You’ve got array a[1], a[2], …, a[n], consisting of n integers. Count the number of ways to split all the elements of the array into three contiguous parts so that the sum of elements in each part is the same.
More formally, you need to find the number of such pairs of indices i, j (2 ≤ i ≤ j ≤ n - 1), that 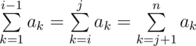 .
.
Input
The first line contains integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 5·105), showing how many numbers are in the array. The second line contains n integers a[1], a[2], …, a[n] (|a[i]| ≤ 109) — the elements of array a.
Output
Print a single integer — the number of ways to split the array into three parts with the same sum.
Examples
input
5
1 2 3 0 3
output
2
input
4
0 1 -1 0
output
1
input
2
4 1
output
0
Solution:
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <deque>
#include <stack>
#include <bitset>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
#include <numeric>
#include <utility>
#include <sstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
#include <memory.h>
#include <cassert>
using namespace std;
long long s[1234567];
int main() {
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
s[0] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int foo;
scanf("%d", &foo);
s[i + 1] = s[i] + foo;
}
long long ans = 0;
if (s[n] % 3 == 0) {
long long u = s[n] / 3, v = 2 * s[n] / 3;
long long cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (s[i] == v) {
ans += cnt;
}
if (s[i] == u) {
cnt++;
}
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
Related posts:
Meaningless Operations
Amr and Pins
Suffix Automaton
Linova and Kingdom
Shave Beaver!
Round Marriage
Finding strongly connected components - Building condensation graph
Game on Tree
Bribes
Cow and Vacation
Rectangle Painting 2
Born This Way
Dreamoon Likes Strings
Check if two segments intersect
Segment Tree
Berland Elections
Polygons
Nested Rubber Bands
Orac and Medians
Hydra
Party
Fair
Flows with demands
Break Up
AND Graph
Restoring Map
Bad Days
Gold Experience
New Year and North Pole
Number of paths of fixed length / Shortest paths of fixed length
Orac and Game of Life
Tape

