Table of Contents
1. Đặc điểm
Những điểm quan trọng về lớp TreeMap trong java cần nhớ là:
- TreeMap lưu trữ dữ liệu dưới dạng cặp key và value.
- TreeMap chỉ chứa các key duy nhất.
- TreeMap KHÔNG cho phép bất kỳ key nào là null và nhưng có thể có nhiều giá trị null.
- TreeMap duy trì các phần tử được thêm vào theo thứ tự key tăng dần.
2. Hierarchy của lớp TreeMap
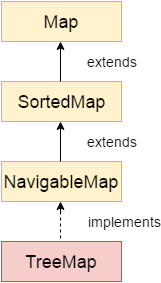
Lớp java.util.TreeMap được định nghĩa như sau:
public class TreeMap<K,V>
extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements NavigableMap<K,V>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {
}
Trong đó:
- K: đây là kiểu key để lưu trữ.
- V: đây là kiểu giá trị được ánh xạ.
3. Các phương thức khởi tạo (constructor) của lớp TreeMap
- LinkedHashMap(): khởi tạo một map trống.
- LinkedHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m): khởi tạo một map với các phần tử của map m.
4. Các phương thức (method) của lớp TreeMap
Xem thêm các phương thức của Map ở bài viết Map Interface trong java.
5. Ví dụ minh họa
5.1. Ví dụ sử dụng TreeMap với kiểu dữ liệu cơ bản (Wrapper)
package com.maixuanviet.collection.treemap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class LinkedHashMapExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// init map
Map<Integer, String> map = new TreeMap<Integer, String>();
map.put(1, "Basic java");
map.put(2, "OOP");
map.put(4, "Multi-Thread");
map.put(3, "Collection");
// show map using method keySet()
for (Integer key : map.keySet()) {
String value = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key + " = " + value);
}
System.out.println("---");
// show map using method keySet()
for (Entry<Integer, String> entry : map.entrySet()) {
Integer key = entry.getKey();
String value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key + " = " + value);
}
}
}
Kết quả thực thi chương trình trên:
1 = Basic java 2 = OOP 3 = Collection 4 = Multi-Thread --- 1 = Basic java 2 = OOP 3 = Collection 4 = Multi-Thread
5.2. Ví dụ sử dụng TreeMap với key có kiểu String, value có kiểu Student
package com.maixuanviet.collection.map;
public class Student {
private int id;
private String name;
public Student(int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + "]";
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
package com.maixuanviet.collection.treemap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class LinkedHashMapExample2 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// Student's data
Student student1 = new Student(1, "Student 1");
Student student2 = new Student(2, "Student 2");
Student student3 = new Student(3, "Student 3");
Student student4 = new Student(4, "Student 4");
// init map
Map<Integer, Student> map = new TreeMap<Integer, Student>();
map.put(student1.getId(), student1);
map.put(student2.getId(), student2);
map.put(student4.getId(), student4);
map.put(student3.getId(), student3);
// show map using method keySet()
for (Integer key : map.keySet()) {
Student value = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key + " = " + value);
}
System.out.println("---");
// show map using method keySet()
for (Entry<Integer, Student> entry : map.entrySet()) {
Integer key = entry.getKey();
Student value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key + " = " + value);
}
}
}
Kết quả thực thi chương trình trên:
1 = Student [id=1, name=Student 1] 2 = Student [id=2, name=Student 2] 3 = Student [id=3, name=Student 3] 4 = Student [id=4, name=Student 4] --- 1 = Student [id=1, name=Student 1] 2 = Student [id=2, name=Student 2] 3 = Student [id=3, name=Student 3] 4 = Student [id=4, name=Student 4]
Related posts:
Creating Docker Images with Spring Boot
Disable DNS caching
Hướng dẫn Java Design Pattern – Prototype
A Guide to EnumMap
Java Program to Represent Graph Using Adjacency List
Java CyclicBarrier vs CountDownLatch
Exception Handling in Java
Lập trình mạng với java
Java Program to Implement Gauss Seidel Method
Java Program to Implement the Binary Counting Method to Generate Subsets of a Set
Spring Data JPA @Query
Spring Security 5 – OAuth2 Login
Beans and Dependency Injection
Guide to BufferedReader
Java Program to Implement Quick Hull Algorithm to Find Convex Hull
So sánh HashMap và Hashtable trong Java
Java Program to Implement Shell Sort
Java Program to Implement Sorted Array
Java Program to Compute Cross Product of Two Vectors
Java Program to Implement Suffix Array
New Features in Java 9
Compact Strings in Java 9
Daemon Threads in Java
Spring Boot - Sending Email
Command-Line Arguments in Java
Hướng dẫn sử dụng Java Generics
Java Program to Implement Counting Sort
Java Program to Print the Kind of Rotation the AVL Tree is Undergoing
Java Program to Implement Meldable Heap
Introduction to Spring Cloud Stream
Collect a Java Stream to an Immutable Collection
Java Program to Implement ArrayList API

