Table of Contents
In this tutorial, you will learn how to insert a key into a btree. Also, you will find working examples of inserting keys into a B-tree in C, C++, Java and Python.
Inserting an element on a B-tree consists of two events: searching the appropriate node to insert the element and splitting the node if required.Insertion operation always takes place in the bottom-up approach.
Let us understand these events below.
1. Insertion Operation
- If the tree is empty, allocate a root node and insert the key.
- Update the allowed number of keys in the node.
- Search the appropriate node for insertion.
- If the node is full, follow the steps below.
- Insert the elements in increasing order.
- Now, there are elements greater than its limit. So, split at the median.
- Push the median key upwards and make the left keys as a left child and the right keys as a right child.
- If the node is not full, follow the steps below.
- Insert the node in increasing order.
2. Insertion Example
Let us understand the insertion operation with the illustrations below.
The elements to be inserted are 8, 9, 10, 11, 15, 16, 17, 18, 20, 23.
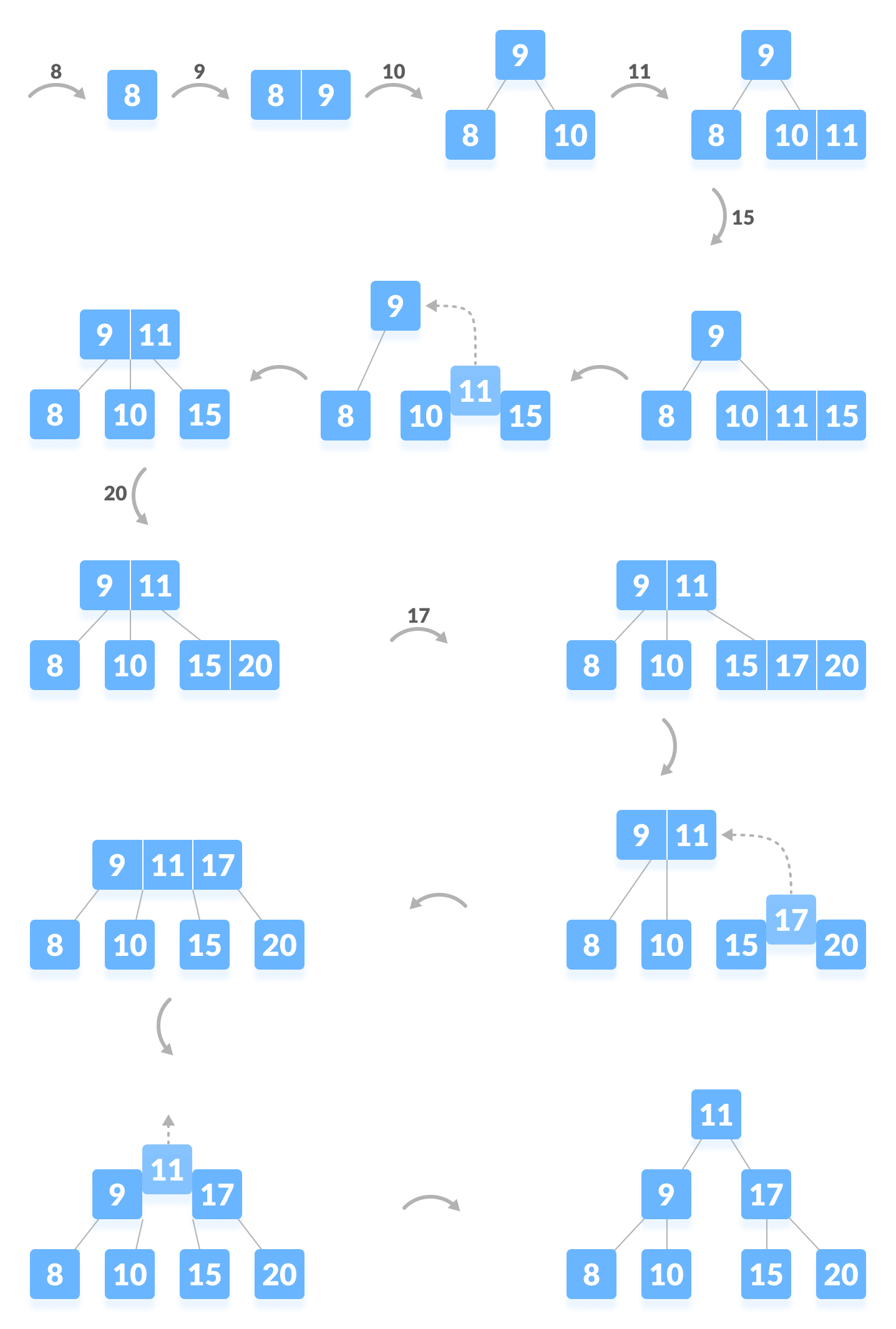
3. Algorithm for Inserting an Element
BreeInsertion(T, k)
r root[T]
if n[r] = 2t - 1
s = AllocateNode()
root[T] = s
leaf[s] = FALSE
n[s] <- 0
c1[s] <- r
BtreeSplitChild(s, 1, r)
BtreeInsertNonFull(s, k)
else BtreeInsertNonFull(r, k)
BtreeInsertNonFull(x, k)
i = n[x]
if leaf[x]
while i ≥ 1 and k < keyi[x]
keyi+1 [x] = keyi[x]
i = i - 1
keyi+1[x] = k
n[x] = n[x] + 1
else while i ≥ 1 and k < keyi[x]
i = i - 1
i = i + 1
if n[ci[x]] == 2t - 1
BtreeSplitChild(x, i, ci[x])
if k &rt; keyi[x]
i = i + 1
BtreeInsertNonFull(ci[x], k)
BtreeSplitChild(x, i)
BtreeSplitChild(x, i, y)
z = AllocateNode()
leaf[z] = leaf[y]
n[z] = t - 1
for j = 1 to t - 1
keyj[z] = keyj+t[y]
if not leaf [y]
for j = 1 to t
cj[z] = cj + t[y]
n[y] = t - 1
for j = n[x] + 1 to i + 1
cj+1[x] = cj[x]
ci+1[x] = z
for j = n[x] to i
keyj+1[x] = keyj[x]
keyi[x] = keyt[y]
n[x] = n[x] + 1
4. Python, Java and C/C++ Examples
Source code by Python Language:
# Inserting a key on a B-tree in Python
# Create a node
class BTreeNode:
def __init__(self, leaf=False):
self.leaf = leaf
self.keys = []
self.child = []
# Tree
class BTree:
def __init__(self, t):
self.root = BTreeNode(True)
self.t = t
# Insert node
def insert(self, k):
root = self.root
if len(root.keys) == (2 * self.t) - 1:
temp = BTreeNode()
self.root = temp
temp.child.insert(0, root)
self.split_child(temp, 0)
self.insert_non_full(temp, k)
else:
self.insert_non_full(root, k)
# Insert nonfull
def insert_non_full(self, x, k):
i = len(x.keys) - 1
if x.leaf:
x.keys.append((None, None))
while i >= 0 and k[0] < x.keys[i][0]:
x.keys[i + 1] = x.keys[i]
i -= 1
x.keys[i + 1] = k
else:
while i >= 0 and k[0] < x.keys[i][0]:
i -= 1
i += 1
if len(x.child[i].keys) == (2 * self.t) - 1:
self.split_child(x, i)
if k[0] > x.keys[i][0]:
i += 1
self.insert_non_full(x.child[i], k)
# Split the child
def split_child(self, x, i):
t = self.t
y = x.child[i]
z = BTreeNode(y.leaf)
x.child.insert(i + 1, z)
x.keys.insert(i, y.keys[t - 1])
z.keys = y.keys[t: (2 * t) - 1]
y.keys = y.keys[0: t - 1]
if not y.leaf:
z.child = y.child[t: 2 * t]
y.child = y.child[0: t - 1]
# Print the tree
def print_tree(self, x, l=0):
print("Level ", l, " ", len(x.keys), end=":")
for i in x.keys:
print(i, end=" ")
print()
l += 1
if len(x.child) > 0:
for i in x.child:
self.print_tree(i, l)
def main():
B = BTree(3)
for i in range(10):
B.insert((i, 2 * i))
B.print_tree(B.root)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Source code by Java Language:
// Inserting a key on a B-tree in Java
public class BTree {
private int T;
// Node Creation
public class Node {
int n;
int key[] = new int[2 * T - 1];
Node child[] = new Node[2 * T];
boolean leaf = true;
public int Find(int k) {
for (int i = 0; i < this.n; i++) {
if (this.key[i] == k) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
};
}
public BTree(int t) {
T = t;
root = new Node();
root.n = 0;
root.leaf = true;
}
private Node root;
// split
private void split(Node x, int pos, Node y) {
Node z = new Node();
z.leaf = y.leaf;
z.n = T - 1;
for (int j = 0; j < T - 1; j++) {
z.key[j] = y.key[j + T];
}
if (!y.leaf) {
for (int j = 0; j < T; j++) {
z.child[j] = y.child[j + T];
}
}
y.n = T - 1;
for (int j = x.n; j >= pos + 1; j--) {
x.child[j + 1] = x.child[j];
}
x.child[pos + 1] = z;
for (int j = x.n - 1; j >= pos; j--) {
x.key[j + 1] = x.key[j];
}
x.key[pos] = y.key[T - 1];
x.n = x.n + 1;
}
// insert key
public void insert(final int key) {
Node r = root;
if (r.n == 2 * T - 1) {
Node s = new Node();
root = s;
s.leaf = false;
s.n = 0;
s.child[0] = r;
split(s, 0, r);
_insert(s, key);
} else {
_insert(r, key);
}
}
// insert node
final private void _insert(Node x, int k) {
if (x.leaf) {
int i = 0;
for (i = x.n - 1; i >= 0 && k < x.key[i]; i--) {
x.key[i + 1] = x.key[i];
}
x.key[i + 1] = k;
x.n = x.n + 1;
} else {
int i = 0;
for (i = x.n - 1; i >= 0 && k < x.key[i]; i--) {
}
;
i++;
Node tmp = x.child[i];
if (tmp.n == 2 * T - 1) {
split(x, i, tmp);
if (k > x.key[i]) {
i++;
}
}
_insert(x.child[i], k);
}
}
public void display() {
display(root);
}
// Display the tree
private void display(Node x) {
assert (x == null);
for (int i = 0; i < x.n; i++) {
System.out.print(x.key[i] + " ");
}
if (!x.leaf) {
for (int i = 0; i < x.n + 1; i++) {
display(x.child[i]);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BTree b = new BTree(3);
b.insert(8);
b.insert(9);
b.insert(10);
b.insert(11);
b.insert(15);
b.insert(20);
b.insert(17);
b.display();
}
}
Source code by C Language:
// insertioning a key on a B-tree in C
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAX 3
#define MIN 2
struct btreeNode {
int item[MAX + 1], count;
struct btreeNode *link[MAX + 1];
};
struct btreeNode *root;
// Node creation
struct btreeNode *createNode(int item, struct btreeNode *child) {
struct btreeNode *newNode;
newNode = (struct btreeNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct btreeNode));
newNode->item[1] = item;
newNode->count = 1;
newNode->link[0] = root;
newNode->link[1] = child;
return newNode;
}
// Insert
void insertValue(int item, int pos, struct btreeNode *node,
struct btreeNode *child) {
int j = node->count;
while (j > pos) {
node->item[j + 1] = node->item[j];
node->link[j + 1] = node->link[j];
j--;
}
node->item[j + 1] = item;
node->link[j + 1] = child;
node->count++;
}
// Split node
void splitNode(int item, int *pval, int pos, struct btreeNode *node,
struct btreeNode *child, struct btreeNode **newNode) {
int median, j;
if (pos > MIN)
median = MIN + 1;
else
median = MIN;
*newNode = (struct btreeNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct btreeNode));
j = median + 1;
while (j <= MAX) {
(*newNode)->item[j - median] = node->item[j];
(*newNode)->link[j - median] = node->link[j];
j++;
}
node->count = median;
(*newNode)->count = MAX - median;
if (pos <= MIN) {
insertValue(item, pos, node, child);
} else {
insertValue(item, pos - median, *newNode, child);
}
*pval = node->item[node->count];
(*newNode)->link[0] = node->link[node->count];
node->count--;
}
// Set the value of node
int setNodeValue(int item, int *pval,
struct btreeNode *node, struct btreeNode **child) {
int pos;
if (!node) {
*pval = item;
*child = NULL;
return 1;
}
if (item < node->item[1]) {
pos = 0;
} else {
for (pos = node->count;
(item < node->item[pos] && pos > 1); pos--)
;
if (item == node->item[pos]) {
printf("Duplicates not allowed\n");
return 0;
}
}
if (setNodeValue(item, pval, node->link[pos], child)) {
if (node->count < MAX) {
insertValue(*pval, pos, node, *child);
} else {
splitNode(*pval, pval, pos, node, *child, child);
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
// Insert the value
void insertion(int item) {
int flag, i;
struct btreeNode *child;
flag = setNodeValue(item, &i, root, &child);
if (flag)
root = createNode(i, child);
}
// Copy the successor
void copySuccessor(struct btreeNode *myNode, int pos) {
struct btreeNode *dummy;
dummy = myNode->link[pos];
for (; dummy->link[0] != NULL;)
dummy = dummy->link[0];
myNode->item[pos] = dummy->item[1];
}
// Do rightshift
void rightShift(struct btreeNode *myNode, int pos) {
struct btreeNode *x = myNode->link[pos];
int j = x->count;
while (j > 0) {
x->item[j + 1] = x->item[j];
x->link[j + 1] = x->link[j];
}
x->item[1] = myNode->item[pos];
x->link[1] = x->link[0];
x->count++;
x = myNode->link[pos - 1];
myNode->item[pos] = x->item[x->count];
myNode->link[pos] = x->link[x->count];
x->count--;
return;
}
// Do leftshift
void leftShift(struct btreeNode *myNode, int pos) {
int j = 1;
struct btreeNode *x = myNode->link[pos - 1];
x->count++;
x->item[x->count] = myNode->item[pos];
x->link[x->count] = myNode->link[pos]->link[0];
x = myNode->link[pos];
myNode->item[pos] = x->item[1];
x->link[0] = x->link[1];
x->count--;
while (j <= x->count) {
x->item[j] = x->item[j + 1];
x->link[j] = x->link[j + 1];
j++;
}
return;
}
// Merge the nodes
void mergeNodes(struct btreeNode *myNode, int pos) {
int j = 1;
struct btreeNode *x1 = myNode->link[pos], *x2 = myNode->link[pos - 1];
x2->count++;
x2->item[x2->count] = myNode->item[pos];
x2->link[x2->count] = myNode->link[0];
while (j <= x1->count) {
x2->count++;
x2->item[x2->count] = x1->item[j];
x2->link[x2->count] = x1->link[j];
j++;
}
j = pos;
while (j < myNode->count) {
myNode->item[j] = myNode->item[j + 1];
myNode->link[j] = myNode->link[j + 1];
j++;
}
myNode->count--;
free(x1);
}
// Adjust the node
void adjustNode(struct btreeNode *myNode, int pos) {
if (!pos) {
if (myNode->link[1]->count > MIN) {
leftShift(myNode, 1);
} else {
mergeNodes(myNode, 1);
}
} else {
if (myNode->count != pos) {
if (myNode->link[pos - 1]->count > MIN) {
rightShift(myNode, pos);
} else {
if (myNode->link[pos + 1]->count > MIN) {
leftShift(myNode, pos + 1);
} else {
mergeNodes(myNode, pos);
}
}
} else {
if (myNode->link[pos - 1]->count > MIN)
rightShift(myNode, pos);
else
mergeNodes(myNode, pos);
}
}
}
// Traverse the tree
void traversal(struct btreeNode *myNode) {
int i;
if (myNode) {
for (i = 0; i < myNode->count; i++) {
traversal(myNode->link[i]);
printf("%d ", myNode->item[i + 1]);
}
traversal(myNode->link[i]);
}
}
int main() {
int item, ch;
insertion(8);
insertion(9);
insertion(10);
insertion(11);
insertion(15);
insertion(16);
insertion(17);
insertion(18);
insertion(20);
insertion(23);
traversal(root);
}
Source code by C++ Language:
// Inserting a key on a B-tree in C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node {
int *keys;
int t;
Node **C;
int n;
bool leaf;
public:
Node(int _t, bool _leaf);
void insertNonFull(int k);
void splitChild(int i, Node *y);
void traverse();
friend class BTree;
};
class BTree {
Node *root;
int t;
public:
BTree(int _t) {
root = NULL;
t = _t;
}
void traverse() {
if (root != NULL)
root->traverse();
}
void insert(int k);
};
Node::Node(int t1, bool leaf1) {
t = t1;
leaf = leaf1;
keys = new int[2 * t - 1];
C = new Node *[2 * t];
n = 0;
}
// Traverse the nodes
void Node::traverse() {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (leaf == false)
C[i]->traverse();
cout << " " << keys[i];
}
if (leaf == false)
C[i]->traverse();
}
// Insert the node
void BTree::insert(int k) {
if (root == NULL) {
root = new Node(t, true);
root->keys[0] = k;
root->n = 1;
} else {
if (root->n == 2 * t - 1) {
Node *s = new Node(t, false);
s->C[0] = root;
s->splitChild(0, root);
int i = 0;
if (s->keys[0] < k)
i++;
s->C[i]->insertNonFull(k);
root = s;
} else
root->insertNonFull(k);
}
}
// Insert non full condition
void Node::insertNonFull(int k) {
int i = n - 1;
if (leaf == true) {
while (i >= 0 && keys[i] > k) {
keys[i + 1] = keys[i];
i--;
}
keys[i + 1] = k;
n = n + 1;
} else {
while (i >= 0 && keys[i] > k)
i--;
if (C[i + 1]->n == 2 * t - 1) {
splitChild(i + 1, C[i + 1]);
if (keys[i + 1] < k)
i++;
}
C[i + 1]->insertNonFull(k);
}
}
// split the child
void Node::splitChild(int i, Node *y) {
Node *z = new Node(y->t, y->leaf);
z->n = t - 1;
for (int j = 0; j < t - 1; j++)
z->keys[j] = y->keys[j + t];
if (y->leaf == false) {
for (int j = 0; j < t; j++)
z->C[j] = y->C[j + t];
}
y->n = t - 1;
for (int j = n; j >= i + 1; j--)
C[j + 1] = C[j];
C[i + 1] = z;
for (int j = n - 1; j >= i; j--)
keys[j + 1] = keys[j];
keys[i] = y->keys[t - 1];
n = n + 1;
}
int main() {
BTree t(3);
t.insert(8);
t.insert(9);
t.insert(10);
t.insert(11);
t.insert(15);
t.insert(16);
t.insert(17);
t.insert(18);
t.insert(20);
t.insert(23);
cout << "The B-tree is: ";
t.traverse();
}
Related posts:
Stack Data Structure
Kruskal's Algorithm
Spanning Tree and Minimum Spanning Tree
Longest Common Subsequence
Data Structure and Types
Linked List Operations: Traverse, Insert and Delete
Radix Sort Algorithm
Backtracking Algorithm
Heap Data Structure
Java Program to Perform Sorting Using B-Tree
Bubble Sort
Sorting Algorithm
Breadth first search
Selection Sort Algorithm
Types of Queues
B-tree
Perfect Binary Tree
Priority Queue
Complete Binary Tree
Tree Traversal - inorder, preorder and postorder
Balanced Binary Tree
Fibonacci Heap
Strongly Connected Components
Types of Linked List - Singly linked, doubly linked and circular
Queue Data Structure
Dijkstra's Algorithm
Insertion in a Red-Black Tree
Quicksort Algorithm
Why Learn Data Structures and Algorithms?
Deletion From a Red-Black Tree
Tree Data Structure
B+ Tree

