (int i = K - k + 1; i <= K; i++) {
int t = i - (K - k);
u = (long long)u * (t + rr - ll) % md;
u = (long long)u * inv[t] % md;
add(ans[i][rr + 1], md - u);
}
}
for (int j = 0; j <= K; j++)
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
add(ans[j][i], ans[j][i - 1]);
if (j > 0) {
add(ans[j][i], ans[j - 1][i]);
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
add(nouse[i], ans[K][i]);
printf("%d", nouse[i] % md);
if (i < n) printf(" ");
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}

