Table of Contents
- 1. Overview
- 2. Operations on a Red-Black Tree
- 2.1. Rotating the subtrees in a Red-Black Tree
- 2.2. Left Rotate
- 2.3. Right Rotate
- 2.4. Left-Right and Right-Left Rotate
- 2.5. Inserting an element into a Red-Black Tree
- 2.6. Algorithm to insert a node
- 2.7. Algorithm to maintain red-black property after insertion
- 2.8. Deleting an element from a Red-Black Tree
- 2.9. Algorithm to delete a node
- 2.9. Algorithm to maintain Red-Black property after deletion
- 3. Python, Java and C/C++ Examples
- 4. Red-Black Tree Applications
1. Overview
In this tutorial, you will learn what a red-black tree is. Also, you will find working examples of various operations performed on a red-black tree in C, C++, Java and Python.
Red-Black tree is a self-balancing binary search tree in which each node contains an extra bit for denoting the color of the node, either red or black.
A red-black tree satisfies the following properties:
- Red/Black Property: Every node is colored, either red or black.
- Root Property: The root is black.
- Leaf Property: Every leaf (NIL) is black.
- Red Property: If a red node has children then, the children are always black.
- Depth Property: For each node, any simple path from this node to any of its descendant leaf has the same black-depth (the number of black nodes).
An example of a red-black tree is:
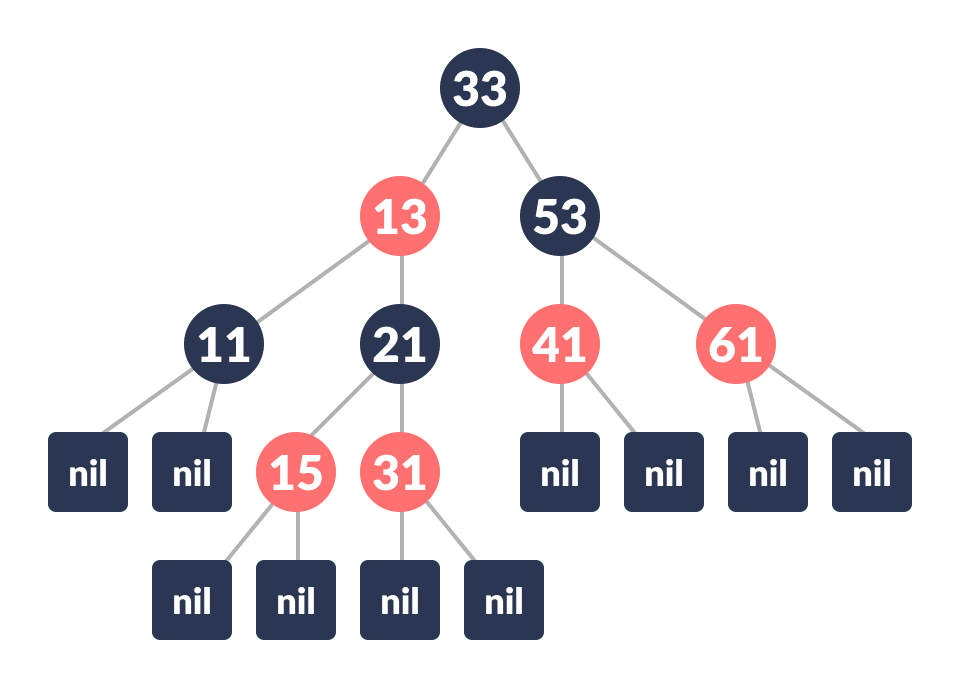
Each node has the following attributes:
- color
- key
- leftChild
- rightChild
- parent (except root node)
How the red-black tree maintains the property of self-balancing?
The red-black color is meant for balancing the tree.
The limitations put on the node colors ensure that any simple path from the root to a leaf is not more than twice as long as any other such path. It helps in maintaining the self-balancing property of the red-black tree.
2. Operations on a Red-Black Tree
Various operations that can be performed on a red-black tree are:
2.1. Rotating the subtrees in a Red-Black Tree
In rotation operation, the positions of the nodes of a subtree are interchanged.
Rotation operation is used for maintaining the properties of a red-black tree when they are violated by other operations such as insertion and deletion.
There are two types of rotations:
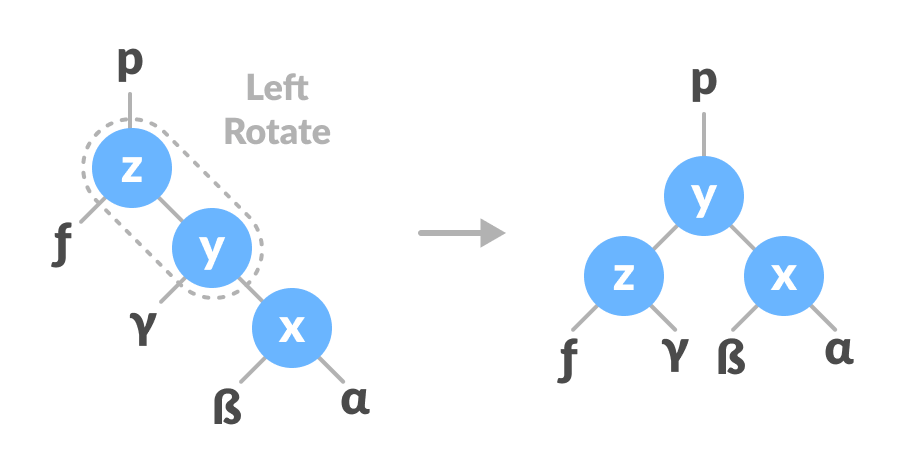
2.2. Left Rotate
In left-rotation, the arrangement of the nodes on the right is transformed into the arrangements on the left node.
Algorithm
Let the initial tree be:
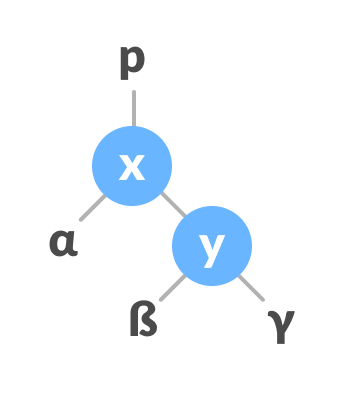
Initial tree
If y has a left subtree, assign x as the parent of the left subtree of y.
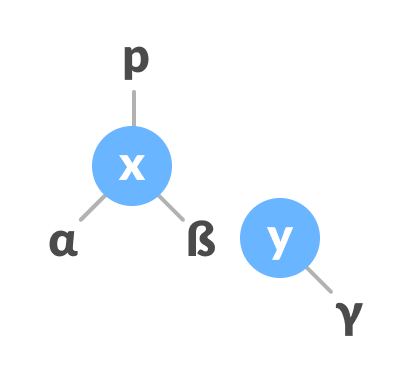
Assign x as the parent of the left subtree of y
If the parent of x is NULL, make y as the root of the tree.
Else if x is the left child of p, make y as the left child of p.
Else assign y as the right child of p.
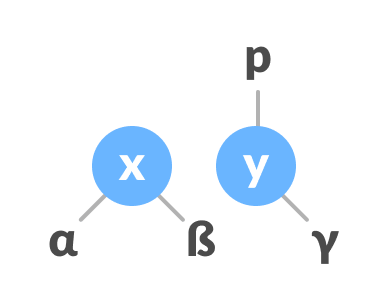
Change the parent of x to that of y
Make y as the parent of x.
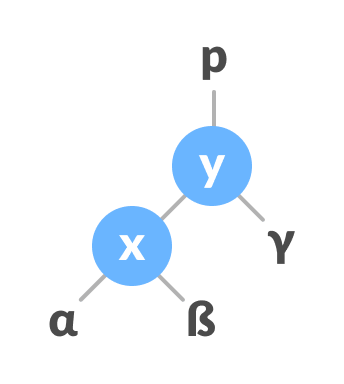
Assign y as the parent of x.
2.3. Right Rotate
In right-rotation, the arrangement of the nodes on the left is transformed into the arrangements on the right node.
Let the initial tree be:
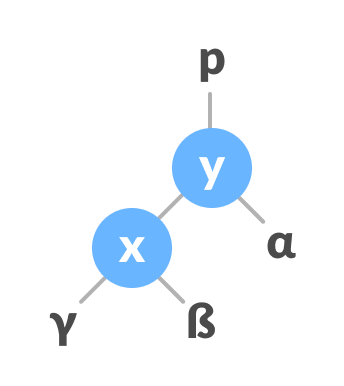
Initial Tree
If x has a right subtree, assign y as the parent of the right subtree of x.
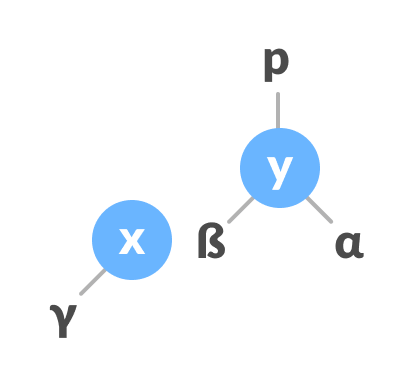
Assign y as the parent of the right subtree of x
If the parent of y is NULL, make x as the root of the tree.
Else if y is the right child of its parent p, make x as the right child of p.
Else assign x as the left child of p.
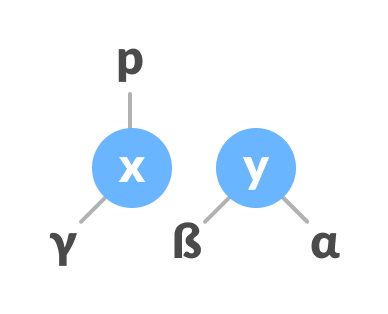
Assign the parent of y as the parent of x
Make x as the parent of y.
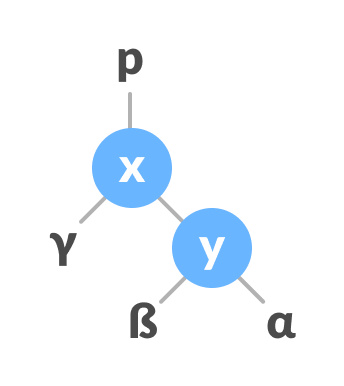
Assign x as the parent of y
2.4. Left-Right and Right-Left Rotate
In left-right rotation, the arrangements are first shifted to the left and then to the right.
Do left rotation on x-y.
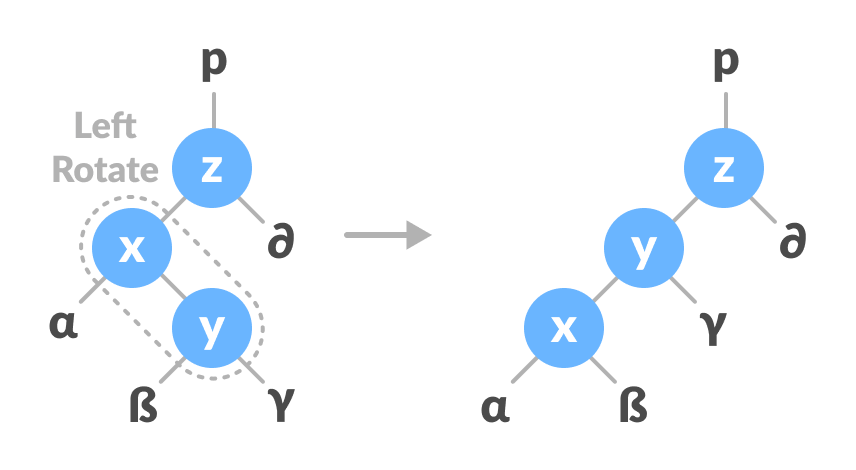
Left rotate x-y
Do right rotation on y-z.
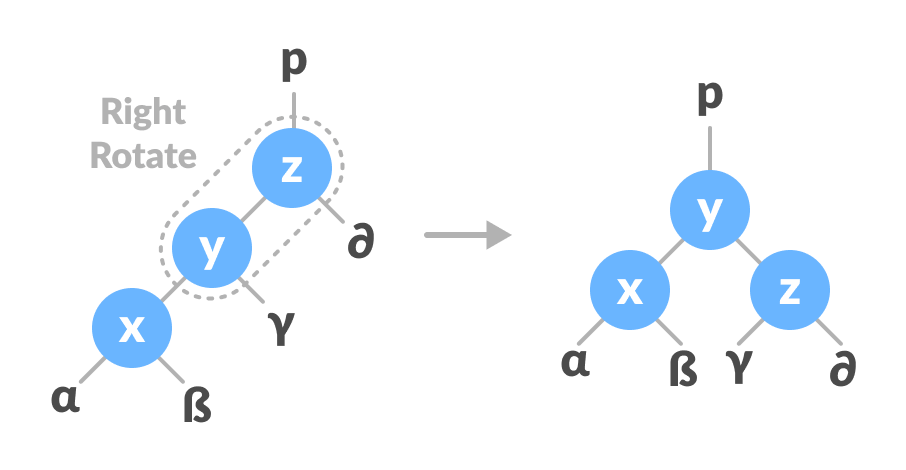
Right rotate z-y
In right-left rotation, the arrangements are first shifted to the right and then to the left.
Do right rotation on x-y.
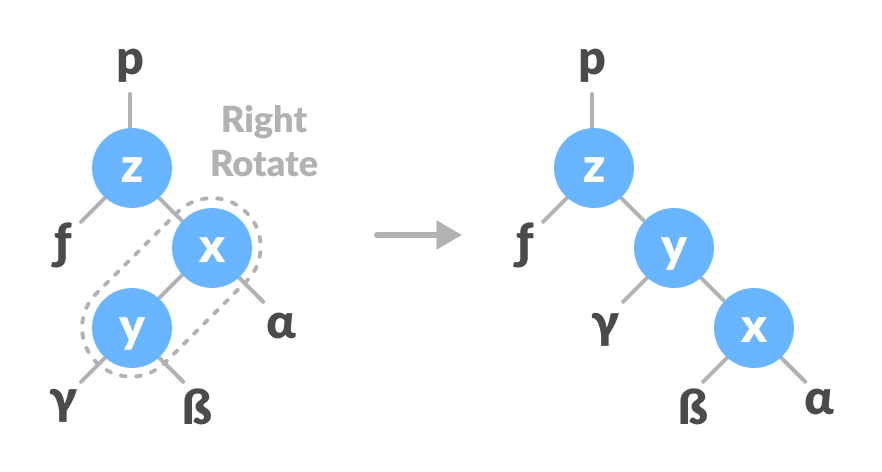
Right rotate x-y
Do left rotation on z-y.
Left rotate z-y
2.5. Inserting an element into a Red-Black Tree
While inserting a new node, the new node is always inserted as a RED node. After insertion of a new node, if the tree is violating the properties of the red-black tree then, we do the following operations.
- Recolor
- Rotation
2.6. Algorithm to insert a node
Following steps are followed for inserting a new element into a red-black tree:
- Let y be the leaf (ie.
NIL) and x be the root of the tree. - Check if the tree is empty (ie. whether x is
NIL). If yes, insert newNode as a root node and color it black. - Else, repeat steps following steps until leaf (
NIL) is reached.- Compare newKey with rootKey.
- If newKey is greater than rootKey, traverse through the right subtree.
- Else traverse through the left subtree.
- Assign the parent of the leaf as a parent of newNode.
- If leafKey is greater than newKey, make newNode as rightChild.
- Else, make newNode as leftChild.
- Assign
NULLto the left and rightChild of newNode. - Assign RED color to newNode.
- Call InsertFix-algorithm to maintain the property of red-black tree if violated.
Why newly inserted nodes are always red in a red-black tree?
This is because inserting a red node does not violate the depth property of a red-black tree.
If you attach a red node to a red node, then the rule is violated but it is easier to fix this problem than the problem introduced by violating the depth property.
2.7. Algorithm to maintain red-black property after insertion
This algorithm is used for maintaining the property of a red-black tree if the insertion of a newNode violates this property.
- Do the following while the parent of newNode p is RED.
- If p is the left child of grandParent gP of z, do the following.
Case-I:- If the color of the right child of gP of z is RED, set the color of both the children of gP as BLACK and the color of gP as RED.
- Assign gP to newNode.
Case-II: - Else if newNode is the right child of p then, assign p to newNode.
- Left-Rotate newNode.
Case-III: - Set color of p as BLACK and color of gP as RED.
- Right-Rotate gP.
- Else, do the following.
- If the color of the left child of gP of z is RED, set the color of both the children of gP as BLACK and the color of gP as RED.
- Assign gP to newNode.
- Else if newNode is the left child of p then, assign p to newNode and Right-Rotate newNode.
- Set color of p as BLACK and color of gP as RED.
- Left-Rotate gP.
- Set the root of the tree as BLACK.
2.8. Deleting an element from a Red-Black Tree
This operation removes a node from the tree. After deleting a node, the red-black property is maintained again.
2.9. Algorithm to delete a node
- Save the color of nodeToBeDeleted in origrinalColor.
- If the left child of nodeToBeDeleted is
NULL- Assign the right child of nodeToBeDeleted to x.
- Transplant nodeToBeDeleted with x.
- Else if the right child of nodeToBeDeleted is
NULL- Assign the left child of nodeToBeDeleted into x.
- Transplant nodeToBeDeleted with x.
- Else
- Assign the minimum of right subtree of noteToBeDeleted into y.
- Save the color of y in originalColor.
- Assign the rightChild of y into x.
- If y is a child of nodeToBeDeleted, then set the parent of x as y.
- Else, transplant y with rightChild of y.
- Transplant nodeToBeDeleted with y.
- Set the color of y with originalColor.
- If the originalColor is BLACK, call DeleteFix(x).
2.9. Algorithm to maintain Red-Black property after deletion
This algorithm is implemented when a black node is deleted because it violates the black depth property of the red-black tree.
This violation is corrected by assuming that node x (which is occupying y‘s original position) has an extra black. This makes node x neither red nor black. It is either doubly black or black-and-red. This violates the red-black properties.
However, the color attribute of x is not changed rather the extra black is represented in x‘s pointing to the node.
The extra black can be removed if
- It reaches the root node.
- If x points to a red-black node. In this case, x is colored black.
- Suitable rotations and recoloring are performed.
The following algorithm retains the properties of a red-black tree.
- Do the following until the x is not the root of the tree and the color of x is BLACK
- If x is the left child of its parent then,
- Assign w to the sibling of x.
- If the right child of parent of x is RED,
Case-I:- Set the color of the right child of the parent of x as BLACK.
- Set the color of the parent of x as RED.
- Left-Rotate the parent of x.
- Assign the rightChild of the parent of x to w.
- If the color of both the right and the leftChild of w is BLACK,
Case-II:- Set the color of w as RED
- Assign the parent of x to x.
- Else if the color of the rightChild of w is BLACK
Case-III:- Set the color of the leftChild of w as BLACK
- Set the color of w as RED
- Right-Rotate w.
- Assign the rightChild of the parent of x to w.
- If any of the above cases do not occur, then do the following.
Case-IV:- Set the color of w as the color of the parent of x.
- Set the color of the parent of x as BLACK.
- Set the color of the right child of w as BLACK.
- Left-Rotate the parent of x.
- Set x as the root of the tree.
- Else the same as above with right changed to left and vice versa.
- Set the color of x as BLACK.
Please refer to insertion and deletion operations for more explanation with examples.
3. Python, Java and C/C++ Examples
Source code by Python Language:
# Implementing Red-Black Tree in Python
import sys
# Node creation
class Node():
def __init__(self, item):
self.item = item
self.parent = None
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.color = 1
class RedBlackTree():
def __init__(self):
self.TNULL = Node(0)
self.TNULL.color = 0
self.TNULL.left = None
self.TNULL.right = None
self.root = self.TNULL
# Preorder
def pre_order_helper(self, node):
if node != TNULL:
sys.stdout.write(node.item + " ")
self.pre_order_helper(node.left)
self.pre_order_helper(node.right)
# Inorder
def in_order_helper(self, node):
if node != TNULL:
self.in_order_helper(node.left)
sys.stdout.write(node.item + " ")
self.in_order_helper(node.right)
# Postorder
def post_order_helper(self, node):
if node != TNULL:
self.post_order_helper(node.left)
self.post_order_helper(node.right)
sys.stdout.write(node.item + " ")
# Search the tree
def search_tree_helper(self, node, key):
if node == TNULL or key == node.item:
return node
if key < node.item:
return self.search_tree_helper(node.left, key)
return self.search_tree_helper(node.right, key)
# Balancing the tree after deletion
def delete_fix(self, x):
while x != self.root and x.color == 0:
if x == x.parent.left:
s = x.parent.right
if s.color == 1:
s.color = 0
x.parent.color = 1
self.left_rotate(x.parent)
s = x.parent.right
if s.left.color == 0 and s.right.color == 0:
s.color = 1
x = x.parent
else:
if s.right.color == 0:
s.left.color = 0
s.color = 1
self.right_rotate(s)
s = x.parent.right
s.color = x.parent.color
x.parent.color = 0
s.right.color = 0
self.left_rotate(x.parent)
x = self.root
else:
s = x.parent.left
if s.color == 1:
s.color = 0
x.parent.color = 1
self.right_rotate(x.parent)
s = x.parent.left
if s.right.color == 0 and s.right.color == 0:
s.color = 1
x = x.parent
else:
if s.left.color == 0:
s.right.color = 0
s.color = 1
self.left_rotate(s)
s = x.parent.left
s.color = x.parent.color
x.parent.color = 0
s.left.color = 0
self.right_rotate(x.parent)
x = self.root
x.color = 0
def __rb_transplant(self, u, v):
if u.parent == None:
self.root = v
elif u == u.parent.left:
u.parent.left = v
else:
u.parent.right = v
v.parent = u.parent
# Node deletion
def delete_node_helper(self, node, key):
z = self.TNULL
while node != self.TNULL:
if node.item == key:
z = node
if node.item <= key:
node = node.right
else:
node = node.left
if z == self.TNULL:
print("Cannot find key in the tree")
return
y = z
y_original_color = y.color
if z.left == self.TNULL:
x = z.right
self.__rb_transplant(z, z.right)
elif (z.right == self.TNULL):
x = z.left
self.__rb_transplant(z, z.left)
else:
y = self.minimum(z.right)
y_original_color = y.color
x = y.right
if y.parent == z:
x.parent = y
else:
self.__rb_transplant(y, y.right)
y.right = z.right
y.right.parent = y
self.__rb_transplant(z, y)
y.left = z.left
y.left.parent = y
y.color = z.color
if y_original_color == 0:
self.delete_fix(x)
# Balance the tree after insertion
def fix_insert(self, k):
while k.parent.color == 1:
if k.parent == k.parent.parent.right:
u = k.parent.parent.left
if u.color == 1:
u.color = 0
k.parent.color = 0
k.parent.parent.color = 1
k = k.parent.parent
else:
if k == k.parent.left:
k = k.parent
self.right_rotate(k)
k.parent.color = 0
k.parent.parent.color = 1
self.left_rotate(k.parent.parent)
else:
u = k.parent.parent.right
if u.color == 1:
u.color = 0
k.parent.color = 0
k.parent.parent.color = 1
k = k.parent.parent
else:
if k == k.parent.right:
k = k.parent
self.left_rotate(k)
k.parent.color = 0
k.parent.parent.color = 1
self.right_rotate(k.parent.parent)
if k == self.root:
break
self.root.color = 0
# Printing the tree
def __print_helper(self, node, indent, last):
if node != self.TNULL:
sys.stdout.write(indent)
if last:
sys.stdout.write("R----")
indent += " "
else:
sys.stdout.write("L----")
indent += "| "
s_color = "RED" if node.color == 1 else "BLACK"
print(str(node.item) + "(" + s_color + ")")
self.__print_helper(node.left, indent, False)
self.__print_helper(node.right, indent, True)
def preorder(self):
self.pre_order_helper(self.root)
def inorder(self):
self.in_order_helper(self.root)
def postorder(self):
self.post_order_helper(self.root)
def searchTree(self, k):
return self.search_tree_helper(self.root, k)
def minimum(self, node):
while node.left != self.TNULL:
node = node.left
return node
def maximum(self, node):
while node.right != self.TNULL:
node = node.right
return node
def successor(self, x):
if x.right != self.TNULL:
return self.minimum(x.right)
y = x.parent
while y != self.TNULL and x == y.right:
x = y
y = y.parent
return y
def predecessor(self, x):
if (x.left != self.TNULL):
return self.maximum(x.left)
y = x.parent
while y != self.TNULL and x == y.left:
x = y
y = y.parent
return y
def left_rotate(self, x):
y = x.right
x.right = y.left
if y.left != self.TNULL:
y.left.parent = x
y.parent = x.parent
if x.parent == None:
self.root = y
elif x == x.parent.left:
x.parent.left = y
else:
x.parent.right = y
y.left = x
x.parent = y
def right_rotate(self, x):
y = x.left
x.left = y.right
if y.right != self.TNULL:
y.right.parent = x
y.parent = x.parent
if x.parent == None:
self.root = y
elif x == x.parent.right:
x.parent.right = y
else:
x.parent.left = y
y.right = x
x.parent = y
def insert(self, key):
node = Node(key)
node.parent = None
node.item = key
node.left = self.TNULL
node.right = self.TNULL
node.color = 1
y = None
x = self.root
while x != self.TNULL:
y = x
if node.item < x.item:
x = x.left
else:
x = x.right
node.parent = y
if y == None:
self.root = node
elif node.item < y.item:
y.left = node
else:
y.right = node
if node.parent == None:
node.color = 0
return
if node.parent.parent == None:
return
self.fix_insert(node)
def get_root(self):
return self.root
def delete_node(self, item):
self.delete_node_helper(self.root, item)
def print_tree(self):
self.__print_helper(self.root, "", True)
if __name__ == "__main__":
bst = RedBlackTree()
bst.insert(55)
bst.insert(40)
bst.insert(65)
bst.insert(60)
bst.insert(75)
bst.insert(57)
bst.print_tree()
print("\nAfter deleting an element")
bst.delete_node(40)
bst.print_tree()
Source code by Java Language:
// Implementing Red-Black Tree in Java
class Node {
int data;
Node parent;
Node left;
Node right;
int color;
}
public class RedBlackTree {
private Node root;
private Node TNULL;
// Preorder
private void preOrderHelper(Node node) {
if (node != TNULL) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
preOrderHelper(node.left);
preOrderHelper(node.right);
}
}
// Inorder
private void inOrderHelper(Node node) {
if (node != TNULL) {
inOrderHelper(node.left);
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
inOrderHelper(node.right);
}
}
// Post order
private void postOrderHelper(Node node) {
if (node != TNULL) {
postOrderHelper(node.left);
postOrderHelper(node.right);
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
}
}
// Search the tree
private Node searchTreeHelper(Node node, int key) {
if (node == TNULL || key == node.data) {
return node;
}
if (key < node.data) {
return searchTreeHelper(node.left, key);
}
return searchTreeHelper(node.right, key);
}
// Balance the tree after deletion of a node
private void fixDelete(Node x) {
Node s;
while (x != root && x.color == 0) {
if (x == x.parent.left) {
s = x.parent.right;
if (s.color == 1) {
s.color = 0;
x.parent.color = 1;
leftRotate(x.parent);
s = x.parent.right;
}
if (s.left.color == 0 && s.right.color == 0) {
s.color = 1;
x = x.parent;
} else {
if (s.right.color == 0) {
s.left.color = 0;
s.color = 1;
rightRotate(s);
s = x.parent.right;
}
s.color = x.parent.color;
x.parent.color = 0;
s.right.color = 0;
leftRotate(x.parent);
x = root;
}
} else {
s = x.parent.left;
if (s.color == 1) {
s.color = 0;
x.parent.color = 1;
rightRotate(x.parent);
s = x.parent.left;
}
if (s.right.color == 0 && s.right.color == 0) {
s.color = 1;
x = x.parent;
} else {
if (s.left.color == 0) {
s.right.color = 0;
s.color = 1;
leftRotate(s);
s = x.parent.left;
}
s.color = x.parent.color;
x.parent.color = 0;
s.left.color = 0;
rightRotate(x.parent);
x = root;
}
}
}
x.color = 0;
}
private void rbTransplant(Node u, Node v) {
if (u.parent == null) {
root = v;
} else if (u == u.parent.left) {
u.parent.left = v;
} else {
u.parent.right = v;
}
v.parent = u.parent;
}
private void deleteNodeHelper(Node node, int key) {
Node z = TNULL;
Node x, y;
while (node != TNULL) {
if (node.data == key) {
z = node;
}
if (node.data <= key) {
node = node.right;
} else {
node = node.left;
}
}
if (z == TNULL) {
System.out.println("Couldn't find key in the tree");
return;
}
y = z;
int yOriginalColor = y.color;
if (z.left == TNULL) {
x = z.right;
rbTransplant(z, z.right);
} else if (z.right == TNULL) {
x = z.left;
rbTransplant(z, z.left);
} else {
y = minimum(z.right);
yOriginalColor = y.color;
x = y.right;
if (y.parent == z) {
x.parent = y;
} else {
rbTransplant(y, y.right);
y.right = z.right;
y.right.parent = y;
}
rbTransplant(z, y);
y.left = z.left;
y.left.parent = y;
y.color = z.color;
}
if (yOriginalColor == 0) {
fixDelete(x);
}
}
// Balance the node after insertion
private void fixInsert(Node k) {
Node u;
while (k.parent.color == 1) {
if (k.parent == k.parent.parent.right) {
u = k.parent.parent.left;
if (u.color == 1) {
u.color = 0;
k.parent.color = 0;
k.parent.parent.color = 1;
k = k.parent.parent;
} else {
if (k == k.parent.left) {
k = k.parent;
rightRotate(k);
}
k.parent.color = 0;
k.parent.parent.color = 1;
leftRotate(k.parent.parent);
}
} else {
u = k.parent.parent.right;
if (u.color == 1) {
u.color = 0;
k.parent.color = 0;
k.parent.parent.color = 1;
k = k.parent.parent;
} else {
if (k == k.parent.right) {
k = k.parent;
leftRotate(k);
}
k.parent.color = 0;
k.parent.parent.color = 1;
rightRotate(k.parent.parent);
}
}
if (k == root) {
break;
}
}
root.color = 0;
}
private void printHelper(Node root, String indent, boolean last) {
if (root != TNULL) {
System.out.print(indent);
if (last) {
System.out.print("R----");
indent += " ";
} else {
System.out.print("L----");
indent += "| ";
}
String sColor = root.color == 1 ? "RED" : "BLACK";
System.out.println(root.data + "(" + sColor + ")");
printHelper(root.left, indent, false);
printHelper(root.right, indent, true);
}
}
public RedBlackTree() {
TNULL = new Node();
TNULL.color = 0;
TNULL.left = null;
TNULL.right = null;
root = TNULL;
}
public void preorder() {
preOrderHelper(this.root);
}
public void inorder() {
inOrderHelper(this.root);
}
public void postorder() {
postOrderHelper(this.root);
}
public Node searchTree(int k) {
return searchTreeHelper(this.root, k);
}
public Node minimum(Node node) {
while (node.left != TNULL) {
node = node.left;
}
return node;
}
public Node maximum(Node node) {
while (node.right != TNULL) {
node = node.right;
}
return node;
}
public Node successor(Node x) {
if (x.right != TNULL) {
return minimum(x.right);
}
Node y = x.parent;
while (y != TNULL && x == y.right) {
x = y;
y = y.parent;
}
return y;
}
public Node predecessor(Node x) {
if (x.left != TNULL) {
return maximum(x.left);
}
Node y = x.parent;
while (y != TNULL && x == y.left) {
x = y;
y = y.parent;
}
return y;
}
public void leftRotate(Node x) {
Node y = x.right;
x.right = y.left;
if (y.left != TNULL) {
y.left.parent = x;
}
y.parent = x.parent;
if (x.parent == null) {
this.root = y;
} else if (x == x.parent.left) {
x.parent.left = y;
} else {
x.parent.right = y;
}
y.left = x;
x.parent = y;
}
public void rightRotate(Node x) {
Node y = x.left;
x.left = y.right;
if (y.right != TNULL) {
y.right.parent = x;
}
y.parent = x.parent;
if (x.parent == null) {
this.root = y;
} else if (x == x.parent.right) {
x.parent.right = y;
} else {
x.parent.left = y;
}
y.right = x;
x.parent = y;
}
public void insert(int key) {
Node node = new Node();
node.parent = null;
node.data = key;
node.left = TNULL;
node.right = TNULL;
node.color = 1;
Node y = null;
Node x = this.root;
while (x != TNULL) {
y = x;
if (node.data < x.data) {
x = x.left;
} else {
x = x.right;
}
}
node.parent = y;
if (y == null) {
root = node;
} else if (node.data < y.data) {
y.left = node;
} else {
y.right = node;
}
if (node.parent == null) {
node.color = 0;
return;
}
if (node.parent.parent == null) {
return;
}
fixInsert(node);
}
public Node getRoot() {
return this.root;
}
public void deleteNode(int data) {
deleteNodeHelper(this.root, data);
}
public void printTree() {
printHelper(this.root, "", true);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
RedBlackTree bst = new RedBlackTree();
bst.insert(55);
bst.insert(40);
bst.insert(65);
bst.insert(60);
bst.insert(75);
bst.insert(57);
bst.printTree();
System.out.println("\nAfter deleting:");
bst.deleteNode(40);
bst.printTree();
}
}
Source code by C Language:
// Implementing Red-Black Tree in C
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
enum nodeColor {
RED,
BLACK
};
struct rbNode {
int data, color;
struct rbNode *link[2];
};
struct rbNode *root = NULL;
// Create a red-black tree
struct rbNode *createNode(int data) {
struct rbNode *newnode;
newnode = (struct rbNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct rbNode));
newnode->data = data;
newnode->color = RED;
newnode->link[0] = newnode->link[1] = NULL;
return newnode;
}
// Insert an node
void insertion(int data) {
struct rbNode *stack[98], *ptr, *newnode, *xPtr, *yPtr;
int dir[98], ht = 0, index;
ptr = root;
if (!root) {
root = createNode(data);
return;
}
stack[ht] = root;
dir[ht++] = 0;
while (ptr != NULL) {
if (ptr->data == data) {
printf("Duplicates Not Allowed!!\n");
return;
}
index = (data - ptr->data) > 0 ? 1 : 0;
stack[ht] = ptr;
ptr = ptr->link[index];
dir[ht++] = index;
}
stack[ht - 1]->link[index] = newnode = createNode(data);
while ((ht >= 3) && (stack[ht - 1]->color == RED)) {
if (dir[ht - 2] == 0) {
yPtr = stack[ht - 2]->link[1];
if (yPtr != NULL && yPtr->color == RED) {
stack[ht - 2]->color = RED;
stack[ht - 1]->color = yPtr->color = BLACK;
ht = ht - 2;
} else {
if (dir[ht - 1] == 0) {
yPtr = stack[ht - 1];
} else {
xPtr = stack[ht - 1];
yPtr = xPtr->link[1];
xPtr->link[1] = yPtr->link[0];
yPtr->link[0] = xPtr;
stack[ht - 2]->link[0] = yPtr;
}
xPtr = stack[ht - 2];
xPtr->color = RED;
yPtr->color = BLACK;
xPtr->link[0] = yPtr->link[1];
yPtr->link[1] = xPtr;
if (xPtr == root) {
root = yPtr;
} else {
stack[ht - 3]->link[dir[ht - 3]] = yPtr;
}
break;
}
} else {
yPtr = stack[ht - 2]->link[0];
if ((yPtr != NULL) && (yPtr->color == RED)) {
stack[ht - 2]->color = RED;
stack[ht - 1]->color = yPtr->color = BLACK;
ht = ht - 2;
} else {
if (dir[ht - 1] == 1) {
yPtr = stack[ht - 1];
} else {
xPtr = stack[ht - 1];
yPtr = xPtr->link[0];
xPtr->link[0] = yPtr->link[1];
yPtr->link[1] = xPtr;
stack[ht - 2]->link[1] = yPtr;
}
xPtr = stack[ht - 2];
yPtr->color = BLACK;
xPtr->color = RED;
xPtr->link[1] = yPtr->link[0];
yPtr->link[0] = xPtr;
if (xPtr == root) {
root = yPtr;
} else {
stack[ht - 3]->link[dir[ht - 3]] = yPtr;
}
break;
}
}
}
root->color = BLACK;
}
// Delete a node
void deletion(int data) {
struct rbNode *stack[98], *ptr, *xPtr, *yPtr;
struct rbNode *pPtr, *qPtr, *rPtr;
int dir[98], ht = 0, diff, i;
enum nodeColor color;
if (!root) {
printf("Tree not available\n");
return;
}
ptr = root;
while (ptr != NULL) {
if ((data - ptr->data) == 0)
break;
diff = (data - ptr->data) > 0 ? 1 : 0;
stack[ht] = ptr;
dir[ht++] = diff;
ptr = ptr->link;
}
if (ptr->link[1] == NULL) {
if ((ptr == root) && (ptr->link[0] == NULL)) {
free(ptr);
root = NULL;
} else if (ptr == root) {
root = ptr->link[0];
free(ptr);
} else {
stack[ht - 1]->link[dir[ht - 1]] = ptr->link[0];
}
} else {
xPtr = ptr->link[1];
if (xPtr->link[0] == NULL) {
xPtr->link[0] = ptr->link[0];
color = xPtr->color;
xPtr->color = ptr->color;
ptr->color = color;
if (ptr == root) {
root = xPtr;
} else {
stack[ht - 1]->link[dir[ht - 1]] = xPtr;
}
dir[ht] = 1;
stack[ht++] = xPtr;
} else {
i = ht++;
while (1) {
dir[ht] = 0;
stack[ht++] = xPtr;
yPtr = xPtr->link[0];
if (!yPtr->link[0])
break;
xPtr = yPtr;
}
dir[i] = 1;
stack[i] = yPtr;
if (i > 0)
stack[i - 1]->link[dir[i - 1]] = yPtr;
yPtr->link[0] = ptr->link[0];
xPtr->link[0] = yPtr->link[1];
yPtr->link[1] = ptr->link[1];
if (ptr == root) {
root = yPtr;
}
color = yPtr->color;
yPtr->color = ptr->color;
ptr->color = color;
}
}
if (ht < 1)
return;
if (ptr->color == BLACK) {
while (1) {
pPtr = stack[ht - 1]->link[dir[ht - 1]];
if (pPtr && pPtr->color == RED) {
pPtr->color = BLACK;
break;
}
if (ht < 2)
break;
if (dir[ht - 2] == 0) {
rPtr = stack[ht - 1]->link[1];
if (!rPtr)
break;
if (rPtr->color == RED) {
stack[ht - 1]->color = RED;
rPtr->color = BLACK;
stack[ht - 1]->link[1] = rPtr->link[0];
rPtr->link[0] = stack[ht - 1];
if (stack[ht - 1] == root) {
root = rPtr;
} else {
stack[ht - 2]->link[dir[ht - 2]] = rPtr;
}
dir[ht] = 0;
stack[ht] = stack[ht - 1];
stack[ht - 1] = rPtr;
ht++;
rPtr = stack[ht - 1]->link[1];
}
if ((!rPtr->link[0] || rPtr->link[0]->color == BLACK) &&
(!rPtr->link[1] || rPtr->link[1]->color == BLACK)) {
rPtr->color = RED;
} else {
if (!rPtr->link[1] || rPtr->link[1]->color == BLACK) {
qPtr = rPtr->link[0];
rPtr->color = RED;
qPtr->color = BLACK;
rPtr->link[0] = qPtr->link[1];
qPtr->link[1] = rPtr;
rPtr = stack[ht - 1]->link[1] = qPtr;
}
rPtr->color = stack[ht - 1]->color;
stack[ht - 1]->color = BLACK;
rPtr->link[1]->color = BLACK;
stack[ht - 1]->link[1] = rPtr->link[0];
rPtr->link[0] = stack[ht - 1];
if (stack[ht - 1] == root) {
root = rPtr;
} else {
stack[ht - 2]->link[dir[ht - 2]] = rPtr;
}
break;
}
} else {
rPtr = stack[ht - 1]->link[0];
if (!rPtr)
break;
if (rPtr->color == RED) {
stack[ht - 1]->color = RED;
rPtr->color = BLACK;
stack[ht - 1]->link[0] = rPtr->link[1];
rPtr->link[1] = stack[ht - 1];
if (stack[ht - 1] == root) {
root = rPtr;
} else {
stack[ht - 2]->link[dir[ht - 2]] = rPtr;
}
dir[ht] = 1;
stack[ht] = stack[ht - 1];
stack[ht - 1] = rPtr;
ht++;
rPtr = stack[ht - 1]->link[0];
}
if ((!rPtr->link[0] || rPtr->link[0]->color == BLACK) &&
(!rPtr->link[1] || rPtr->link[1]->color == BLACK)) {
rPtr->color = RED;
} else {
if (!rPtr->link[0] || rPtr->link[0]->color == BLACK) {
qPtr = rPtr->link[1];
rPtr->color = RED;
qPtr->color = BLACK;
rPtr->link[1] = qPtr->link[0];
qPtr->link[0] = rPtr;
rPtr = stack[ht - 1]->link[0] = qPtr;
}
rPtr->color = stack[ht - 1]->color;
stack[ht - 1]->color = BLACK;
rPtr->link[0]->color = BLACK;
stack[ht - 1]->link[0] = rPtr->link[1];
rPtr->link[1] = stack[ht - 1];
if (stack[ht - 1] == root) {
root = rPtr;
} else {
stack[ht - 2]->link[dir[ht - 2]] = rPtr;
}
break;
}
}
ht--;
}
}
}
// Print the inorder traversal of the tree
void inorderTraversal(struct rbNode *node) {
if (node) {
inorderTraversal(node->link[0]);
printf("%d ", node->data);
inorderTraversal(node->link[1]);
}
return;
}
// Driver code
int main() {
int ch, data;
while (1) {
printf("1. Insertion\t2. Deletion\n");
printf("3. Traverse\t4. Exit");
printf("\nEnter your choice:");
scanf("%d", &ch);
switch (ch) {
case 1:
printf("Enter the element to insert:");
scanf("%d", &data);
insertion(data);
break;
case 2:
printf("Enter the element to delete:");
scanf("%d", &data);
deletion(data);
break;
case 3:
inorderTraversal(root);
printf("\n");
break;
case 4:
exit(0);
default:
printf("Not available\n");
break;
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
Source code by C++ Language:
// Implementing Red-Black Tree in C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
Node *parent;
Node *left;
Node *right;
int color;
};
typedef Node *NodePtr;
class RedBlackTree {
private:
NodePtr root;
NodePtr TNULL;
void initializeNULLNode(NodePtr node, NodePtr parent) {
node->data = 0;
node->parent = parent;
node->left = nullptr;
node->right = nullptr;
node->color = 0;
}
// Preorder
void preOrderHelper(NodePtr node) {
if (node != TNULL) {
cout << node->data << " ";
preOrderHelper(node->left);
preOrderHelper(node->right);
}
}
// Inorder
void inOrderHelper(NodePtr node) {
if (node != TNULL) {
inOrderHelper(node->left);
cout << node->data << " ";
inOrderHelper(node->right);
}
}
// Post order
void postOrderHelper(NodePtr node) {
if (node != TNULL) {
postOrderHelper(node->left);
postOrderHelper(node->right);
cout << node->data << " ";
}
}
NodePtr searchTreeHelper(NodePtr node, int key) {
if (node == TNULL || key == node->data) {
return node;
}
if (key < node->data) {
return searchTreeHelper(node->left, key);
}
return searchTreeHelper(node->right, key);
}
// For balancing the tree after deletion
void deleteFix(NodePtr x) {
NodePtr s;
while (x != root && x->color == 0) {
if (x == x->parent->left) {
s = x->parent->right;
if (s->color == 1) {
s->color = 0;
x->parent->color = 1;
leftRotate(x->parent);
s = x->parent->right;
}
if (s->left->color == 0 && s->right->color == 0) {
s->color = 1;
x = x->parent;
} else {
if (s->right->color == 0) {
s->left->color = 0;
s->color = 1;
rightRotate(s);
s = x->parent->right;
}
s->color = x->parent->color;
x->parent->color = 0;
s->right->color = 0;
leftRotate(x->parent);
x = root;
}
} else {
s = x->parent->left;
if (s->color == 1) {
s->color = 0;
x->parent->color = 1;
rightRotate(x->parent);
s = x->parent->left;
}
if (s->right->color == 0 && s->right->color == 0) {
s->color = 1;
x = x->parent;
} else {
if (s->left->color == 0) {
s->right->color = 0;
s->color = 1;
leftRotate(s);
s = x->parent->left;
}
s->color = x->parent->color;
x->parent->color = 0;
s->left->color = 0;
rightRotate(x->parent);
x = root;
}
}
}
x->color = 0;
}
void rbTransplant(NodePtr u, NodePtr v) {
if (u->parent == nullptr) {
root = v;
} else if (u == u->parent->left) {
u->parent->left = v;
} else {
u->parent->right = v;
}
v->parent = u->parent;
}
void deleteNodeHelper(NodePtr node, int key) {
NodePtr z = TNULL;
NodePtr x, y;
while (node != TNULL) {
if (node->data == key) {
z = node;
}
if (node->data <= key) {
node = node->right;
} else {
node = node->left;
}
}
if (z == TNULL) {
cout << "Key not found in the tree" << endl;
return;
}
y = z;
int y_original_color = y->color;
if (z->left == TNULL) {
x = z->right;
rbTransplant(z, z->right);
} else if (z->right == TNULL) {
x = z->left;
rbTransplant(z, z->left);
} else {
y = minimum(z->right);
y_original_color = y->color;
x = y->right;
if (y->parent == z) {
x->parent = y;
} else {
rbTransplant(y, y->right);
y->right = z->right;
y->right->parent = y;
}
rbTransplant(z, y);
y->left = z->left;
y->left->parent = y;
y->color = z->color;
}
delete z;
if (y_original_color == 0) {
deleteFix(x);
}
}
// For balancing the tree after insertion
void insertFix(NodePtr k) {
NodePtr u;
while (k->parent->color == 1) {
if (k->parent == k->parent->parent->right) {
u = k->parent->parent->left;
if (u->color == 1) {
u->color = 0;
k->parent->color = 0;
k->parent->parent->color = 1;
k = k->parent->parent;
} else {
if (k == k->parent->left) {
k = k->parent;
rightRotate(k);
}
k->parent->color = 0;
k->parent->parent->color = 1;
leftRotate(k->parent->parent);
}
} else {
u = k->parent->parent->right;
if (u->color == 1) {
u->color = 0;
k->parent->color = 0;
k->parent->parent->color = 1;
k = k->parent->parent;
} else {
if (k == k->parent->right) {
k = k->parent;
leftRotate(k);
}
k->parent->color = 0;
k->parent->parent->color = 1;
rightRotate(k->parent->parent);
}
}
if (k == root) {
break;
}
}
root->color = 0;
}
void printHelper(NodePtr root, string indent, bool last) {
if (root != TNULL) {
cout << indent;
if (last) {
cout << "R----";
indent += " ";
} else {
cout << "L----";
indent += "| ";
}
string sColor = root->color ? "RED" : "BLACK";
cout << root->data << "(" << sColor << ")" << endl;
printHelper(root->left, indent, false);
printHelper(root->right, indent, true);
}
}
public:
RedBlackTree() {
TNULL = new Node;
TNULL->color = 0;
TNULL->left = nullptr;
TNULL->right = nullptr;
root = TNULL;
}
void preorder() {
preOrderHelper(this->root);
}
void inorder() {
inOrderHelper(this->root);
}
void postorder() {
postOrderHelper(this->root);
}
NodePtr searchTree(int k) {
return searchTreeHelper(this->root, k);
}
NodePtr minimum(NodePtr node) {
while (node->left != TNULL) {
node = node->left;
}
return node;
}
NodePtr maximum(NodePtr node) {
while (node->right != TNULL) {
node = node->right;
}
return node;
}
NodePtr successor(NodePtr x) {
if (x->right != TNULL) {
return minimum(x->right);
}
NodePtr y = x->parent;
while (y != TNULL && x == y->right) {
x = y;
y = y->parent;
}
return y;
}
NodePtr predecessor(NodePtr x) {
if (x->left != TNULL) {
return maximum(x->left);
}
NodePtr y = x->parent;
while (y != TNULL && x == y->left) {
x = y;
y = y->parent;
}
return y;
}
void leftRotate(NodePtr x) {
NodePtr y = x->right;
x->right = y->left;
if (y->left != TNULL) {
y->left->parent = x;
}
y->parent = x->parent;
if (x->parent == nullptr) {
this->root = y;
} else if (x == x->parent->left) {
x->parent->left = y;
} else {
x->parent->right = y;
}
y->left = x;
x->parent = y;
}
void rightRotate(NodePtr x) {
NodePtr y = x->left;
x->left = y->right;
if (y->right != TNULL) {
y->right->parent = x;
}
y->parent = x->parent;
if (x->parent == nullptr) {
this->root = y;
} else if (x == x->parent->right) {
x->parent->right = y;
} else {
x->parent->left = y;
}
y->right = x;
x->parent = y;
}
// Inserting a node
void insert(int key) {
NodePtr node = new Node;
node->parent = nullptr;
node->data = key;
node->left = TNULL;
node->right = TNULL;
node->color = 1;
NodePtr y = nullptr;
NodePtr x = this->root;
while (x != TNULL) {
y = x;
if (node->data < x->data) {
x = x->left;
} else {
x = x->right;
}
}
node->parent = y;
if (y == nullptr) {
root = node;
} else if (node->data < y->data) {
y->left = node;
} else {
y->right = node;
}
if (node->parent == nullptr) {
node->color = 0;
return;
}
if (node->parent->parent == nullptr) {
return;
}
insertFix(node);
}
NodePtr getRoot() {
return this->root;
}
void deleteNode(int data) {
deleteNodeHelper(this->root, data);
}
void printTree() {
if (root) {
printHelper(this->root, "", true);
}
}
};
int main() {
RedBlackTree bst;
bst.insert(55);
bst.insert(40);
bst.insert(65);
bst.insert(60);
bst.insert(75);
bst.insert(57);
bst.printTree();
cout << endl
<< "After deleting" << endl;
bst.deleteNode(40);
bst.printTree();
}
4. Red-Black Tree Applications
- To implement finite maps
- To implement Java packages:
java.util.TreeMapandjava.util.TreeSet - To implement Standard Template Libraries (STL) in C++: multiset, map, multimap
- In Linux Kernel

