Table of Contents
1. Overview
In this article, we are going to add Zipkin to our spring cloud project. Zipkin is an open source project that provides mechanisms for sending, receiving, storing, and visualizing traces. This allows us to correlate activity between servers and get a much clearer picture of exactly what is happening in our services.
This article is not an introductory article to distributed tracing or spring cloud. If you would like more information about distributed tracing, read our introduction to spring sleuth.
2. Zipkin Service
Our Zipkin service will serve as the store for all our spans. Each span is sent to this service and collected into traces for future identification.
2.1. Setup
Create a new Spring Boot project and add these dependencies to pom.xml:
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.java</groupId>
<artifactId>zipkin-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.zipkin.java</groupId>
<artifactId>zipkin-autoconfigure-ui</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
For reference: you can find the latest version on Maven Central (zipkin-server, zipkin-autoconfigure-ui). Versions of the dependencies are inherited from spring-boot-starter-parent.
2.2. Enabling Zipkin Server
To enable the Zipkin server, we must add some annotations to the main application class:
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableZipkinServer
public class ZipkinApplication {...}
The new annotation @EnableZipkinServer will set up this server to listen for incoming spans and act as our UI for querying.
2.3. Configuration
First, let’s create a file called bootstrap.properties in src/main/resources. Remember that this file is needed to fetch our configuration from out config server.
Let’s add these properties to it:
spring.cloud.config.name=zipkin spring.cloud.config.discovery.service-id=config spring.cloud.config.discovery.enabled=true spring.cloud.config.username=configUser spring.cloud.config.password=configPassword eureka.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone=http://discUser:discPassword@localhost:8082/eureka/
Now let’s add a configuration file to our config repo, located at c:\Users\{username}\ on Windows or /home/{username}/ on *nix.
In this directory let’s add a file named zipkin.properties and add these contents:
spring.application.name=zipkin server.port=9411 eureka.client.region=default eureka.client.registryFetchIntervalSeconds=5 logging.level.org.springframework.web=debug
Remember to commit the changes in this directory so that the config service will detect the changes and load the file.
2.4. Run
Now let’s run our application and navigate to http://localhost:9411. We should be greeted with Zipkin’s homepage:
Great! Now we are ready to add some dependencies and configuration to our services that we want to trace.
3. Service Configuration
The setup for the resource servers is pretty much the same. In the following sections, we will detail how to set up the book-service. We will follow that up by explaining the modifications needed to apply these updates to the rating-service and gateway-service.
3.1. Setup
To begin sending spans to our Zipkin server, we will add this dependency to our pom.xml file:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-zipkin</artifactId>
</dependency>
For reference: you can find the latest version on Maven Central (spring-cloud-starter-zipkin).
3.2. Spring Config
We need to add some configuration so that book-service will use Eureka to find our Zipkin service. Open BookServiceApplication.java and add this code to the file:
@Autowired
private EurekaClient eurekaClient;
@Autowired
private SpanMetricReporter spanMetricReporter;
@Autowired
private ZipkinProperties zipkinProperties;
@Value("${spring.sleuth.web.skipPattern}")
private String skipPattern;
// ... the main method goes here
@Bean
public ZipkinSpanReporter makeZipkinSpanReporter() {
return new ZipkinSpanReporter() {
private HttpZipkinSpanReporter delegate;
private String baseUrl;
@Override
public void report(Span span) {
InstanceInfo instance = eurekaClient
.getNextServerFromEureka("zipkin", false);
if (!(baseUrl != null &&
instance.getHomePageUrl().equals(baseUrl))) {
baseUrl = instance.getHomePageUrl();
delegate = new HttpZipkinSpanReporter(new RestTemplate(),
baseUrl, zipkinProperties.getFlushInterval(), spanMetricReporter);
if (!span.name.matches(skipPattern)) delegate.report(span);
}
}
};
}
The above configuration registers a custom ZipkinSpanReporter that gets its URL from eureka. This code also keeps track of the existing URL and only updates the HttpZipkinSpanReporter if the URL changes. This way no matter where we deploy our Zipkin server to we will always be able to locate it without restarting the service.
We also import the default Zipkin properties that are loaded by spring boot and use them to manage our custom reporter.
3.3. Configuration
Now let’s add some configuration to our book-service.properties file in the config repository:
spring.sleuth.sampler.percentage=1.0 spring.sleuth.web.skipPattern=(^cleanup.*)
Zipkin works by sampling actions on a server. By setting the spring.sleuth.sampler.percentage to 1.0, we are setting the sampling rate to 100%. The skip pattern is simply a regex used for excluding spans whose name matches.
The skip pattern will block all spans from being reported that start with the word ‘cleanup’. This is to stop spans originating from the spring session code base.
3.4. Rating Service
Follow the same steps from the book-service section above, applying the changes to the equivalent files for rating-service.
3.5. Gateway Service
Follow the same steps book-service. But when adding the configuration to the gateway.properties add these instead:
spring.sleuth.sampler.percentage=1.0 spring.sleuth.web.skipPattern=(^cleanup.*|.+favicon.*)
This will configure the gateway service not to send spans about the favicon or spring session.
3.6. Run
If you haven’t done so already, start the config, discovery, gateway, book, rating, and zipkin services.
Navigate to http://localhost:8080/book-service/books.
Open a new tab and navigate to http://localhost:9411. Select book-service and press the ‘Find Traces’ button. You should see a trace appear in the search results. Click that trace of opening it:
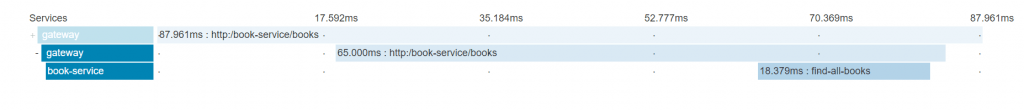
On the trace page, we can see the request broken down by service. The first two spans are created by the gateway, and the last is created by the book-service. This shows us how much time the request spent processing on the book-service, 18.379 ms, and on the gateway, 87.961 ms.
4. Conclusion
We have seen how easy it is to integrate Zipkin into our cloud application.
This gives us some much-needed insight into how communication travels through our application. As our application grows in complexity, Zipkin can provide us with much-needed information on where requests are spending their time. This can help us determine where things are slowing down and indicate what areas of our application need improvement.
As always you can find the source code over on Github.