You are given an undirected graph consisting of $n$ vertices and $m$ edges.
Recall that a cycle is a path that starts and ends in the same vertex. A cycle in a graph is called simple if it contains each vertex (except the starting and ending one) no more than once (the starting and the ending one is contained always twice). Note that loops are considered to be simple cycles.
In one move you can choose any simple cycle in this graph and erase the edges corresponding to this cycle (corresponding vertices remain in the graph). It is allowed to erase the loop or two copies of the same edge (take a look at examples).
Your problem is to apply some sequence of moves to obtain the graph without edges. It is not necessary to minimize the number of cycles. If it is impossible, print “NO”.
Input
The first line of the input contains two integers $n$ and $m$ ($1 \le n, m \le 2 \cdot 10^5$) — the number of vertices and the number of edges in the graph.
The next $m$ lines contain edges of the graph. The $i$-th line contains the $i$-th edge $x_i, y_i$ ($1 \le x_i, y_i \le n$), where $x_i$ and $y_i$ are vertices connected by the $i$-th edge. The graph can contain loops or multiple edges.
Output
If it is impossible to decompose the given graph into simple cycles, print “NO” in the first line.
Otherwise print “YES” in the first line. In the second line print $k$ — the number of simple cycles in the graph decomposition.
In the next $k$ lines print cycles themselves. The $j$-th line should contain the $j$-th cycle. First, print $c_j$ — the number of vertices in the $j$-th cycle. Then print the cycle as a sequence of vertices. All neighbouring (adjacent) vertices in the printed path should be connected by an edge that isn’t contained in other cycles.
Examples
input
6 9 1 2 2 3 1 3 2 4 2 5 4 5 3 5 3 6 5 6
output
YES 3 4 2 5 4 2 4 3 6 5 3 4 1 3 2 1
input
4 7 1 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 1 1 3 1 3
output
YES 3 2 1 1 5 1 4 3 2 1 3 1 3 1
input
4 8 1 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 1 2 4 1 3 1 3
output
NO
Note
The picture corresponding to the first example:
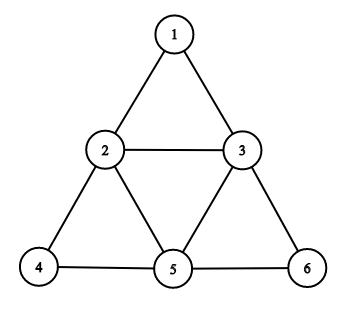
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
val (n, m) = readLine()!!.split(" ").map { it.toInt() }
val from = IntArray(m)
val to = IntArray(m)
for (i in 0 until m) {
val (foo, bar) = readLine()!!.split(" ").map { it.toInt() }
from[i] = foo - 1
to[i] = bar - 1
}
val g = Array<MutableList<Int>>(n, { i -> mutableListOf() })
for (i in 0 until m) {
g[from[i]].add(i)
g[to[i]].add(i)
}
val deg = IntArray(n)
for (i in 0 until m) {
deg[from[i]]++
deg[to[i]]++
}
for (i in 0 until n) {
if (deg[i] % 2 == 1) {
println("NO")
return
}
}
println("YES")
val used = BooleanArray(m)
val ptr = IntArray(n)
val res = IntArray(m)
var write_ptr = m
var stack_ptr = 0
for (root in 0 until n) {
var v = root
while (true) {
var found = false
while (ptr[v] < g[v].size) {
var id = g[v][ptr[v]++]
if (used[id]) {
continue
}
used[id] = true
res[stack_ptr++] = id
v = v xor from[id] xor to[id]
found = true
break
}
if (!found) {
if (stack_ptr == 0) {
break;
}
var id = res[--stack_ptr]
res[--write_ptr] = id
v = v xor from[id] xor to[id]
}
}
}
val cycles: MutableList<MutableList<Int>> = mutableListOf()
var seen = IntArray(4 * n)
for (i in 0 until 4 * n) {
seen[i] = -1
}
var now = 0
seen[0] = 0
stack_ptr = 0
for (i in 0 until m) {
now = now xor from[res[i]] xor to[res[i]]
res[stack_ptr++] = res[i]
if (seen[now] != -1) {
var ver = from[res[seen[now]]]
var cycle: MutableList<Int> = mutableListOf(ver + 1)
val start = seen[now]
var ok = 1
for (j in start until stack_ptr) {
if (ver != from[res[j]] && ver != to[res[j]]) {
ok = 0
}
ver = ver xor from[res[j]] xor to[res[j]]
cycle.add(ver + 1)
now = now xor from[res[j]] xor to[res[j]]
seen[now] = -1
}
if (ok == 0) {
ver = to[res[start]]
cycle = mutableListOf(ver + 1)
for (j in start until stack_ptr) {
ver = ver xor from[res[j]] xor to[res[j]]
cycle.add(ver + 1)
}
}
stack_ptr -= cycle.size - 1
cycles.add(cycle)
}
seen[now] = stack_ptr
}
println(cycles.size)
var s = Array<String>(cycles.size, { i -> "" })
for (i in 0 until cycles.size) {
s[i] = cycles[i].size.toString() + " " + cycles[i].joinToString(" ")
}
println(s.joinToString("\n"))
}

