We’ll call an array of n non-negative integers a[1], a[2], …, a[n] interesting, if it meets m constraints. The i-th of the m constraints consists of three integers l i, r i, q i (1 ≤ l i ≤ r i ≤ n) meaning that value 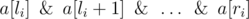 should be equal to q i.
should be equal to q i.
Your task is to find any interesting array of n elements or state that such array doesn’t exist.
Expression x&y means the bitwise AND of numbers x and y. In programming languages C++, Java and Python this operation is represented as “&”, in Pascal — as “and”.
Input
The first line contains two integers n, m (1 ≤ n ≤ 105, 1 ≤ m ≤ 105) — the number of elements in the array and the number of limits.
Each of the next m lines contains three integers l i, r i, q i (1 ≤ l i ≤ r i ≤ n, 0 ≤ q i < 230) describing the i-th limit.
Output
If the interesting array exists, in the first line print “YES” (without the quotes) and in the second line print n integers a[1], a[2], …, a[n] (0 ≤ a[i] < 230) decribing the interesting array. If there are multiple answers, print any of them.
If the interesting array doesn’t exist, print “NO” (without the quotes) in the single line.
Examples
input
3 1
1 3 3
output
YES
3 3 3
input
3 2
1 3 3
1 3 2
output
NO
Solution:
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <deque>
#include <stack>
#include <bitset>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
#include <numeric>
#include <utility>
#include <sstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
#include <memory.h>
#include <cassert>
using namespace std;
const int N = 200010;
int from[N], to[N], num[N];
int s[N][30];
int a[N][30];
int sum[N][30];
int main() {
int n, m;
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 30; j++) {
s[i][j] = 0;
}
}
for (int k = 0; k < m; k++) {
scanf("%d %d %d", from + k, to + k, num + k);
from[k]--; to[k]--;
for (int j = 0; j < 30; j++) {
if (num[k] & (1 << j)) {
s[from[k]][j]++;
s[to[k] + 1][j]--;
}
}
}
for (int j = 0; j < 30; j++) {
int bal = 0;
sum[0][j] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
bal += s[i][j];
a[i][j] = (bal > 0);
sum[i + 1][j] = sum[i][j] + a[i][j];
}
}
for (int k = 0; k < m; k++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 30; j++) {
if (!(num[k] & (1 << j))) {
int get = sum[to[k] + 1][j] - sum[from[k]][j];
int need = (to[k] + 1) - (from[k]);
if (get == need) {
puts("NO");
return 0;
}
}
}
}
puts("YES");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int res = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < 30; j++) {
if (a[i][j]) {
res += (1 << j);
}
}
if (i > 0) printf(" ");
printf("%d", res);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}

