Table of Contents
In this article, you will learn to use break and continue statements to alter the flow of a loop.
1. What is the use of break and continue in Python?
In Python, break and continue statements can alter the flow of a normal loop.
Loops iterate over a block of code until the test expression is false, but sometimes we wish to terminate the current iteration or even the whole loop without checking test expression.
The break and continue statements are used in these cases.
2. Python break statement
The break statement terminates the loop containing it. Control of the program flows to the statement immediately after the body of the loop.
If the break statement is inside a nested loop (loop inside another loop), the break statement will terminate the innermost loop.
2.1. Syntax of break
break
2.2. Flowchart of break
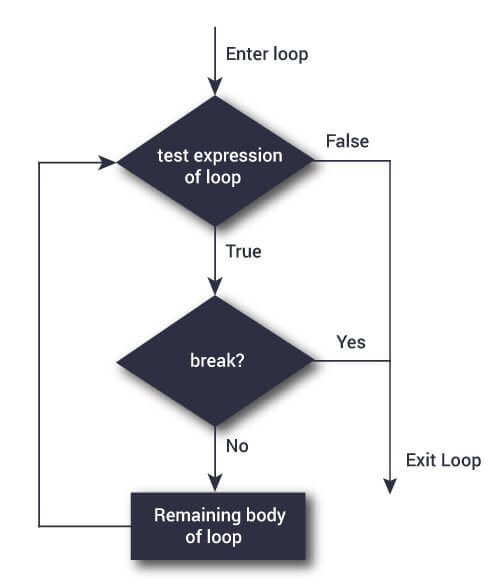
The working of break statement in for loop and while loop is shown below.

2.3. Example: Python break
# Use of break statement inside the loop
for val in "string":
if val == "i":
break
print(val)
print("The end")
Output
s t r The end
In this program, we iterate through the “string” sequence. We check if the letter is i, upon which we break from the loop. Hence, we see in our output that all the letters up till i gets printed. After that, the loop terminates.
3. Python continue statement
The continue statement is used to skip the rest of the code inside a loop for the current iteration only. Loop does not terminate but continues on with the next iteration.
3.1. Syntax of Continue
continue
3.2. Flowchart of continue
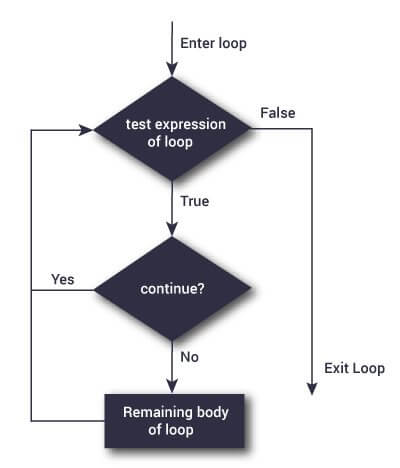
The working of the continue statement in for and while loop is shown below.
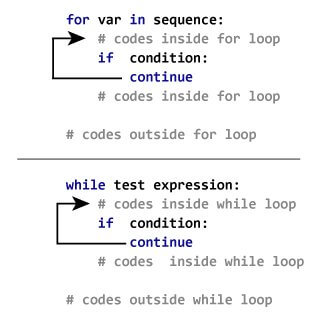
3.3. Example: Python continue
# Program to show the use of continue statement inside loops
for val in "string":
if val == "i":
continue
print(val)
print("The end")
Output
s t r n g The end
This program is same as the above example except the break statement has been replaced with continue.
We continue with the loop, if the string is i, not executing the rest of the block. Hence, we see in our output that all the letters except i gets printed.

