Table of Contents
In this article, you’ll learn to iterate over a sequence of elements using the different variations of for loop.
1. What is for loop in Python?
The for loop in Python is used to iterate over a sequence (list, tuple, string) or other iterable objects. Iterating over a sequence is called traversal.
1.1. Syntax of for Loop
for val in sequence:
loop body
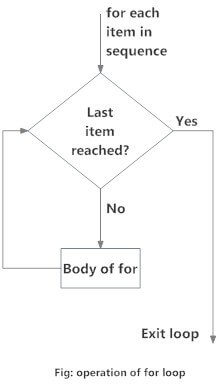
Here, val is the variable that takes the value of the item inside the sequence on each iteration.
Loop continues until we reach the last item in the sequence. The body of for loop is separated from the rest of the code using indentation.
1.2. Flowchart of for Loop
1.3. Example: Python for Loop
# Program to find the sum of all numbers stored in a list
# List of numbers
numbers = [6, 5, 3, 8, 4, 2, 5, 4, 11]
# variable to store the sum
sum = 0
# iterate over the list
for val in numbers:
sum = sum+val
print("The sum is", sum)
When you run the program, the output will be:
The sum is 48
2. The range() function
We can generate a sequence of numbers using range() function. range(10) will generate numbers from 0 to 9 (10 numbers).
We can also define the start, stop and step size as range(start, stop,step_size). step_size defaults to 1 if not provided.
The range object is “lazy” in a sense because it doesn’t generate every number that it “contains” when we create it. However, it is not an iterator since it supports in, len and __getitem__ operations.
This function does not store all the values in memory; it would be inefficient. So it remembers the start, stop, step size and generates the next number on the go.
To force this function to output all the items, we can use the function list().
The following example will clarify this.
print(range(10)) print(list(range(10))) print(list(range(2, 8))) print(list(range(2, 20, 3)))
Output
range(0, 10) [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] [2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7] [2, 5, 8, 11, 14, 17]
We can use the range() function in for loops to iterate through a sequence of numbers. It can be combined with the len() function to iterate through a sequence using indexing. Here is an example.
# Program to iterate through a list using indexing
genre = ['pop', 'rock', 'jazz']
# iterate over the list using index
for i in range(len(genre)):
print("I like", genre[i])
Output
I like pop I like rock I like jazz
3. for loop with else
A for loop can have an optional else block as well. The else part is executed if the items in the sequence used in for loop exhausts.
The break keyword can be used to stop a for loop. In such cases, the else part is ignored.
Hence, a for loop’s else part runs if no break occurs.
Here is an example to illustrate this.
digits = [0, 1, 5]
for i in digits:
print(i)
else:
print("No items left.")
When you run the program, the output will be:
0 1 5 No items left.
Here, the for loop prints items of the list until the loop exhausts. When the for loop exhausts, it executes the block of code in the else and prints No items left.
This for...else statement can be used with the break keyword to run the else block only when the break keyword was not executed. Let’s take an example:
# program to display student's marks from record
student_name = 'Soyuj'
marks = {'James': 90, 'Jules': 55, 'Arthur': 77}
for student in marks:
if student == student_name:
print(marks[student])
break
else:
print('No entry with that name found.')
Output
No entry with that name found.

