Table of Contents
In this tutorial, you will learn about the radix sort algorithm and its implementation in Python, Java, C, and C++.
Radix sort is a sorting algorithm that sorts the elements by first grouping the individual digits of the same place value. Then, sort the elements according to their increasing/decreasing order.
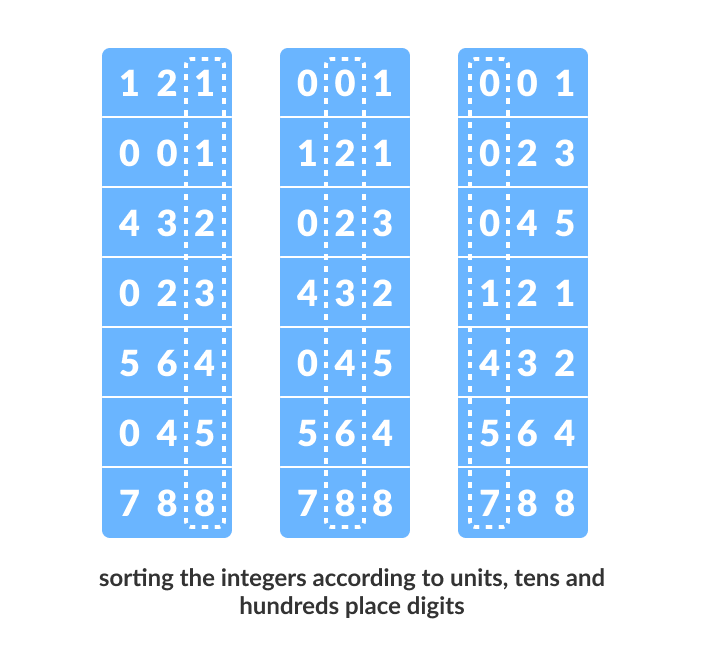
Suppose, we have an array of 8 elements. First, we will sort elements based on the value of the unit place. Then, we will sort elements based on the value of the tenth place. This process goes on until the last significant place.
Let the initial array be [121, 432, 564, 23, 1, 45, 788]. It is sorted according to radix sort as shown in the figure below.
Please go through the counting sort before reading this article because counting sort is used as an intermediate sort in radix sort.
1. Working of Radix Sort
Find the largest element in the array, i.e. max. Let X be the number of digits in max. X is calculated because we have to go through all the significant places of all elements.
In this array [121, 432, 564, 23, 1, 45, 788], we have the largest number 788. It has 3 digits. Therefore, the loop should go up to hundreds place (3 times).
Now, go through each significant place one by one.
Use any stable sorting technique to sort the digits at each significant place. We have used counting sort for this.
Sort the elements based on the unit place digits (X=0).
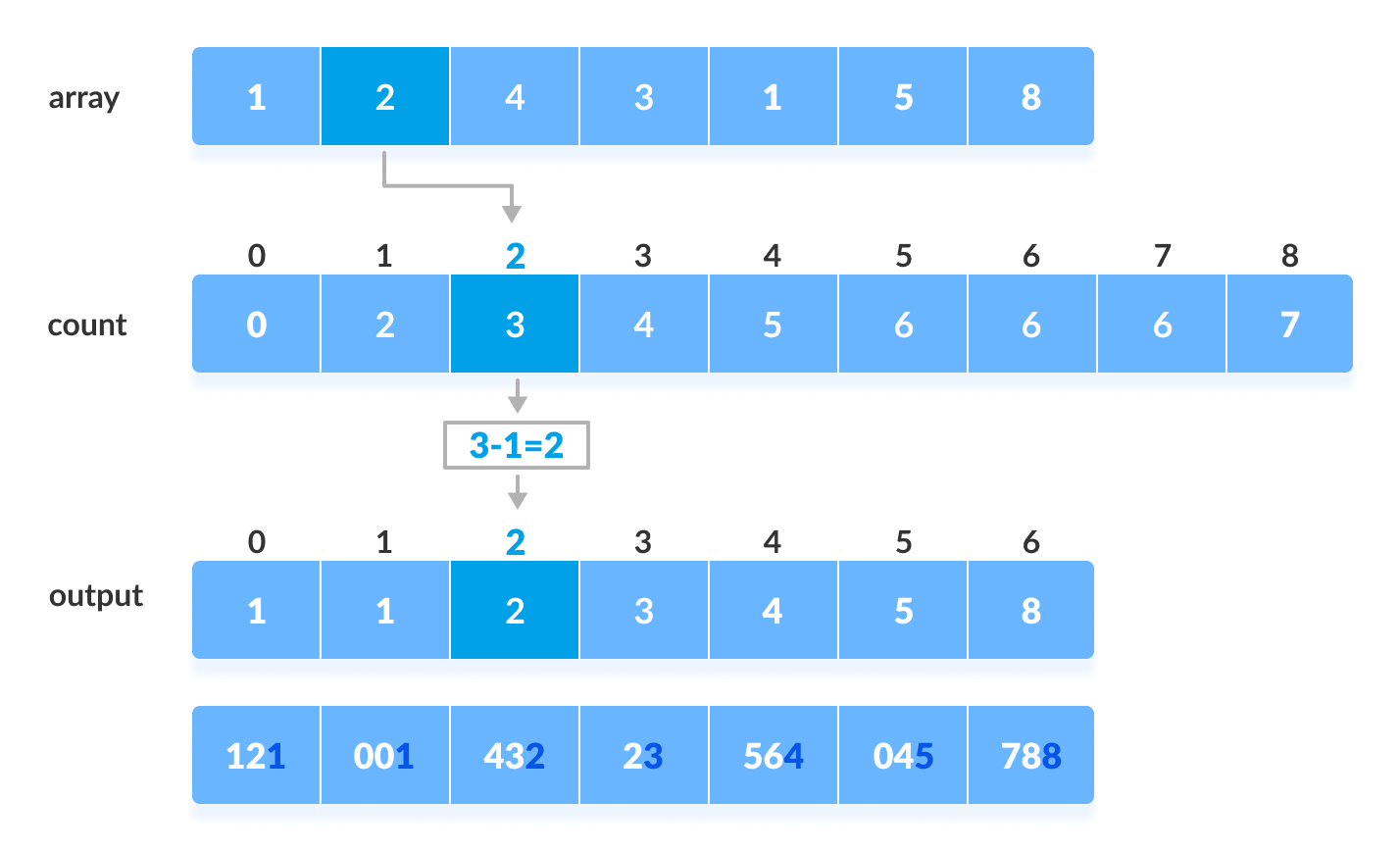
Using counting sort to sort elements based on unit place
Now, sort the elements based on digits at tens place.

Sort elements based on tens place
Finally, sort the elements based on the digits at hundreds place.
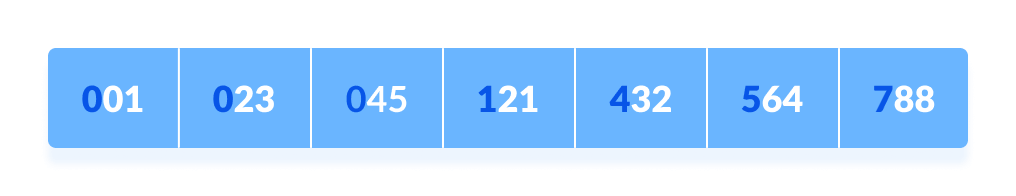
Sort elements based on hundreds place
2. Radix Sort Algorithm
radixSort(array)
d <- maximum number of digits in the largest element
create d buckets of size 0-9
for i <- 0 to d
sort the elements according to ith place digits using countingSort
countingSort(array, d)
max <- find largest element among dth place elements
initialize count array with all zeros
for j <- 0 to size
find the total count of each unique digit in dth place of elements and
store the count at jth index in count array
for i <- 1 to max
find the cumulative sum and store it in count array itself
for j <- size down to 1
restore the elements to array
decrease count of each element restored by 1
3. Radix Sort Code in Python, Java, and C/C++
Source code by Python Language:
# Radix sort in Python
# Using counting sort to sort the elements in the basis of significant places
def countingSort(array, place):
size = len(array)
output = [0] * size
count = [0] * 10
# Calculate count of elements
for i in range(0, size):
index = array[i] // place
count[index % 10] += 1
# Calculate cumulative count
for i in range(1, 10):
count[i] += count[i - 1]
# Place the elements in sorted order
i = size - 1
while i >= 0:
index = array[i] // place
output[count[index % 10] - 1] = array[i]
count[index % 10] -= 1
i -= 1
for i in range(0, size):
array[i] = output[i]
# Main function to implement radix sort
def radixSort(array):
# Get maximum element
max_element = max(array)
# Apply counting sort to sort elements based on place value.
place = 1
while max_element // place > 0:
countingSort(array, place)
place *= 10
data = [121, 432, 564, 23, 1, 45, 788]
radixSort(data)
print(data)
Source code by Java Language:
// Radix Sort in Java Programming
import java.util.Arrays;
class RadixSort {
// Using counting sort to sort the elements in the basis of significant places
void countingSort(int array[], int size, int place) {
int[] output = new int[size + 1];
int max = array[0];
for (int i = 1; i < size; i++) {
if (array[i] > max)
max = array[i];
}
int[] count = new int[max + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < max; ++i)
count[i] = 0;
// Calculate count of elements
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
count[(array[i] / place) % 10]++;
// Calculate cumulative count
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++)
count[i] += count[i - 1];
// Place the elements in sorted order
for (int i = size - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
output[count[(array[i] / place) % 10] - 1] = array[i];
count[(array[i] / place) % 10]--;
}
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
array[i] = output[i];
}
// Function to get the largest element from an array
int getMax(int array[], int n) {
int max = array[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
if (array[i] > max)
max = array[i];
return max;
}
// Main function to implement radix sort
void radixSort(int array[], int size) {
// Get maximum element
int max = getMax(array, size);
// Apply counting sort to sort elements based on place value.
for (int place = 1; max / place > 0; place *= 10)
countingSort(array, size, place);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[]) {
int[] data = { 121, 432, 564, 23, 1, 45, 788 };
int size = data.length;
RadixSort rs = new RadixSort();
rs.radixSort(data, size);
System.out.println("Sorted Array in Ascending Order: ");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(data));
}
}
Source code by C Language:
// Radix Sort in C Programming
#include <stdio.h>
// Function to get the largest element from an array
int getMax(int array[], int n) {
int max = array[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
if (array[i] > max)
max = array[i];
return max;
}
// Using counting sort to sort the elements in the basis of significant places
void countingSort(int array[], int size, int place) {
int output[size + 1];
int max = (array[0] / place) % 10;
for (int i = 1; i < size; i++) {
if (((array[i] / place) % 10) > max)
max = array[i];
}
int count[max + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < max; ++i)
count[i] = 0;
// Calculate count of elements
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
count[(array[i] / place) % 10]++;
// Calculate cumulative count
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++)
count[i] += count[i - 1];
// Place the elements in sorted order
for (int i = size - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
output[count[(array[i] / place) % 10] - 1] = array[i];
count[(array[i] / place) % 10]--;
}
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
array[i] = output[i];
}
// Main function to implement radix sort
void radixsort(int array[], int size) {
// Get maximum element
int max = getMax(array, size);
// Apply counting sort to sort elements based on place value.
for (int place = 1; max / place > 0; place *= 10)
countingSort(array, size, place);
}
// Print an array
void printArray(int array[], int size) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
printf("%d ", array[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
// Driver code
int main() {
int array[] = {121, 432, 564, 23, 1, 45, 788};
int n = sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]);
radixsort(array, n);
printArray(array, n);
}
Source code by C++ Language:
// Radix Sort in C++ Programming
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Function to get the largest element from an array
int getMax(int array[], int n) {
int max = array[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
if (array[i] > max)
max = array[i];
return max;
}
// Using counting sort to sort the elements in the basis of significant places
void countingSort(int array[], int size, int place) {
const int max = 10;
int output[size];
int count[max];
for (int i = 0; i < max; ++i)
count[i] = 0;
// Calculate count of elements
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
count[(array[i] / place) % 10]++;
// Calculate cumulative count
for (int i = 1; i < max; i++)
count[i] += count[i - 1];
// Place the elements in sorted order
for (int i = size - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
output[count[(array[i] / place) % 10] - 1] = array[i];
count[(array[i] / place) % 10]--;
}
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
array[i] = output[i];
}
// Main function to implement radix sort
void radixsort(int array[], int size) {
// Get maximum element
int max = getMax(array, size);
// Apply counting sort to sort elements based on place value.
for (int place = 1; max / place > 0; place *= 10)
countingSort(array, size, place);
}
// Print an array
void printArray(int array[], int size) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
cout << array[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
// Driver code
int main() {
int array[] = {121, 432, 564, 23, 1, 45, 788};
int n = sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]);
radixsort(array, n);
printArray(array, n);
}
4. Radix Sort Complexity
| Time Complexity | |
|---|---|
| Best | O(n+k) |
| Worst | O(n+k) |
| Average | O(n+k) |
| Space Complexity | O(max) |
| Stability | Yes |
Since radix sort is a non-comparative algorithm, it has advantages over comparative sorting algorithms.
For the radix sort that uses counting sort as an intermediate stable sort, the time complexity is O(d(n+k)).
Here, d is the number cycle and O(n+k) is the time complexity of counting sort.
Thus, radix sort has linear time complexity which is better than O(nlog n) of comparative sorting algorithms.
If we take very large digit numbers or the number of other bases like 32-bit and 64-bit numbers then it can perform in linear time however the intermediate sort takes large space.
This makes radix sort space inefficient. This is the reason why this sort is not used in software libraries.
5. Radix Sort Applications
Radix sort is implemented in
- DC3 algorithm (Kärkkäinen-Sanders-Burkhardt) while making a suffix array.
- places where there are numbers in large ranges.
6. Similar Sorting Algorithms
- Quicksort
- Merge Sort
- Bucket Sort
- Counting Sort

