You are given a Young diagram.
Given diagram is a histogram with $n$ columns of lengths $a_1, a_2, \ldots, a_n$ ($a_1 \geq a_2 \geq \ldots \geq a_n \geq 1$).
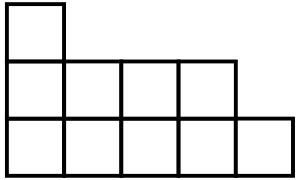
Young diagram for $a=[3,2,2,2,1]$.
Your goal is to find the largest number of non-overlapping dominos that you can draw inside of this histogram, a domino is a $1 \times 2$ or $2 \times 1$ rectangle.Input
The first line of input contain one integer $n$ ($1 \leq n \leq 300\,000$): the number of columns in the given histogram.
The next line of input contains $n$ integers $a_1, a_2, \ldots, a_n$ ($1 \leq a_i \leq 300\,000, a_i \geq a_{i+1}$): the lengths of columns.Output
Output one integer: the largest number of non-overlapping dominos that you can draw inside of the given Young diagram.Exampleinput
5 3 2 2 2 1
output
4
Note
Some of the possible solutions for the example:
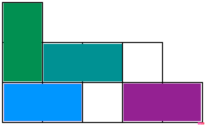
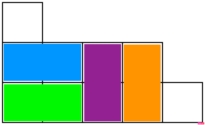
Solution:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> a(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
vector<long long> cnt(2, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cnt[i % 2] += a[i] / 2;
cnt[(i + 1) % 2] += (a[i] + 1) / 2;
}
cout << min(cnt[0], cnt[1]) << '\n';
return 0;
}

