Table of Contents
1. Đặc điểm
Những điểm quan trọng về lớp LinkedHashMap trong java cần nhớ là:
- LinkedHashMap lưu trữ dữ liệu dưới dạng cặp key và value.
- LinkedHashMap chỉ chứa các key duy nhất.
- LinkedHashMap có thể có 1 key là null và nhiều giá trị null.
- LinkedHashMap duy trì các phần tử theo thứ tự chèn.
2. Hierarchy của lớp LinkedHashMap
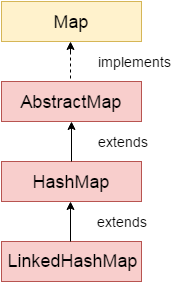
Lớp java.util.LinkedHashMap được định nghĩa như sau:
public class LinkedHashMap<K,V>
extends HashMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V> {
}
Trong đó:
- K: đây là kiểu key để lưu trữ.
- V: đây là kiểu giá trị được ánh xạ.
3. Các phương thức khởi tạo (constructor) của lớp LinkedHashMap
- LinkedHashMap(): khởi tạo một map trống.
- LinkedHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m): khởi tạo một map với các phần tử của map m.
4. Các phương thức (method) của lớp LinkedHashMap
Xem thêm các phương thức của Map ở bài viết Map Interface trong java.
5. Ví dụ minh họa
5.1. Ví dụ sử dụng LinkedHashMap với kiểu dữ liệu cơ bản (Wrapper)
package com.maixuanviet.collection.linkedhashmap;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
public class LinkedHashMapExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// init map
Map<Integer, String> map = new LinkedHashMap<Integer, String>();
map.put(1, "Basic java");
map.put(2, "OOP");
map.put(4, "Multi-Thread");
map.put(3, "Collection");
// show map using method keySet()
for (Integer key : map.keySet()) {
String value = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key + " = " + value);
}
System.out.println("---");
// show map using method keySet()
for (Entry<Integer, String> entry : map.entrySet()) {
Integer key = entry.getKey();
String value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key + " = " + value);
}
}
}
Kết quả thực thi chương trình trên:
1 = Basic java 2 = OOP 4 = Multi-Thread 3 = Collection --- 1 = Basic java 2 = OOP 4 = Multi-Thread 3 = Collection
5.2. Ví dụ sử dụng LinkedHashMap với key có kiểu String, value có kiểu Student
package com.maixuanviet.collection.map;
public class Student {
private int id;
private String name;
public Student(int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + "]";
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
package com.maixuanviet.collection.linkedhashmap;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
public class LinkedHashMapExample2 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// Student's data
Student student1 = new Student(1, "Student 1");
Student student2 = new Student(2, "Student 2");
Student student3 = new Student(3, "Student 3");
Student student4 = new Student(4, "Student 4");
// init map
Map<Integer, Student> map = new LinkedHashMap<Integer, Student>();
map.put(student1.getId(), student1);
map.put(student2.getId(), student2);
map.put(student4.getId(), student4);
map.put(student3.getId(), student3);
// show map using method keySet()
for (Integer key : map.keySet()) {
Student value = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key + " = " + value);
}
System.out.println("---");
// show map using method keySet()
for (Entry<Integer, Student> entry : map.entrySet()) {
Integer key = entry.getKey();
Student value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key + " = " + value);
}
}
}
Kết quả thực thi chương trình trên:
1 = Student [id=1, name=Student 1] 2 = Student [id=2, name=Student 2] 4 = Student [id=4, name=Student 4] 3 = Student [id=3, name=Student 3] --- 1 = Student [id=1, name=Student 1] 2 = Student [id=2, name=Student 2] 4 = Student [id=4, name=Student 4] 3 = Student [id=3, name=Student 3]
Related posts:
Implementing a Runnable vs Extending a Thread
Java Program to Generate N Number of Passwords of Length M Each
Java Program to Check if it is a Sparse Matrix
Java CyclicBarrier vs CountDownLatch
Spring Boot - Cloud Configuration Client
SOAP Web service: Authentication trong JAX-WS
Spring REST API + OAuth2 + Angular
Mảng (Array) trong Java
TreeSet và sử dụng Comparable, Comparator trong java
Transactions with Spring and JPA
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor corePoolSize vs. maxPoolSize
Tính kế thừa (Inheritance) trong java
Spring Cloud AWS – EC2
Difference Between Wait and Sleep in Java
Java Program to Implement an Algorithm to Find the Global min Cut in a Graph
Java – Generate Random String
Java 8 StringJoiner
Programmatic Transaction Management in Spring
Java Program to Implement Triply Linked List
Introduction to the Java NIO Selector
Using a Spring Cloud App Starter
Java Program to Implement SynchronosQueue API
Java InputStream to String
Creating a Custom Starter with Spring Boot
Java Program to Implement Kosaraju Algorithm
Java Program to Implement PriorityBlockingQueue API
Java Program to Implement Weight Balanced Tree
Autoboxing và Unboxing trong Java
Toán tử instanceof trong java
A Guide to JPA with Spring
Create a Custom Exception in Java
Java Program to Permute All Letters of an Input String

