You have n friends and you want to take m pictures of them. Exactly two of your friends should appear in each picture and no two pictures should contain the same pair of your friends. So if you have n = 3 friends you can take 3 different pictures, each containing a pair of your friends.
Each of your friends has an attractiveness level which is specified by the integer number a i for the i-th friend. You know that the attractiveness of a picture containing the i-th and the j-th friends is equal to the exclusive-or ( xor operation) of integers a i and a j.
You want to take pictures in a way that the total sum of attractiveness of your pictures is maximized. You have to calculate this value. Since the result may not fit in a 32-bit integer number, print it modulo 1000000007 (109 + 7).
Input
The first line of input contains two integers n and m 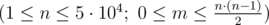 — the number of friends and the number of pictures that you want to take.
— the number of friends and the number of pictures that you want to take.
Next line contains n space-separated integers a 1, a 2, …, a n (0 ≤ a i ≤ 109) — the values of attractiveness of the friends.
Output
The only line of output should contain an integer — the optimal total sum of attractiveness of your pictures.
Examples
input
3 1
1 2 3
output
3
input
3 2
1 2 3
output
5
input
3 3
1 2 3
output
6
Solution:
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iomanip>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <memory.h>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
const int md = 1000000007;
int a[55555];
int s[33][55555];
map < vector <int>, int > mp;
int count(int l, int r, int ll, int rr, int k, int th) {
if (l > r || ll > rr) return 0;
vector <int> u(6);
u[0] = l; u[1] = r; u[2] = ll; u[3] = rr; u[4] = k; u[5] = th;
if (mp.find(u) != mp.end()) return mp[u];
mp[u] = 0;
int &res = mp[u];
if (th == 0) return res = (r-l+1)*(rr-ll+1);
if (l == ll && r == rr) {
if (th & (1 << k)) {
for (int i=l; i<=r; i++)
if (a[i] & (1 << k))
return res = count(l, i-1, i, r, k-1, th-(1 << k));
return res = 0;
} else {
for (int i=l; i<=r; i++)
if (a[i] & (1 << k))
return res = (i-l)*(r-i+1) + count(l, i-1, l, i-1, k-1, th) + count(i, r, i, r, k-1, th);
return res = count(l, r, l, r, k-1, th);
}
} else {
int x = l, y = ll;
while (x <= r && (!(a[x] & (1 << k)))) x++;
while (y <= rr && (!(a[y] & (1 << k)))) y++;
if (th & (1 << k)) {
return res = count(l, x-1, y, rr, k-1, th-(1 << k)) + count(x, r, ll, y-1, k-1, th-(1 << k));
} else {
return res = (x-l)*(rr-y+1) + (r-x+1)*(y-ll) + count(l, x-1, ll, y-1, k-1, th) + count(x, r, y, rr, k-1, th);
}
}
}
int pairwise(int k, int l, int r, int ll, int rr) {
if (l > r || ll > rr) return 0;
int ans = 0, a = r-l+1, b = rr-ll+1;
while (k >= 0) {
int x = s[k][r+1]-s[k][l], y = s[k][rr+1]-s[k][ll];
ans = (ans+(long long)(x*(b-y) + (a-x)*y)*(1 << k)) % md;
k--;
}
return ans;
}
int sum(int l, int r, int ll, int rr, int k, int th) {
if (l > r || ll > rr) return 0;
if (k == -1) return 0;
if (l == ll && r == rr) {
if (th & (1 << k)) {
for (int i=l; i<=r; i++)
if (a[i] & (1 << k))
return ((long long)count(l, i-1, i, r, k-1, th-(1 << k))*(1 << k) + sum(l, i-1, i, r, k-1, th-(1 << k))) % md;
return 0;
} else {
for (int i=l; i<=r; i++)
if (a[i] & (1 << k))
return ((long long)pairwise(k, l, i-1, i, r) + sum(l, i-1, l, i-1, k-1, th) + sum(i, r, i, r, k-1, th)) % md;
return sum(l, r, l, r, k-1, th);
}
} else {
int x = l, y = ll;
while (x <= r && (!(a[x] & (1 << k)))) x++;
while (y <= rr && (!(a[y] & (1 << k)))) y++;
if (th & (1 << k)) {
return ((long long)(count(l, x-1, y, rr, k-1, th-(1 << k)) + count(x, r, ll, y-1, k-1, th-(1 << k)))*(1 << k)
+ sum(l, x-1, y, rr, k-1, th-(1 << k)) + sum(x, r, ll, y-1, k-1, th-(1 << k))) % md;
} else {
int ret = ((long long)pairwise(k, l, x-1, y, rr) + pairwise(k, x, r, ll, y-1) + sum(l, x-1, ll, y-1, k-1, th) + sum(x, r, y, rr, k-1, th)) % md;
return ret;
}
}
}
int main() {
// freopen("in", "r", stdin);
// freopen("out", "w", stdout);
int n, m, i;
cin >> n >> m;
for (i=0;i<n;i++) scanf("%d", a+i);
sort(a, a+n);
for (int k=0;k<30;k++) {
s[k][0] = 0;
for (i=0;i<n;i++) s[k][i+1] = s[k][i] + (!!(a[i] & (1 << k)));
}
mp.clear();
int ll = 0, rr = (1 << 30)-1;
while (ll < rr) {
int mid = (ll+rr+1) >> 1;
if (count(0, n-1, 0, n-1, 29, mid) >= m) ll = mid;
else rr = mid-1;
}
int ans = sum(0, n-1, 0, n-1, 29, ll);
ans = (ans-(long long)(count(0, n-1, 0, n-1, 29, ll)-m)*ll) % md;
if (ans < 0) ans += md;
printf("%d\n", ans);
return 0;
}

