You are given a set of $n$ points in a 2D plane. No three points are collinear.
A pentagram is a set of $5$ points $A,B,C,D,E$ that can be arranged as follows.
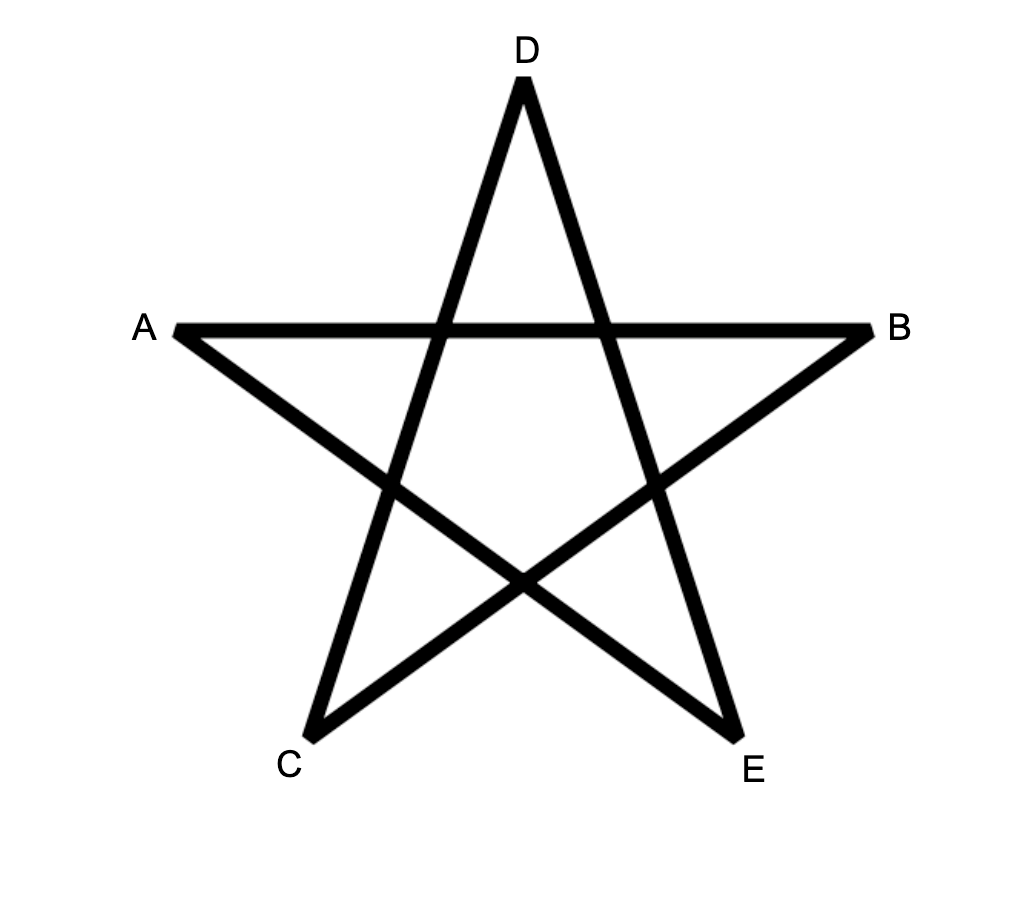
Note the length of the line segments don’t matter, only that those particular intersections exist.
Count the number of ways to choose $5$ points from the given set that form a pentagram.
Input
The first line contains an integer $n$ ($5 \leq n \leq 300$) — the number of points.
Each of the next $n$ lines contains two integers $x_i, y_i$ ($-10^6 \leq x_i,y_i \leq 10^6$) — the coordinates of the $i$-th point. It is guaranteed that no three points are collinear.
Output
Print a single integer, the number of sets of $5$ points that form a pentagram.
Examples
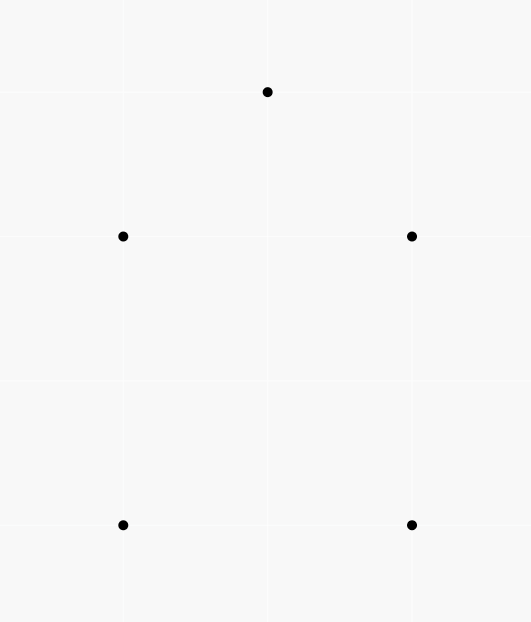
input
5 0 0 0 2 2 0 2 2 1 3
output
1
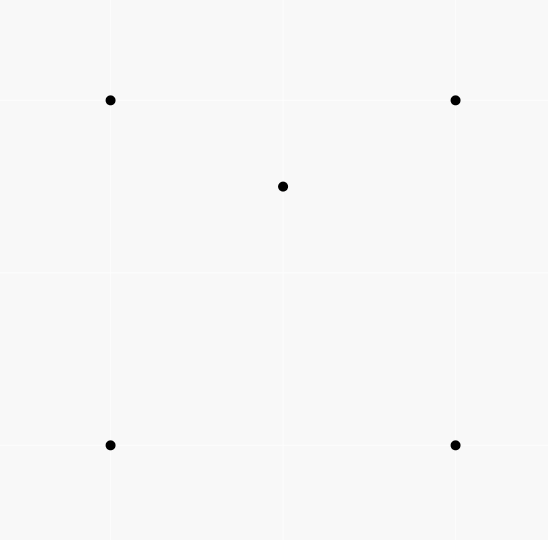
input
5 0 0 4 0 0 4 4 4 2 3
output
0
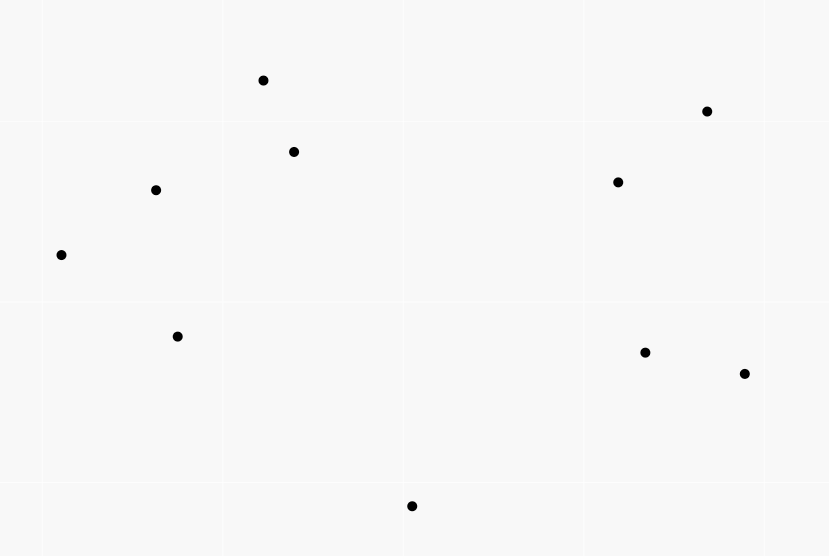
input
10 841746 527518 595261 331297 -946901 129987 670374 -140388 -684770 309555 -302589 415564 -387435 613331 -624940 -95922 945847 -199224 24636 -565799
output
85
Note
A picture of the first sample:
A picture of the second sample:
A picture of the third sample:
Solution:
#undef _GLIBCXX_DEBUG
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Point {
int x;
int y;
int id;
};
const int N = 310;
long long dp[N][N][4];
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<Point> p(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> p[i].x >> p[i].y;
p[i].id = i;
}
sort(p.begin(), p.end(), [&](const Point& a, const Point& b) {
return (a.y < b.y || (a.y == b.y && a.x < b.x));
});
vector<vector<int>> orders(n, vector<int>(n));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
iota(orders[i].begin(), orders[i].end(), 0);
orders[i].erase(orders[i].begin() + i);
sort(orders[i].begin(), orders[i].end(), [&](int j, int k) {
long long xj = p[j].x - p[i].x;
long long yj = p[j].y - p[i].y;
long long xk = p[k].x - p[i].x;
long long yk = p[k].y - p[i].y;
int sj = (yj > 0 || (yj == 0 && xj > 0));
int sk = (yk > 0 || (yk == 0 && xk > 0));
if (sj != sk) {
return sj > sk;
}
long long vmul = xj * yk - yj * xk;
return vmul > 0;
});
}
long long ans = 0;
for (int start = 0; start <= n - 5; start++) {
sort(p.begin() + start + 1, p.end(), [&](const Point& a, const Point& b) {
long long xa = a.x - p[start].x;
long long ya = a.y - p[start].y;
long long xb = b.x - p[start].x;
long long yb = b.y - p[start].y;
long long vmul = xa * yb - ya * xb;
return vmul > 0;
});
for (int i = start; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
dp[i][j][k] = (i == start && k == 0 ? 1 : 0);
}
}
}
for (int i = start; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
ans += dp[i][j][3];
long long xa = p[j].x - p[i].x;
long long ya = p[j].y - p[i].y;
for (int t = j + 1; t < n; t++) {
if (xa * (p[t].y - p[j].y) - ya * (p[t].x - p[j].x) > 0) {
for (int k = 0; k < 3; k++) {
dp[j][t][k + 1] += dp[i][j][k];
}
}
}
}
}
sort(p.begin() + start + 1, p.end(), [&](const Point& a, const Point& b) {
return (a.y < b.y || (a.y == b.y && a.x < b.x));
});
}
cout << ans << '\n';
return 0;
}

