Table of Contents
Web applications have access to large amounts of data that belongs to people, organizations, and governments. The more the data is accessed, the higher the threat to data security. In the software development industry, developers use cryptography and encryption techniques to protect sensitive data from malicious parties.
Cryptography is used to secure data stored in a database or transferred over a software development industry network. When handling, moving, and storing data, you must do it safely and securely.
Thus as a node.js developer, you should understand how to encrypt and decrypt data to secure data processed by your system. Node.js has a built-in library called crypto for data encryption and decryption.
Encryption and decryption aim to enhance safety. This article will help you learn how to use the Node.js crypto module to encrypt and decrypt data in your applications. Also, it will summarize cryptography in node.js.
1. Prerequisites
A comprehensive understanding of cryptography and node.js is required before reading this article. Also, you should have:
- Node.js installed on your computer.
- A Text editor such as Visual Studio Code.
2. Cryptography in node.js
Cryptography is crucial for software development. Data must be protected. Cryptography is a study of techniques on how to keep the data secure. It converts the data into a secret by converting plaintext into unreadable text and vice versa. Hence only the sender and the receiver of that data can understand its content.
The three main components of a cryptosystem include plaintext, ciphertext, and algorithm. To make information a secret, we use a cipher and an algorithm that turns plaintext into ciphertext. Converting data into unreadable text is called encryption, and reversing it back to plaintext is decryption.
Cryptographic algorithms use a key to convert plaintext to ciphertext. Converting ciphertext back to plaintext is possible only if you have the right key with you.
You use symmetric encryption if you encrypt and decrypt data using the same key. Asymmetric encryption is used if different keys are used for encryption and decryption.
To protect data in Node.js applications, you have to store the hashed passwords in the database. This way, you cannot convert data into plaintext after it is hashed. It has to be verified.
If malicious attackers gain access to the database, they won’t read the data since it’s encrypted. Moreover, they do not have the key to help them do so.
3. Node.js crypto module
The Node.js crypto module provides cryptographic operations to help you secure your Node.js application. It supports hashes, HMAC for authentication, ciphers, deciphers, and more.
As stated earlier, crypto is a built-in library in Node.js. Thus it doesn’t require installation and configuration before using it in your Node.js applications. The crypto module handles an algorithm that performs encryption and decryption of data.
The crypto module authorizes you to hash plain texts before storing data in a database. Hashed data can not be decrypted with a specific key, like encrypted data. Instead, an HMAC is responsible for a Hash-based Message Authentication Code, which hashes keys and values to create a final hash.
You may want to encrypt and decrypt data for transmission purposes. This is where cipher and decipher functions come in. You encrypt data with a cipher and decrypt it with a decipher. Also, you may want to encrypt data before storing it in the database.
To verify encrypted or hashed passwords. It would be best to have a verify function. Let us explore data encryption and decryption and implement Node.js applications using crypto.
4. Getting started with a Node.js project
We’ll create a Node.js project to work with crypto. You’ll learn how to encrypt and decrypt data. To begin, execute this command:
npm init -y
By default, the crypto module is an in-built Node.js library. But if Node.js is installed manually, crypto may not be delivered with it. To install, execute the following command:
npm install crypto --save
You do not need to execute the command if crypto is installed using pre-built packages.
5. How to encrypt data in Node.js
To get started, create the app.js file and define our encryption functions as shown below.
First, you will import the crypto module:
const crypto = require ("crypto");
While encrypting data, it’s vital to use an algorithm. In this project, we use aes-256-cbc.
The crypto.randomBytes() method is used to generate cryptographically built random data generated in the written code.
The initVector (initialization vector) is used here to hold 16 bytes of random data from the randomBytes() method, and Securitykey contains 32 bytes of random data.
// crypto module
const crypto = require("crypto");
const algorithm = "aes-256-cbc";
// generate 16 bytes of random data
const initVector = crypto.randomBytes(16);
// protected data
const message = "This is a secret message";
// secret key generate 32 bytes of random data
const Securitykey = crypto.randomBytes(32);
To encrypt the data, the cipher function is used. Our project’s cipher function is made using createCipheriv(), the initialization vector from the crypto module.
Pass the first argument as the algorithm we are using, the second argument as the Securitykey, and initVector as the third argument.
To encrypt the message, use the update() method on the cipher. Pass the first argument as the message, the second argument as utf-8 (input encoding), and hex (output encoding) as the third argument.
// crypto module
const crypto = require("crypto");
const algorithm = "aes-256-cbc";
// generate 16 bytes of random data
const initVector = crypto.randomBytes(16);
// protected data
const message = "This is a secret message";
// secret key generate 32 bytes of random data
const Securitykey = crypto.randomBytes(32);
// the cipher function
const cipher = crypto.createCipheriv(algorithm, Securitykey, initVector);
// encrypt the message
// input encoding
// output encoding
let encryptedData = cipher.update(message, "utf-8", "hex");
The code tells cipher to stop the encryption using the final() method. When the final() method is called, the cipher can’t be used once more to encrypt data.
The message is then encrypted, and malicious attackers can’t understand the encoded data. Below is an example of how to encrypt data:
// crypto module
const crypto = require("crypto");
const algorithm = "aes-256-cbc";
// generate 16 bytes of random data
const initVector = crypto.randomBytes(16);
// protected data
const message = "This is a secret message";
// secret key generate 32 bytes of random data
const Securitykey = crypto.randomBytes(32);
// the cipher function
const cipher = crypto.createCipheriv(algorithm, Securitykey, initVector);
// encrypt the message
// input encoding
// output encoding
let encryptedData = cipher.update(message, "utf-8", "hex");
encryptedData += cipher.final("hex");
console.log("Encrypted message: " + encryptedData);
Here is the output:
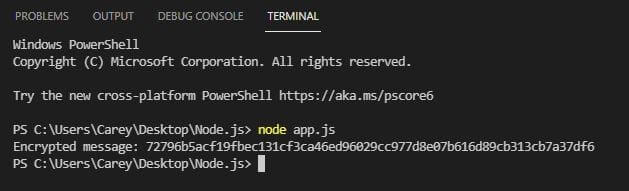
6. How to decrypt data in Node.js
Decrypting data follows a similar format to that of encrypting data. In our Node.js project, we will use the decipher function to decrypt data. Thus, our project encrypts and decrypts data.
Below is an example of how to decrypt data:
// the decipher function
const decipher = crypto.createDecipheriv(algorithm, Securitykey, initVector);
let decryptedData = decipher.update(encryptedData, "hex", "utf-8");
decryptedData += decipher.final("utf8");
console.log("Decrypted message: " + decryptedData);
Follow the below example to encrypt and decrypt data using crypto:
// crypto module
const crypto = require("crypto");
const algorithm = "aes-256-cbc";
// generate 16 bytes of random data
const initVector = crypto.randomBytes(16);
// protected data
const message = "This is a secret message";
// secret key generate 32 bytes of random data
const Securitykey = crypto.randomBytes(32);
// the cipher function
const cipher = crypto.createCipheriv(algorithm, Securitykey, initVector);
// encrypt the message
// input encoding
// output encoding
let encryptedData = cipher.update(message, "utf-8", "hex");
encryptedData += cipher.final("hex");
console.log("Encrypted message: " + encryptedData);
// the decipher function
const decipher = crypto.createDecipheriv(algorithm, Securitykey, initVector);
let decryptedData = decipher.update(encryptedData, "hex", "utf-8");
decryptedData += decipher.final("utf8");
console.log("Decrypted message: " + decryptedData);
Here is the output:
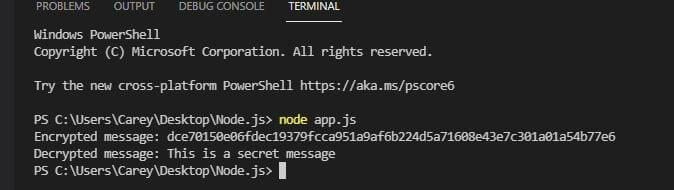
7. Wrapping up
This article looked at data encryption and decryption in Node.js using the crypto module. Also, it touched on:
- Cryptography in Node.js.
- Node.js crypto module.
I hope you’ve gained a solid knowledge about encryption and decryption and how to use the crypto module in Node.js applications to implement encryption and decryption.

