Table of Contents
In this tutorial, you will learn about the quick sort algorithm and its implementation in Python, Java, C, and C++.
Quicksort is a sorting algorithm based on the divide and conquer approach where
- An array is divided into subarrays by selecting a pivot element (element selected from the array).
While dividing the array, the pivot element should be positioned in such a way that elements less than pivot are kept on the left side and elements greater than pivot are on the right side of the pivot. - The left and right subarrays are also divided using the same approach. This process continues until each subarray contains a single element.
- At this point, elements are already sorted. Finally, elements are combined to form a sorted array.
1. Working of Quicksort Algorithm
1. Select the Pivot Element
There are different variations of quicksort where the pivot element is selected from different positions. Here, we will be selecting the rightmost element of the array as the pivot element.
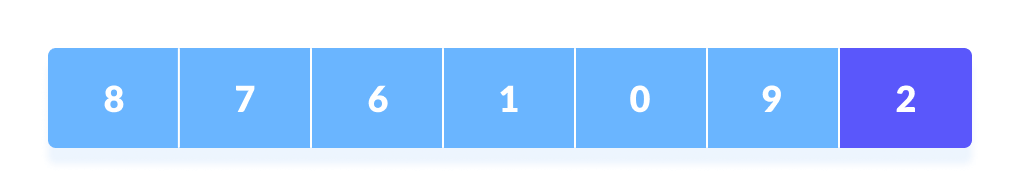
2. Rearrange the Array
Now the elements of the array are rearranged so that elements that are smaller than the pivot are put on the left and the elements greater than the pivot are put on the right.

Here’s how we rearrange the array:
A pointer is fixed at the pivot element. The pivot element is compared with the elements beginning from the first index.
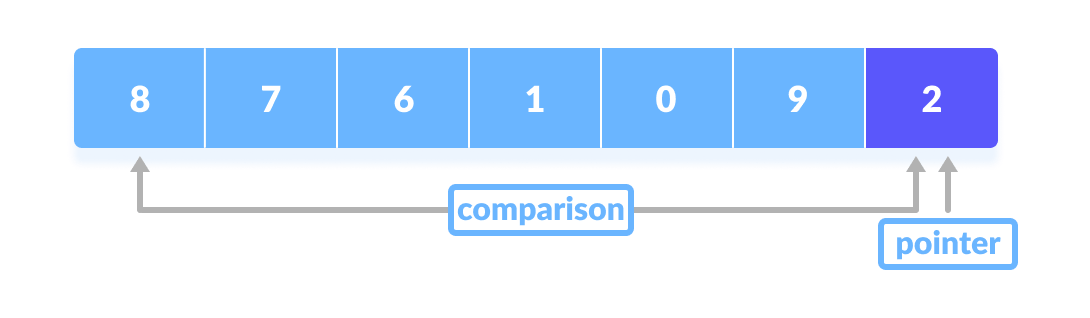
Comparison of pivot element with element beginning from the first index
If the element is greater than the pivot element, a second pointer is set for that element.
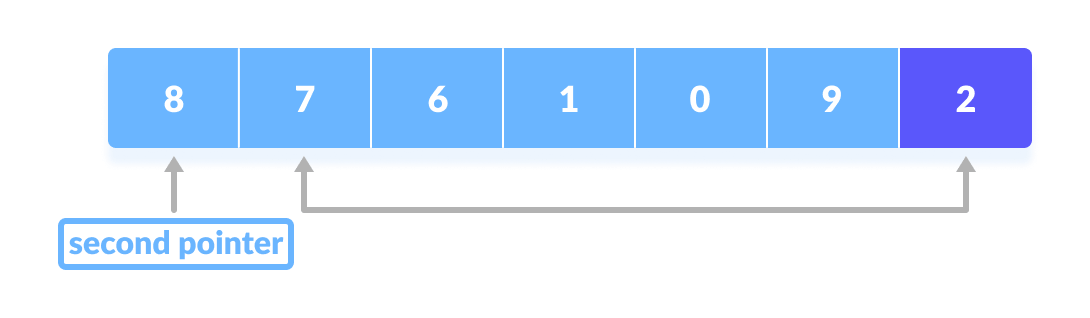
If the element is greater than the pivot element, a second pointer is set for that element.
Now, pivot is compared with other elements. If an element smaller than the pivot element is reached, the smaller element is swapped with the greater element found earlier.
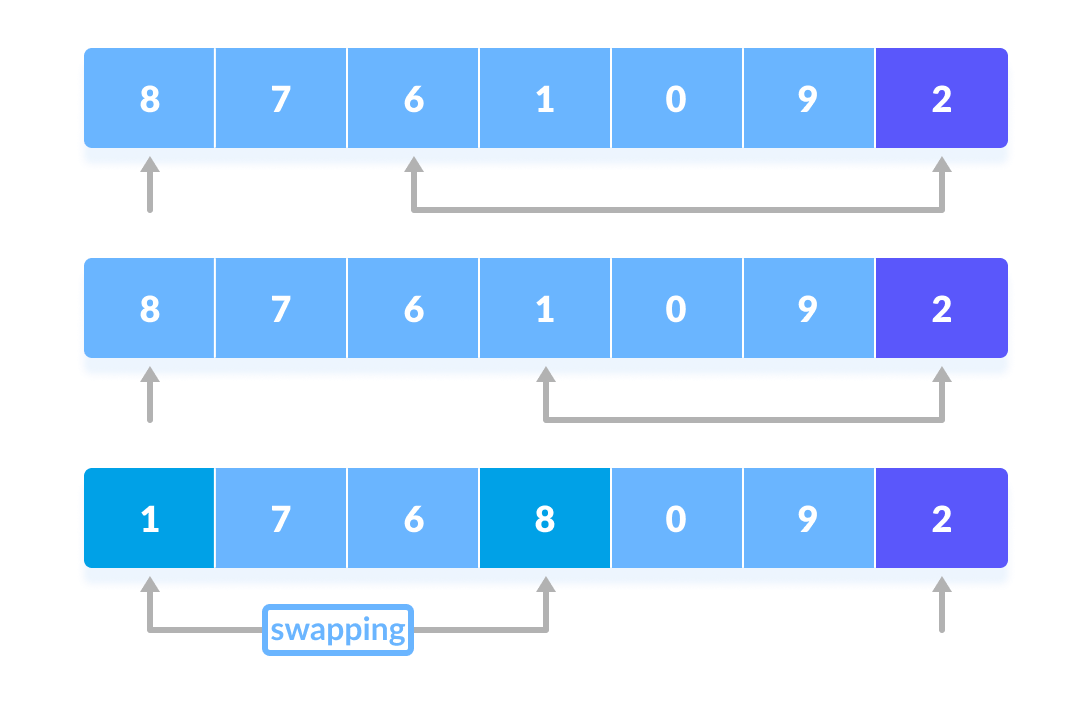
Pivot is compared with other elements.
Again, the process is repeated to set the next greater element as the second pointer. And, swap it with another smaller element.
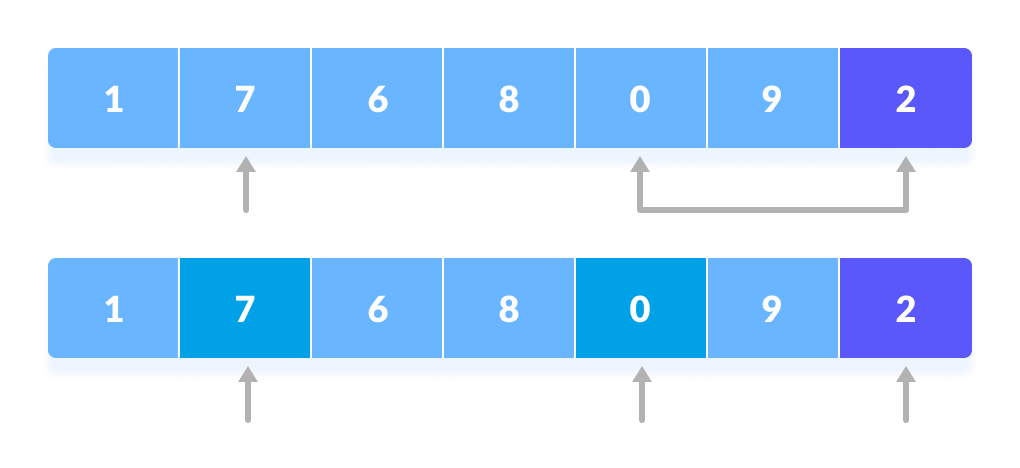
The process is repeated to set the next greater element as the second pointer.
The process goes on until the second last element is reached.
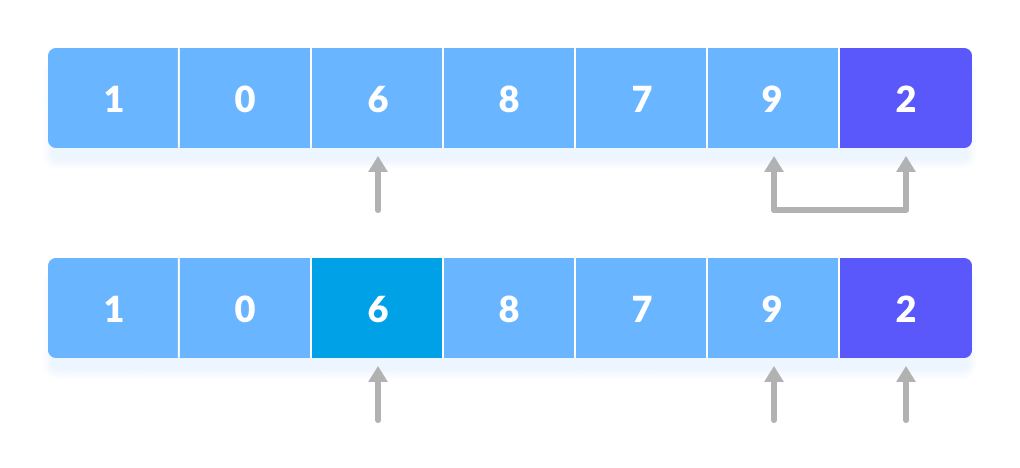
The process goes on until the second last element is reached.
Finally, the pivot element is swapped with the second pointer.
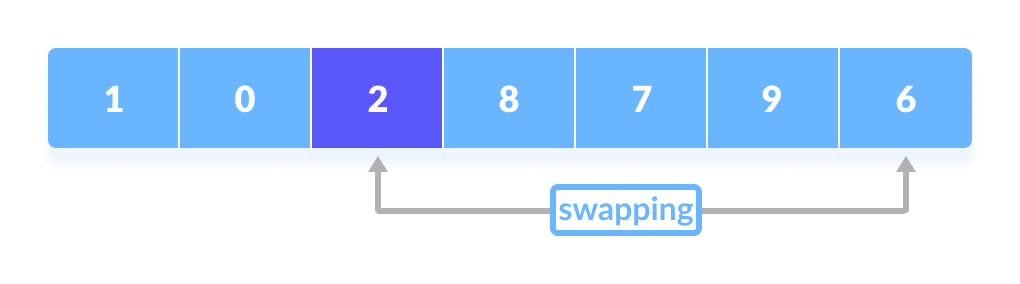
Finally, the pivot element is swapped with the second pointer.
3. Divide Subarrays
Pivot elements are again chosen for the left and the right sub-parts separately. And, step 2 is repeated.
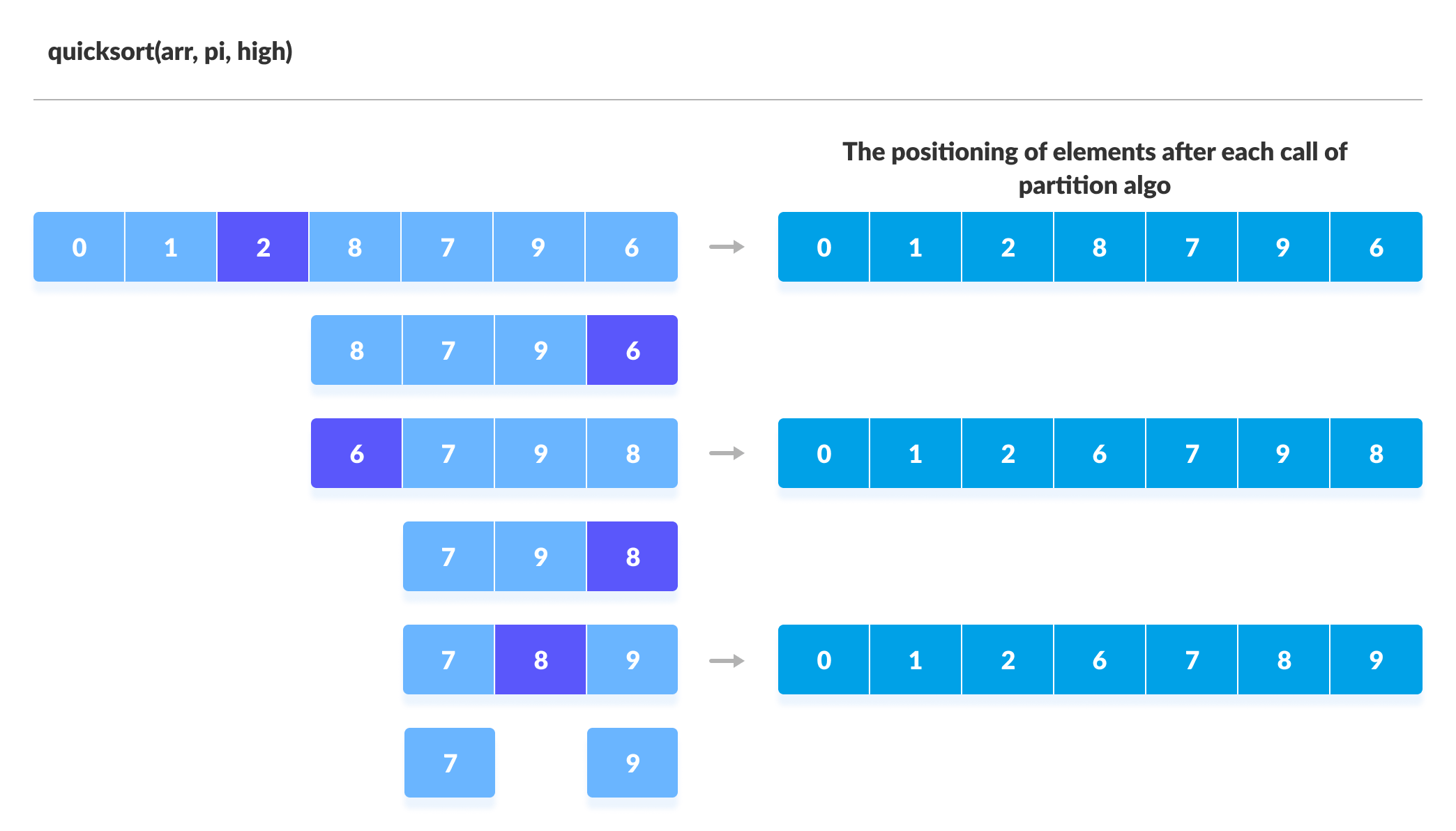
The subarrays are divided until each subarray is formed of a single element. At this point, the array is already sorted.
2. Quick Sort Algorithm
quickSort(array, leftmostIndex, rightmostIndex)
if (leftmostIndex < rightmostIndex)
pivotIndex <- partition(array,leftmostIndex, rightmostIndex)
quickSort(array, leftmostIndex, pivotIndex - 1)
quickSort(array, pivotIndex, rightmostIndex)
partition(array, leftmostIndex, rightmostIndex)
set rightmostIndex as pivotIndex
storeIndex <- leftmostIndex - 1
for i <- leftmostIndex + 1 to rightmostIndex
if element[i] < pivotElement
swap element[i] and element[storeIndex]
storeIndex++
swap pivotElement and element[storeIndex+1]
return storeIndex + 1
2.1. Visual Illustration of Quicksort Algorithm
You can understand the working of quicksort algorithm with the help of the illustrations below.
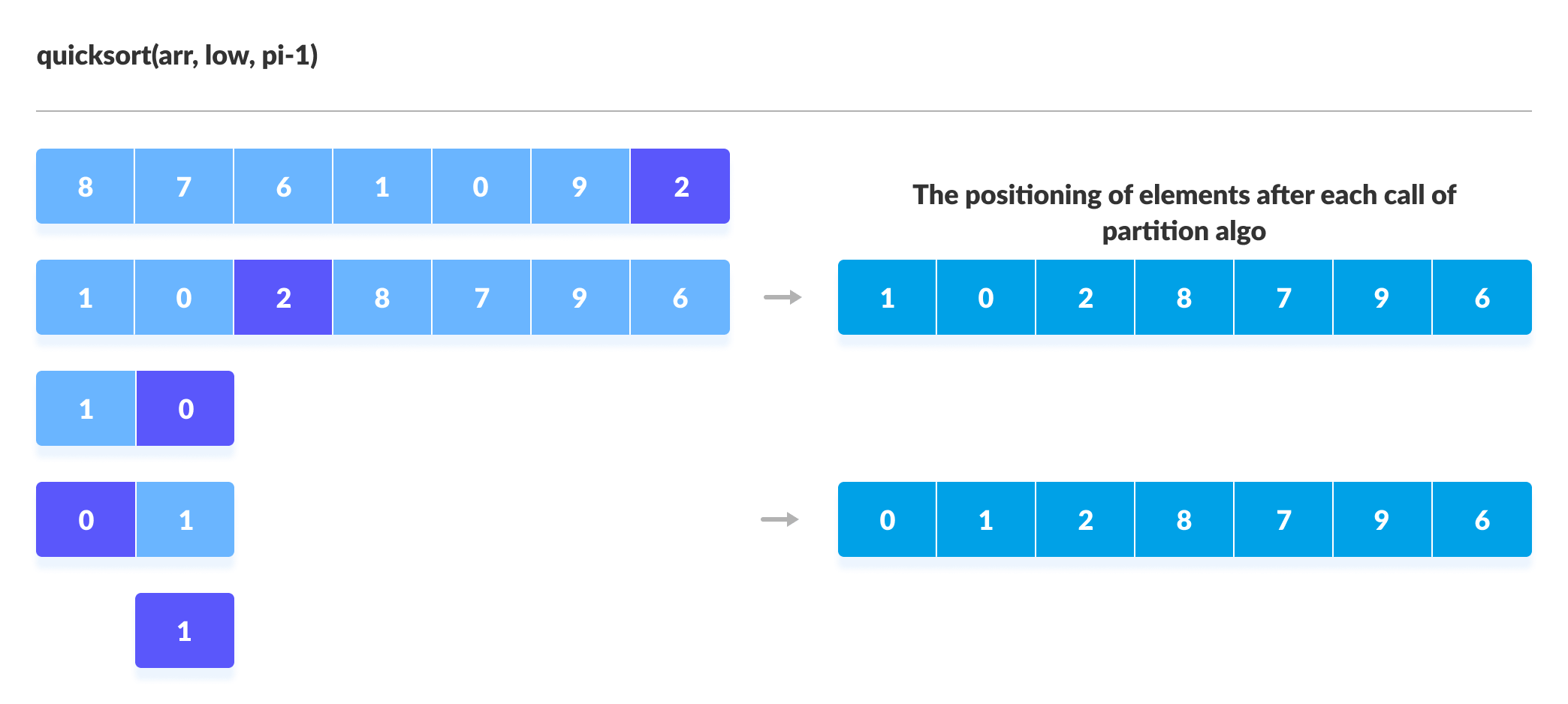
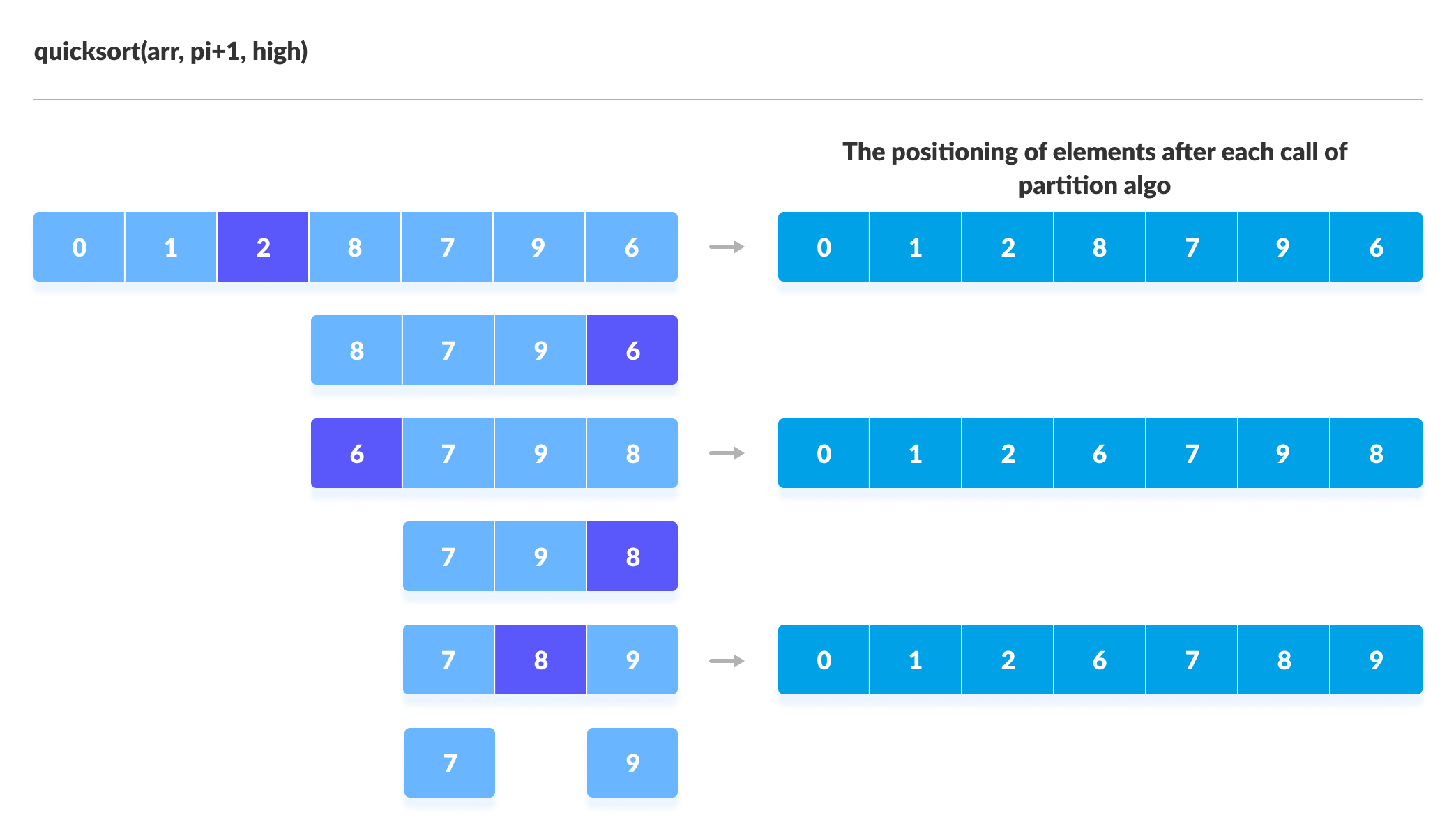
3. Quicksort Code in Python, Java, and C/C++
Source code by Python Language:
# Quick sort in Python
# function to find the partition position
def partition(array, low, high):
# choose the rightmost element as pivot
pivot = array[high]
# pointer for greater element
i = low - 1
# traverse through all elements
# compare each element with pivot
for j in range(low, high):
if array[j] <= pivot:
# if element smaller than pivot is found
# swap it with the greater element pointed by i
i = i + 1
# swapping element at i with element at j
(array[i], array[j]) = (array[j], array[i])
# swap the pivot element with the greater element specified by i
(array[i + 1], array[high]) = (array[high], array[i + 1])
# return the position from where partition is done
return i + 1
# function to perform quicksort
def quickSort(array, low, high):
if low < high:
# find pivot element such that
# element smaller than pivot are on the left
# element greater than pivot are on the right
pi = partition(array, low, high)
# recursive call on the left of pivot
quickSort(array, low, pi - 1)
# recursive call on the right of pivot
quickSort(array, pi + 1, high)
data = [8, 7, 2, 1, 0, 9, 6]
print("Unsorted Array")
print(data)
size = len(data)
quickSort(data, 0, size - 1)
print('Sorted Array in Ascending Order:')
print(data)
Source code by Java Language:
// Quick sort in Java
import java.util.Arrays;
class Quicksort {
// method to find the partition position
static int partition(int array[], int low, int high) {
// choose the rightmost element as pivot
int pivot = array[high];
// pointer for greater element
int i = (low - 1);
// traverse through all elements
// compare each element with pivot
for (int j = low; j < high; j++) {
if (array[j] <= pivot) {
// if element smaller than pivot is found
// swap it with the greatr element pointed by i
i++;
// swapping element at i with element at j
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = temp;
}
}
// swapt the pivot element with the greater element specified by i
int temp = array[i + 1];
array[i + 1] = array[high];
array[high] = temp;
// return the position from where partition is done
return (i + 1);
}
static void quickSort(int array[], int low, int high) {
if (low < high) {
// find pivot element such that
// elements smaller than pivot are on the left
// elements greater than pivot are on the right
int pi = partition(array, low, high);
// recursive call on the left of pivot
quickSort(array, low, pi - 1);
// recursive call on the right of pivot
quickSort(array, pi + 1, high);
}
}
}
// Main class
class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int[] data = { 8, 7, 2, 1, 0, 9, 6 };
System.out.println("Unsorted Array");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(data));
int size = data.length;
// call quicksort() on array data
Quicksort.quickSort(data, 0, size - 1);
System.out.println("Sorted Array in Ascending Order: ");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(data));
}
}
Source code by C Language:
// Quick sort in C
#include <stdio.h>
// function to swap elements
void swap(int *a, int *b) {
int t = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = t;
}
// function to find the partition position
int partition(int array[], int low, int high) {
// select the rightmost element as pivot
int pivot = array[high];
// pointer for greater element
int i = (low - 1);
// traverse each element of the array
// compare them with the pivot
for (int j = low; j < high; j++) {
if (array[j] <= pivot) {
// if element smaller than pivot is found
// swap it with the greater element pointed by i
i++;
// swap element at i with element at j
swap(&array[i], &array[j]);
}
}
// swap the pivot element with the greater element at i
swap(&array[i + 1], &array[high]);
// return the partition point
return (i + 1);
}
void quickSort(int array[], int low, int high) {
if (low < high) {
// find the pivot element such that
// elements smaller than pivot are on left of pivot
// elements greater than pivot are on right of pivot
int pi = partition(array, low, high);
// recursive call on the left of pivot
quickSort(array, low, pi - 1);
// recursive call on the right of pivot
quickSort(array, pi + 1, high);
}
}
// function to print array elements
void printArray(int array[], int size) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
printf("%d ", array[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
// main function
int main() {
int data[] = {8, 7, 2, 1, 0, 9, 6};
int n = sizeof(data) / sizeof(data[0]);
printf("Unsorted Array\n");
printArray(data, n);
// perform quicksort on data
quickSort(data, 0, n - 1);
printf("Sorted array in ascending order: \n");
printArray(data, n);
}
Source code by C++ Language:
// Quick sort in C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// function to swap elements
void swap(int *a, int *b) {
int t = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = t;
}
// function to print the array
void printArray(int array[], int size) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
cout << array[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
// function to rearrange array (find the partition point)
int partition(int array[], int low, int high) {
// select the rightmost element as pivot
int pivot = array[high];
// pointer for greater element
int i = (low - 1);
// traverse each element of the array
// compare them with the pivot
for (int j = low; j < high; j++) {
if (array[j] <= pivot) {
// if element smaller than pivot is found
// swap it with the greater element pointed by i
i++;
// swap element at i with element at j
swap(&array[i], &array[j]);
}
}
// swap pivot with the greater element at i
swap(&array[i + 1], &array[high]);
// return the partition point
return (i + 1);
}
void quickSort(int array[], int low, int high) {
if (low < high) {
// find the pivot element such that
// elements smaller than pivot are on left of pivot
// elements greater than pivot are on righ of pivot
int pi = partition(array, low, high);
// recursive call on the left of pivot
quickSort(array, low, pi - 1);
// recursive call on the right of pivot
quickSort(array, pi + 1, high);
}
}
// Driver code
int main() {
int data[] = {8, 7, 6, 1, 0, 9, 2};
int n = sizeof(data) / sizeof(data[0]);
cout << "Unsorted Array: \n";
printArray(data, n);
// perform quicksort on data
quickSort(data, 0, n - 1);
cout << "Sorted array in ascending order: \n";
printArray(data, n);
}
4. Quicksort Complexity
| Time Complexity | |
|---|---|
| Best | O(n*log n) |
| Worst | O(n2) |
| Average | O(n*log n) |
| Space Complexity | O(log n) |
| Stability | No |
4.1. Time Complexities
- Worst Case Complexity [Big-O]:
O(n2)
It occurs when the pivot element picked is either the greatest or the smallest element.
This condition leads to the case in which the pivot element lies in an extreme end of the sorted array. One sub-array is always empty and another sub-array containsn - 1elements. Thus, quicksort is called only on this sub-array.
However, the quicksort algorithm has better performance for scattered pivots.
- Best Case Complexity [Big-omega]:
O(n*log n)
It occurs when the pivot element is always the middle element or near to the middle element. - Average Case Complexity [Big-theta]:
O(n*log n)
It occurs when the above conditions do not occur.
4.2. Space Complexity
The space complexity for quicksort is O(log n).
5. Quicksort Applications
Quicksort algorithm is used when
- the programming language is good for recursion
- time complexity matters
- space complexity matters
6. Similar Sorting Algorithms
- Insertion Sort
- Merge Sort
- Selection Sort
- Bucket Sort

