Table of Contents
- 1. How to Connect MongoDB to Node.js Using Mongoose
- 2. Prerequisites
- 3. Step 1 – Installing Mongoose on a Node.js environment
- 4. Step 2 – Creating the connection
- 5. Step 3 – Creating the schema
- 6. Step 4 – Creating the POST endpoint
- 7. Step 5 – Creating the GET endpoint
- 8. Step 6 – Testing the endpoints
- 9. Conclusion
Mongoose.js connects your MongoDB clusters or collections with your Node.js app. It enables you to create schemas for your documents. Mongoose provides a lot of functionality when creating and working with schemas.
In this tutorial we will look at how to connect a MongoDB instance with a Node.js application.
1. How to Connect MongoDB to Node.js Using Mongoose
MongoDB is one of the most widely used No-SQL databases in the developer world today. No-SQL databases allow developers to send and retrieve data as JSON documents, instead of SQL objects. To work with MongoDB in a Node.js app, we can use Mongoose.
2. Prerequisites
Before we move on, you’ll need to have the following:
- Node.js installed on your machine.
- A MongoDB instance running on your machine. You won’t need this if you want to use MongoDB Atlas.
- Some knowledge of Node.js and Express.js.
3. Step 1 – Installing Mongoose on a Node.js environment
Create and navigate to a new folder by running the following commands on a terminal.
$ mkdir mongoose_tutorial $ cd mongoose_tutorial
Then install Express and Mongoose by executing the following command on a terminal.
$ npm install express mongoose --save
If you are using Yarn, run:
$ yarn add express mongoose
4. Step 2 – Creating the connection
Create a new file server.js to start our Express.js server. Load mongoose and express by adding the following code to server.js.
server.js
const express = require("express");
const mongoose = require("mongoose");
const Router = require("./routes")
const app = express();
app.use(express.json());
Then connect to a local MongoDB instance using the mongoose.connect() function.
server.js
mongoose.connect('mongodb://localhost:27017/usersdb',
{
useNewUrlParser: true,
useFindAndModify: false,
useUnifiedTopology: true
}
);
We pass the useNewUrlParser: true, etc. to mongoose.connect() to avoid the DeprecationWarning.
To create a connection to MongoDB Atlas, follow the next steps.
- Open your Cluster tab in MongoDb Atlas and click
CONNECT.
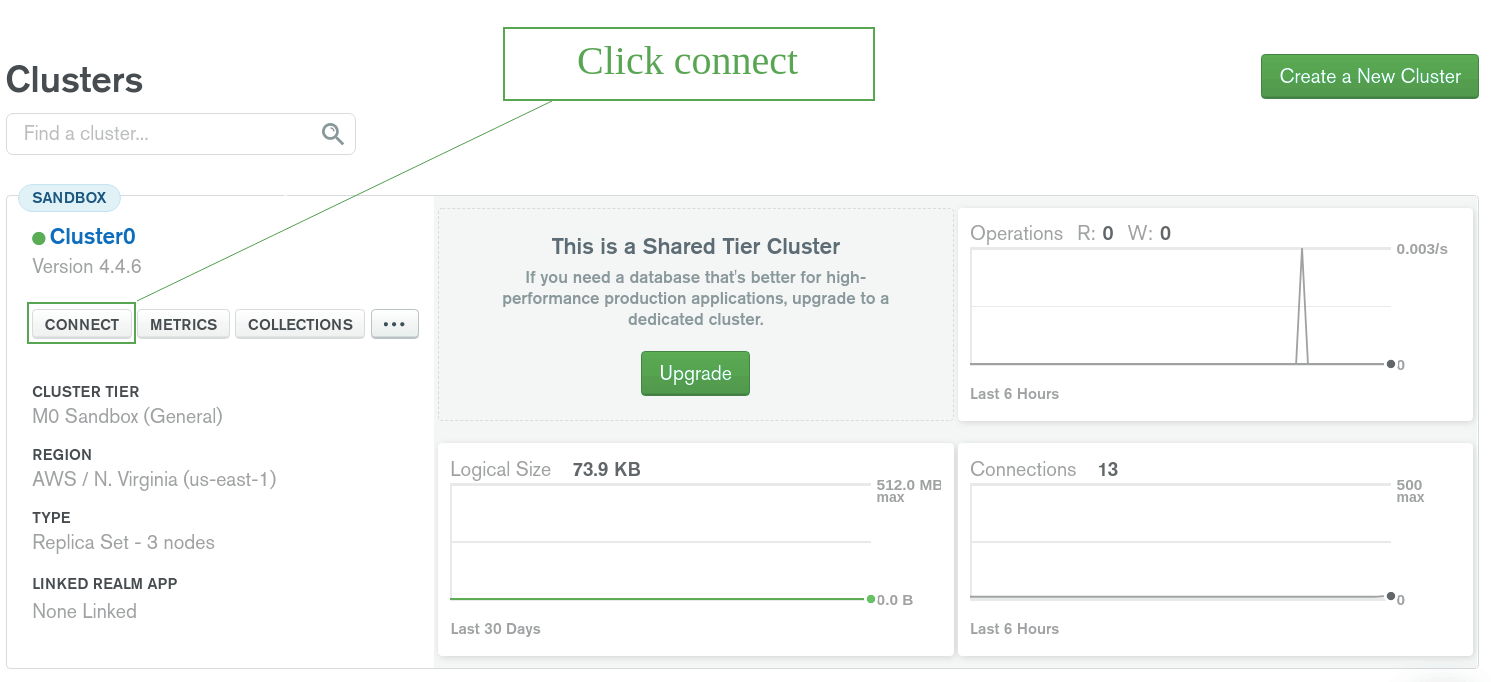
- Select
Connect your applicationand choose Node.js for the driver. - Copy the connection string.
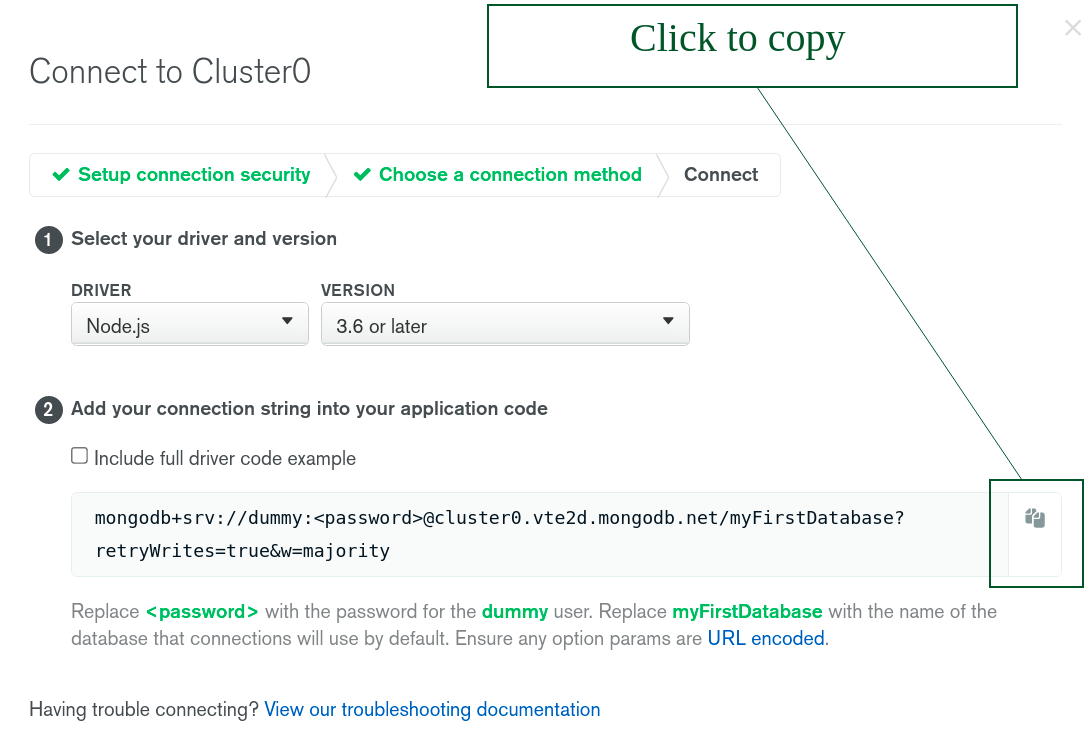
With the connection at hand, create the following variables and replace their values using your actual credentials.
server.js
const username = "<mongodb username>";
const password = "<password>";
const cluster = "<cluster name>";
const dbname = "myFirstDatabase";
mongoose.connect(
`mongodb+srv://${username}:${password}@${cluster}.mongodb.net/${dbname}?retryWrites=true&w=majority`,
{
useNewUrlParser: true,
useFindAndModify: false,
useUnifiedTopology: true
}
);
It’s important to note that the cluster variable is the values appearing between the
@and.mongodb.net. In my case the cluster variable iscluster0.vte2d.
To make sure your connection was successful, add the following code right below your mongoose.connect().
server.js
// ...
const db = mongoose.connection;
db.on("error", console.error.bind(console, "connection error: "));
db.once("open", function () {
console.log("Connected successfully");
});
Then, set the app to listen to port 3000.
server.js
// ...
app.use(Router);
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log("Server is running at port 3000");
});
We will create the Router later.
5. Step 3 – Creating the schema
Now let’s define a collection schema for our application.
Create another file models.js and add the following code.
models.js
const mongoose = require("mongoose");
const UserSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
name: {
type: String,
required: true,
},
age: {
type: Number,
default: 0,
},
});
const User = mongoose.model("User", UserSchema);
module.exports = User;
We create a schema UserSchema using the mongoose.Schema() method. The schema collects the name and age fields sent from the request.
We then export the schema using the last 2 lines.
6. Step 4 – Creating the POST endpoint
Create a new file routes.js. This file defines the endpoints for our app.
Load express and the schema we created in Step 3 by adding the following code.
routes.js
const express = require("express");
const userModel = require("./models");
const app = express();
Then create the POST endpoint by adding the following code.
routes.js
// ...
app.post("/add_user", async (request, response) => {
const user = new userModel(request.body);
try {
await user.save();
response.send(user);
} catch (error) {
response.status(500).send(error);
}
});
We create a route /add_user to add a new user to the database. We parse the content to be saved to the database using the line const user = new userModel(request.body);.
We then use a try/catch block to save the object to the database using the .save() method.
7. Step 5 – Creating the GET endpoint
Add the following lines of code to the routes.js file.
routes.js
// ...
app.get("/users", async (request, response) => {
const users = await userModel.find({});
try {
response.send(users);
} catch (error) {
response.status(500).send(error);
}
});
We create a route /users to retrieve all the users saved using the /add_user route. We collect these users from the database using the .find() method. We then use a try/catch block to ‘send’ the users to this endpoint.
Finally, export these endpoints by adding the line below.
routes.js
// ... module.exports = app;
At this point, your application is ready. Serve the app by running the command below.
$ node server.js
8. Step 6 – Testing the endpoints
Now, let’s test the two endpoints we created above.
Open Postman and make a POST request to the http://localhost:3000/add_user endpoint.
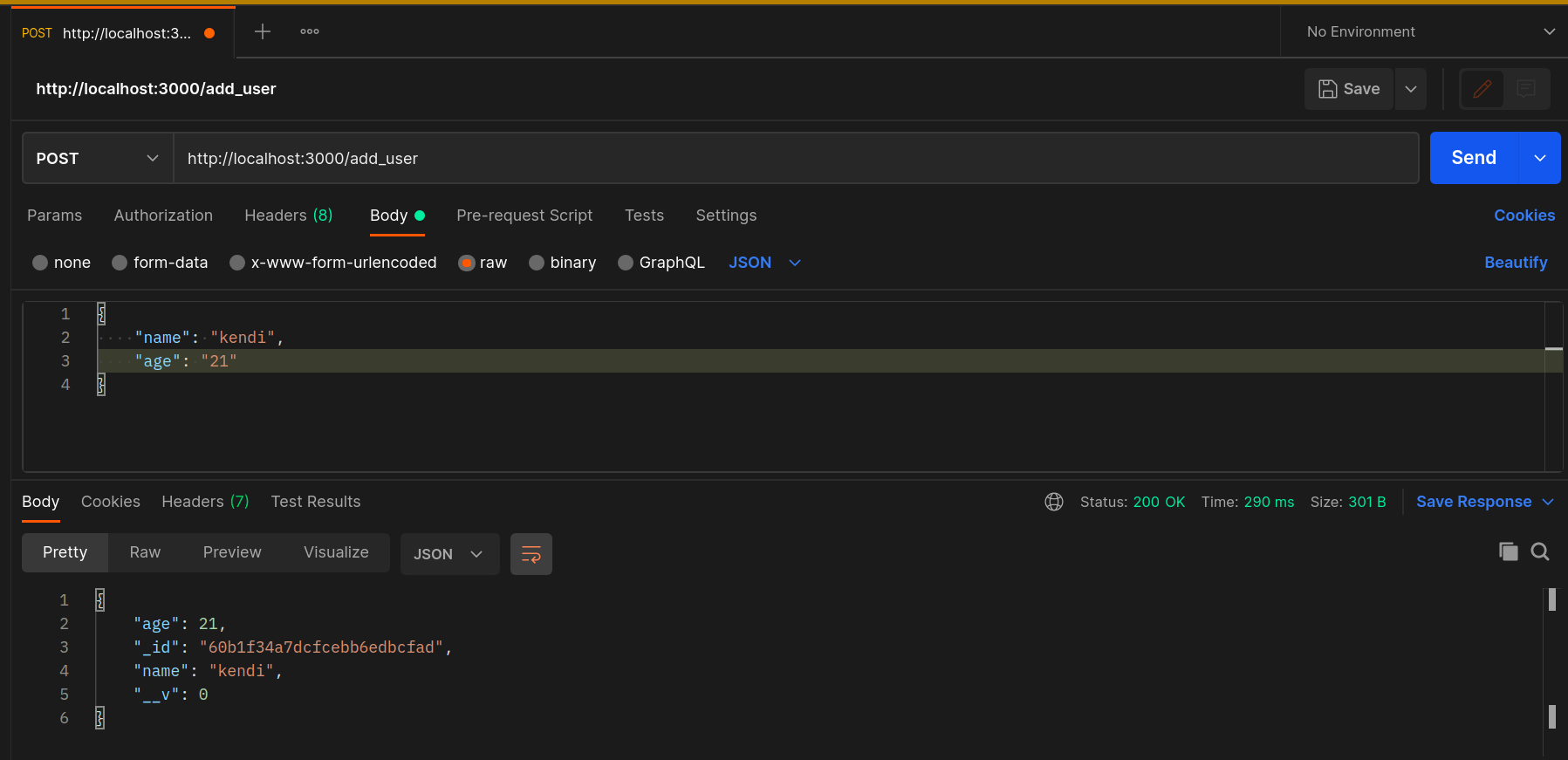
A new user is added to the database. You can check your collections to confirm this.
Make a GET request to the http://localhost:3000/users endpoint.
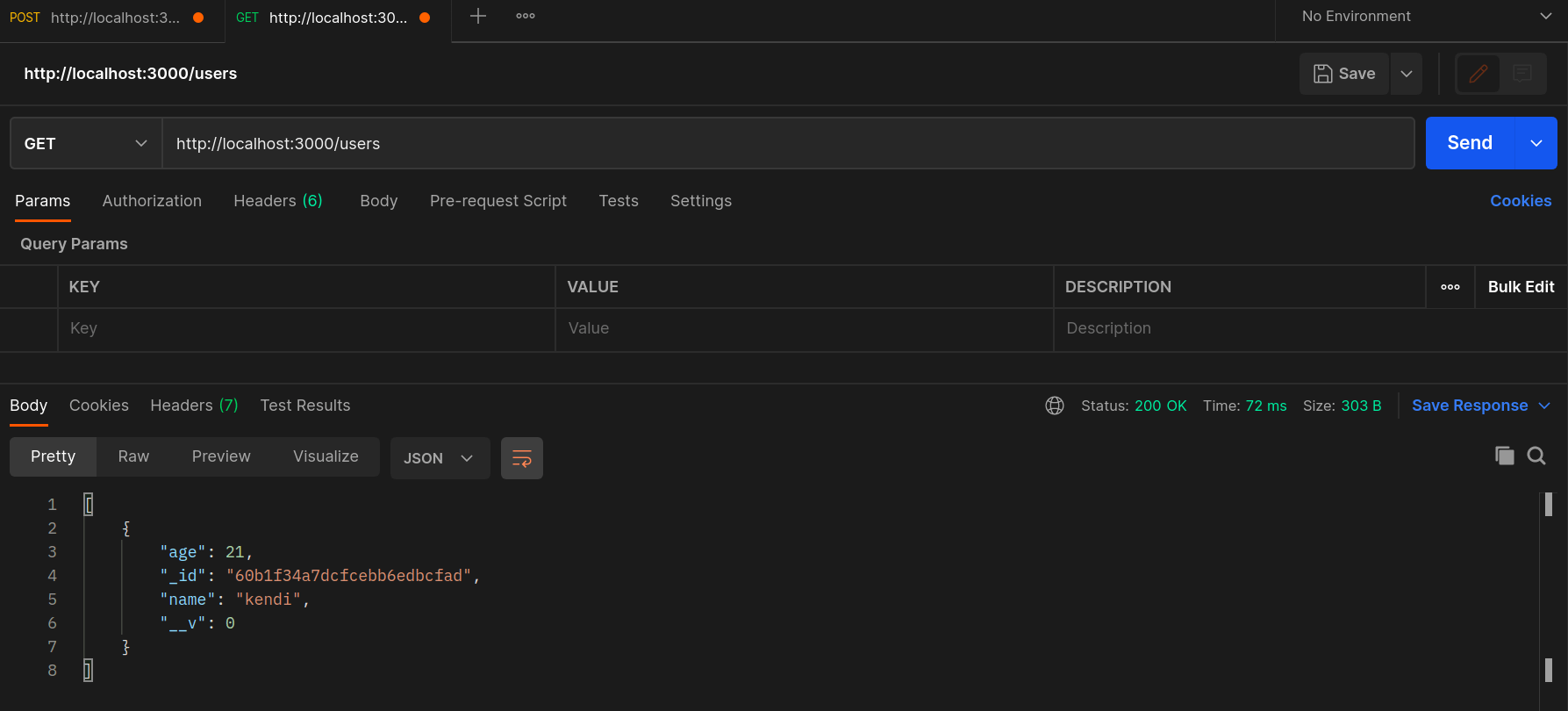
The endpoint returns a list of all the users added to the database.
9. Conclusion
In this tutorial, we have looked at how to set up Mongoose. We have also looked at how to establish a database connection and how to create a schema for our collections. Mongoose can be used to connect to both MongoDB and MongoDB Atlas to your Node.js app.
I hope you found this article helpful.
Happy coding!

