You are given a positive integer $D$. Let’s build the following graph from it:
- each vertex is a divisor of $D$ (not necessarily prime, $1$ and $D$ itself are also included);
- two vertices $x$ and $y$ ($x > y$) have an undirected edge between them if $x$ is divisible by $y$ and $\frac x y$ is a prime;
- the weight of an edge is the number of divisors of $x$ that are not divisors of $y$.
For example, here is the graph for $D=12$:
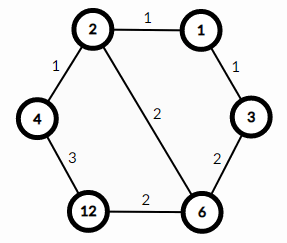
Edge $(4,12)$ has weight $3$ because $12$ has divisors $[1,2,3,4,6,12]$ and $4$ has divisors $[1,2,4]$. Thus, there are $3$ divisors of $12$ that are not divisors of $4$ — $[3,6,12]$.
There is no edge between $3$ and $2$ because $3$ is not divisible by $2$. There is no edge between $12$ and $3$ because $\frac{12}{3}=4$ is not a prime.
Let the length of the path between some vertices $v$ and $u$ in the graph be the total weight of edges on it. For example, path $[(1, 2), (2, 6), (6, 12), (12, 4), (4, 2), (2, 6)]$ has length $1+2+2+3+1+2=11$. The empty path has length $0$.
So the shortest path between two vertices $v$ and $u$ is the path that has the minimal possible length.
Two paths $a$ and $b$ are different if there is either a different number of edges in them or there is a position $i$ such that $a_i$ and $b_i$ are different edges.
You are given $q$ queries of the following form:
- $v$ $u$ — calculate the number of the shortest paths between vertices $v$ and $u$.
The answer for each query might be large so print it modulo $998244353$.
Input
The first line contains a single integer $D$ ($1 \le D \le 10^{15}$) — the number the graph is built from.
The second line contains a single integer $q$ ($1 \le q \le 3 \cdot 10^5$) — the number of queries.
Each of the next $q$ lines contains two integers $v$ and $u$ ($1 \le v, u \le D$). It is guaranteed that $D$ is divisible by both $v$ and $u$ (both $v$ and $u$ are divisors of $D$).
Output
Print $q$ integers — for each query output the number of the shortest paths between the two given vertices modulo $998244353$.
Examples
input
12 3 4 4 12 1 3 4
output
1 3 1
input
1 1 1 1
output
1
input
288807105787200 4 46 482955026400 12556830686400 897 414 12556830686400 4443186242880 325
output
547558588 277147129 457421435 702277623
Note
In the first example:
- The first query is only the empty path — length $0$;
- The second query are paths $[(12, 4), (4, 2), (2, 1)]$ (length $3+1+1=5$), $[(12, 6), (6, 2), (2, 1)]$ (length $2+2+1=5$) and $[(12, 6), (6, 3), (3, 1)]$ (length $2+2+1=5$).
- The third query is only the path $[(3, 1), (1, 2), (2, 4)]$ (length $1+1+1=3$).
Solution:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define rep(i,a,n) for (int i=a;i<n;i++)
#define per(i,a,n) for (int i=n-1;i>=a;i--)
#define pb push_back
#define mp make_pair
#define all(x) (x).begin(),(x).end()
#define fi first
#define se second
#define SZ(x) ((int)(x).size())
typedef vector<int> VI;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
typedef double db;
mt19937 mrand(random_device{}());
const ll mod=998244353;
int rnd(int x) { return mrand() % x;}
ll powmod(ll a,ll b) {ll res=1;a%=mod; assert(b>=0); for(;b;b>>=1){if(b&1)res=res*a%mod;a=a*a%mod;}return res;}
ll gcd(ll a,ll b) { return b?gcd(b,a%b):a;}
// head
typedef pair<ll,ll> PLL;
namespace Factor {
const int N=1010000;
ll C,fac[10010],n,mut,a[1001000];
int T,cnt,i,l,prime[N],p[N],psize,_cnt;
ll _e[100],_pr[100];
vector<ll> d;
inline ll mul(ll a,ll b,ll p) {
if (p<=1000000000) return a*b%p;
else if (p<=1000000000000ll) return (((a*(b>>20)%p)<<20)+(a*(b&((1<<20)-1))))%p;
else {
ll d=(ll)floor(a*(long double)b/p+0.5);
ll ret=(a*b-d*p)%p;
if (ret<0) ret+=p;
return ret;
}
}
void prime_table(){
int i,j,tot,t1;
for (i=1;i<=psize;i++) p[i]=i;
for (i=2,tot=0;i<=psize;i++){
if (p[i]==i) prime[++tot]=i;
for (j=1;j<=tot && (t1=prime[j]*i)<=psize;j++){
p[t1]=prime[j];
if (i%prime[j]==0) break;
}
}
}
void init(int ps) {
psize=ps;
prime_table();
}
ll powl(ll a,ll n,ll p) {
ll ans=1;
for (;n;n>>=1) {
if (n&1) ans=mul(ans,a,p);
a=mul(a,a,p);
}
return ans;
}
bool witness(ll a,ll n) {
int t=0;
ll u=n-1;
for (;~u&1;u>>=1) t++;
ll x=powl(a,u,n),_x=0;
for (;t;t--) {
_x=mul(x,x,n);
if (_x==1 && x!=1 && x!=n-1) return 1;
x=_x;
}
return _x!=1;
}
bool miller(ll n) {
if (n<2) return 0;
if (n<=psize) return p[n]==n;
if (~n&1) return 0;
for (int j=0;j<=7;j++) if (witness(rand()%(n-1)+1,n)) return 0;
return 1;
}
ll gcd(ll a,ll b) {
ll ret=1;
while (a!=0) {
if ((~a&1) && (~b&1)) ret<<=1,a>>=1,b>>=1;
else if (~a&1) a>>=1; else if (~b&1) b>>=1;
else {
if (a<b) swap(a,b);
a-=b;
}
}
return ret*b;
}
ll rho(ll n) {
for (;;) {
ll X=rand()%n,Y,Z,T=1,*lY=a,*lX=lY;
int tmp=20;
C=rand()%10+3;
X=mul(X,X,n)+C;*(lY++)=X;lX++;
Y=mul(X,X,n)+C;*(lY++)=Y;
for(;X!=Y;) {
ll t=X-Y+n;
Z=mul(T,t,n);
if(Z==0) return gcd(T,n);
tmp--;
if (tmp==0) {
tmp=20;
Z=gcd(Z,n);
if (Z!=1 && Z!=n) return Z;
}
T=Z;
Y=*(lY++)=mul(Y,Y,n)+C;
Y=*(lY++)=mul(Y,Y,n)+C;
X=*(lX++);
}
}
}
void _factor(ll n) {
for (int i=0;i<cnt;i++) {
if (n%fac[i]==0) n/=fac[i],fac[cnt++]=fac[i];}
if (n<=psize) {
for (;n!=1;n/=p[n]) fac[cnt++]=p[n];
return;
}
if (miller(n)) fac[cnt++]=n;
else {
ll x=rho(n);
_factor(x);_factor(n/x);
}
}
void dfs(ll x,int dep) {
if (dep==_cnt) d.pb(x);
else {
dfs(x,dep+1);
for (int i=1;i<=_e[dep];i++) dfs(x*=_pr[dep],dep+1);
}
}
void norm() {
sort(fac,fac+cnt);
_cnt=0;
rep(i,0,cnt) if (i==0||fac[i]!=fac[i-1]) _pr[_cnt]=fac[i],_e[_cnt++]=1;
else _e[_cnt-1]++;
}
vector<ll> getd() {
d.clear();
dfs(1,0);
return d;
}
vector<ll> factor(ll n) {
cnt=0;
_factor(n);
norm();
return getd();
}
vector<PLL> factorG(ll n) {
cnt=0;
_factor(n);
norm();
vector<PLL> d;
rep(i,0,_cnt) d.pb(mp(_pr[i],_e[i]));
return d;
}
bool is_primitive(ll a,ll p) {
assert(miller(p));
vector<PLL> D=factorG(p-1);
rep(i,0,SZ(D)) if (powl(a,(p-1)/D[i].fi,p)==1) return 0;
return 1;
}
}
ll d,fac[1010],fnv[1010];
vector<PLL> x;
int q;
ll way(ll u,ll v) {
ll f=1;
int s=0;
rep(i,0,SZ(x)) {
int p=0,q=0;
while (u%x[i].fi==0) u/=x[i].fi,p++;
while (v%x[i].fi==0) v/=x[i].fi,q++;
f=f*fnv[abs(p-q)]%mod;
s+=abs(p-q);
}
f=f*fac[s]%mod;
return f;
}
int main() {
Factor::init(100000);
fac[0]=fnv[0]=1;
rep(i,1,1000) fac[i]=fac[i-1]*i%mod,fnv[i]=powmod(fac[i],mod-2);
scanf("%lld",&d);
x=Factor::factorG(d);
sort(all(x));
scanf("%d",&q);
rep(i,0,q) {
ll u,v;
scanf("%lld%lld",&u,&v);
ll w=gcd(u,v);
ll f=way(u,w)*way(v,w)%mod;
printf("%lld\n",f);
}
}

