You are given an array with n integers a i and m queries. Each query is described by two integers (l j, r j).
Let’s define the function 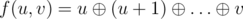 . The function is defined for only u ≤ v.
. The function is defined for only u ≤ v.
For each query print the maximal value of the function f(a x, a y) over all l j ≤ x, y ≤ r j, a x ≤ a y.
Input
The first line contains two integers n, m (1 ≤ n ≤ 5·104, 1 ≤ m ≤ 5·103) — the size of the array and the number of the queries.
The second line contains n integers a i (1 ≤ a i ≤ 106) — the elements of the array a.
Each of the next m lines contains two integers l j, r j (1 ≤ l j ≤ r j ≤ n) – the parameters of the j-th query.
Output
For each query print the value a j on a separate line — the maximal value of the function f(a x, a y) over all l j ≤ x, y ≤ r j, a x ≤ a y.
Examples
input
6 3
1 2 3 4 5 6
1 6
2 5
3 4
output
7
7
7
input
1 1
1
1 1
output
1
input
6 20
10 21312 2314 214 1 322
1 1
1 2
1 3
1 4
1 5
1 6
2 2
2 3
2 4
2 5
2 6
3 4
3 5
3 6
4 4
4 5
4 6
5 5
5 6
6 6
output
10
21313
21313
21313
21313
21313
21312
21313
21313
21313
21313
2314
2315
2315
214
215
323
1
323
322
Solution:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int MAX = 1000010;
int z[MAX];
const int N = 50010;
int a[N], g[N], b[N];
int from[N], to[N], best[N];
int main() {
z[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < MAX; i++) {
z[i] = z[i - 1] ^ i;
}
int n, m;
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%d", a + i);
g[i] = z[a[i]];
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
scanf("%d %d", from + i, to + i);
from[i]--; to[i]--;
best[i] = -1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int mx = 0;
for (int j = i; j < n; j++) {
int cur = g[i] ^ g[j] ^ (a[i] < a[j] ? a[i] : a[j]);
mx = max(mx, cur);
b[j] = mx;
}
for (int k = 0; k < m; k++) {
if (from[k] <= i && i <= to[k]) {
best[k] = max(best[k], b[to[k]]);
}
}
}
for (int k = 0; k < m; k++) {
printf("%d\n", best[k]);
}
return 0;
}

