Table of Contents
Trong bài này, tôi sẽ giới thiệu với các bạn các đặc điểm của HashMap và các ví dụ cơ bản về sử dụng HashMap trong java. Trong bài viết tiếp theo, chúng ta sẽ tìm hiểu kỹ hơn về cách thức hoạt động bên trong của HashMap trong Java.
1. Đặc điểm
Những điểm quan trọng về lớp HashMap trong java cần nhớ là:
- HashMap lưu trữ dữ liệu dưới dạng cặp key và value.
- HashMap chỉ chứa các key duy nhất.
- HashMap có thể có 1 key là null và nhiều giá trị null.
- HashMap duy trì các phần tử KHÔNG theo thứ tự chèn.
2. Hierarchy của lớp HashMap
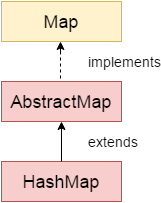
Lớp java.util.HashMap được định nghĩa như sau:
public class HashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable {
}
Trong đó:
- K: đây là kiểu key để lưu trữ.
- V: đây là kiểu giá trị được ánh xạ.
3. Các phương thức khởi tạo (constructor) của lớp HashMap
- HashMap(): khởi tạo một map trống.
- HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m): khởi tạo một map với các phần tử của map m.
4. Các phương thức (method) của lớp HashMap
Xem thêm các phương thức của Map ở bài viết Map Interface trong java.
5. Ví dụ minh họa
5.1. Ví dụ sử dụng HashMap với kiểu dữ liệu cơ bản (Wrapper)
package com.maixuanviet.collection.map;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
public class HashMapExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// init map
Map<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<Integer, String>();
map.put(1, "Basic java");
map.put(2, "OOP");
map.put(3, "Collection");
// show map using method keySet()
for (Integer key : map.keySet()) {
String value = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key + " = " + value);
}
System.out.println("---");
// show map using method keySet()
for (Entry<Integer, String> entry : map.entrySet()) {
Integer key = entry.getKey();
String value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key + " = " + value);
}
}
}
Kết quả thực thi chương trình trên:
1 = Basic java 2 = OOP 3 = Collection --- 1 = Basic java 2 = OOP 3 = Collection
5.2. Ví dụ sử dụng HashMap với key có kiểu String, value có kiểu Student
package com.maixuanviet.collection.map;
public class Student {
private int id;
private String name;
public Student(int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + "]";
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
package com.maixuanviet.collection.map;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
public class HashMapExample2 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// Student's data
Student student1 = new Student(1, "Student 1");
Student student2 = new Student(2, "Student 2");
Student student3 = new Student(3, "Student 3");
// init map
Map<Integer, Student> map = new HashMap<Integer, Student>();
map.put(student1.getId(), student1);
map.put(student2.getId(), student2);
map.put(student3.getId(), student3);
// show map using method keySet()
for (Integer key : map.keySet()) {
Student value = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key + " = " + value);
}
System.out.println("---");
// show map using method keySet()
for (Entry<Integer, Student> entry : map.entrySet()) {
Integer key = entry.getKey();
Student value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key + " = " + value);
}
}
}
Kết quả thực thi chương trình trên:
1 = Student [id=1, name=Student 1] 2 = Student [id=2, name=Student 2] 3 = Student [id=3, name=Student 3] --- 1 = Student [id=1, name=Student 1] 2 = Student [id=2, name=Student 2] 3 = Student [id=3, name=Student 3]
Related posts:
Java Program to Implement Floyd Cycle Algorithm
Introduction to Spring Method Security
Java Program to Implement WeakHashMap API
How to Read a File in Java
Use Liquibase to Safely Evolve Your Database Schema
Hướng dẫn Java Design Pattern – Intercepting Filter
Java Program to Perform Optimal Paranthesization Using Dynamic Programming
Java Program to Implement Bubble Sort
Spring Security Custom AuthenticationFailureHandler
Guide to Dynamic Tests in Junit 5
Hướng dẫn Java Design Pattern – Object Pool
Java InputStream to String
Guide to the Java TransferQueue
OAuth2 Remember Me with Refresh Token
Java Program to Find Location of a Point Placed in Three Dimensions Using K-D Trees
Java Program to Implement Gale Shapley Algorithm
Java Program to Search Number Using Divide and Conquer with the Aid of Fibonacci Numbers
Spring Security OAuth Login with WebFlux
MyBatis with Spring
New Features in Java 11
Introduction to Spring Security Expressions
Comparing Strings in Java
Jackson – JsonMappingException (No serializer found for class)
What is Thread-Safety and How to Achieve it?
A Guide to HashSet in Java
Java Program to Implement Word Wrap Problem
Using JWT with Spring Security OAuth (legacy stack)
Quick Guide on Loading Initial Data with Spring Boot
Java Program to Find the Median of two Sorted Arrays using Binary Search Approach
Tránh lỗi ConcurrentModificationException trong Java như thế nào?
JPA/Hibernate Persistence Context
Quick Guide to Spring Controllers

