Fox Ciel is participating in a party in Prime Kingdom. There are n foxes there (include Fox Ciel). The i-th fox is a i years old.
They will have dinner around some round tables. You want to distribute foxes such that:
- Each fox is sitting at some table.
- Each table has at least 3 foxes sitting around it.
- The sum of ages of any two adjacent foxes around each table should be a prime number.
If k foxes f 1, f 2, …, f k are sitting around table in clockwise order, then for 1 ≤ i ≤ k - 1: f i and f i + 1 are adjacent, and f 1 and f k are also adjacent.
If it is possible to distribute the foxes in the desired manner, find out a way to do that.
Input
The first line contains single integer n (3 ≤ n ≤ 200): the number of foxes in this party.
The second line contains n integers a i (2 ≤ a i ≤ 104).
Output
If it is impossible to do this, output “Impossible”.
Otherwise, in the first line output an integer m (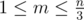 ): the number of tables.
): the number of tables.
Then output m lines, each line should start with an integer k -=– the number of foxes around that table, and then k numbers — indices of fox sitting around that table in clockwise order.
If there are several possible arrangements, output any of them.
Examples
input
4
3 4 8 9
output
1
4 1 2 4 3
input
5
2 2 2 2 2
output
Impossible
input
12
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
output
1
12 1 2 3 6 5 12 9 8 7 10 11 4
input
24
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
output
3
6 1 2 3 6 5 4
10 7 8 9 12 15 14 13 16 11 10
8 17 18 23 22 19 20 21 24
Note
In example 1, they can sit around one table, their ages are: 3-8-9-4, adjacent sums are: 11, 17, 13 and 7, all those integers are primes.
In example 2, it is not possible: the sum of 2+2 = 4 is not a prime number.
Solution:
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include
<map>
#include <set>
#include <deque>
#include <stack>
#include <bitset>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
#include <numeric>
#include <utility>
#include <sstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
#include <memory.h>
#include <cassert>
using namespace std;
const int inf = (int)1e6;
const int N = 100010;
int fin;
int ss[N], ff[N], c[N], f[N], obr[N], pred[N], last[N], st[N];
int m;
void add(int x, int y, int z, int xx, int yy) {
m++;
ss[m] = x;
ff[m] = y;
c[m] = z;
f[m] = xx;
obr[m] = yy;
}
int x[N], d[N];
bool expath() {
for (int i = 0; i <= fin; i++) d[i] = -1;
int b = 1, e = 1;
x[1] = 0;
d[0] = 0;
while (b <= e) {
int j = last[x[b]];
while (j > 0) {
if (c[j] > f[j] && d[ff[j]] == -1) {
e++;
x[e] = ff[j];
d[x[e]] = d[x[b]] + 1;
if (x[e] == fin) {
return true;
}
}
j = pred[j];
}
b++;
}
return false;
}
int rec(int v, int w) {
if (v == fin) {
return w;
}
int r = 0, j = last[v];
while (j > 0) {
last[v] = pred[j];
if (c[j] > f[j] && d[ff[j]] == d[v] + 1) {
int ww = c[j] - f[j];
if (w - r < ww) ww = w - r;
int t = rec(ff[j], ww);
if (t > 0) {
f[j] += t;
if (obr[j] != 0) f[obr[j]] -= t;
r += t;
if (r == w) break;
}
}
j = pred[j];
}
return r;
}
bool prime[N];
bool was[N];
vector <int> nei[N];
int main() {
for (int q = 2; q < N; q++) {
prime[q] = true;
}
for (int i = 2; i < N; i++) {
if (prime[i]) {
for (int j = i + i; j < N; j += i) {
prime[j] = false;
}
}
}
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
vector < pair <int, int> > even, odd;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int a;
scanf("%d", &a);
if (a % 2 == 0) {
even.push_back(make_pair(a, i));
} else {
odd.push_back(make_pair(a, i));
}
}
if (even.size() != odd.size()) {
puts("Impossible");
return 0;
}
int cnt = even.size();
fin = cnt + cnt + 1;
m = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++) {
add(0, i + 1, 2, 0, 0);
add(cnt + 1 + i, fin, 2, 0, 0);
}
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cnt; j++) {
if (prime[even[i].first + odd[j].first]) {
add(1 + i, 1 + cnt + j, 1, 0, m + 2);
add(1 + cnt + j, 1 + i, 0, 0, m);
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i <= fin; i++) {
last[i] = 0;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
pred[i] = last[ss[i]];
last[ss[i]] = i;
}
for (int i = 0; i <= fin; i++) {
st[i] = last[i];
}
int ans = 0;
while (expath()) {
int t = rec(0, inf);
ans += t;
for (int i = 0; i <= fin; i++) {
last[i] = st[i];
}
}
if (ans != 2 * cnt) {
puts("Impossible");
return 0;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
nei[i].clear();
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
if (1 <= ss[i] && ss[i] <= cnt && cnt + 1 <= ff[i] && ff[i] <= cnt + cnt) {
if (f[i] == 1) {
int x = even[ss[i] - 1].second;
int y = odd[ff[i] - cnt - 1].second;
nei[x].push_back(y);
nei[y].push_back(x);
}
}
}
vector < vector <int> > ret;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
was[i] = false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (was[i]) {
continue;
}
vector <int> add;
int cur = i;
int pr = nei[i][0];
while (true) {
add.push_back(cur);
was[cur] = true;
int to = nei[cur][0] + nei[cur][1] - pr;
pr = cur;
cur = to;
if (cur == i) {
break;
}
}
ret.push_back(add);
}
int sz = ret.size();
printf("%d\n", sz);
for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {
int cc = ret[i].size();
printf("%d", cc);
for (int j = 0; j < cc; j++) {
printf(" %d", ret[i][j] + 1);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}

