Let us start by getting a better understanding of what Node.js is. Node.js is a runtime environment used for executing server-side code with higher efficiency and it presents a larger bandwidth to handle large code payloads. The objective of this article is as follows:
- Understand and clarify any doubt of whether Node.js is frontend or backend application
- List out various applications in both frontend and backend
- Understand how Node.js complements other technologies in the frontend and backend
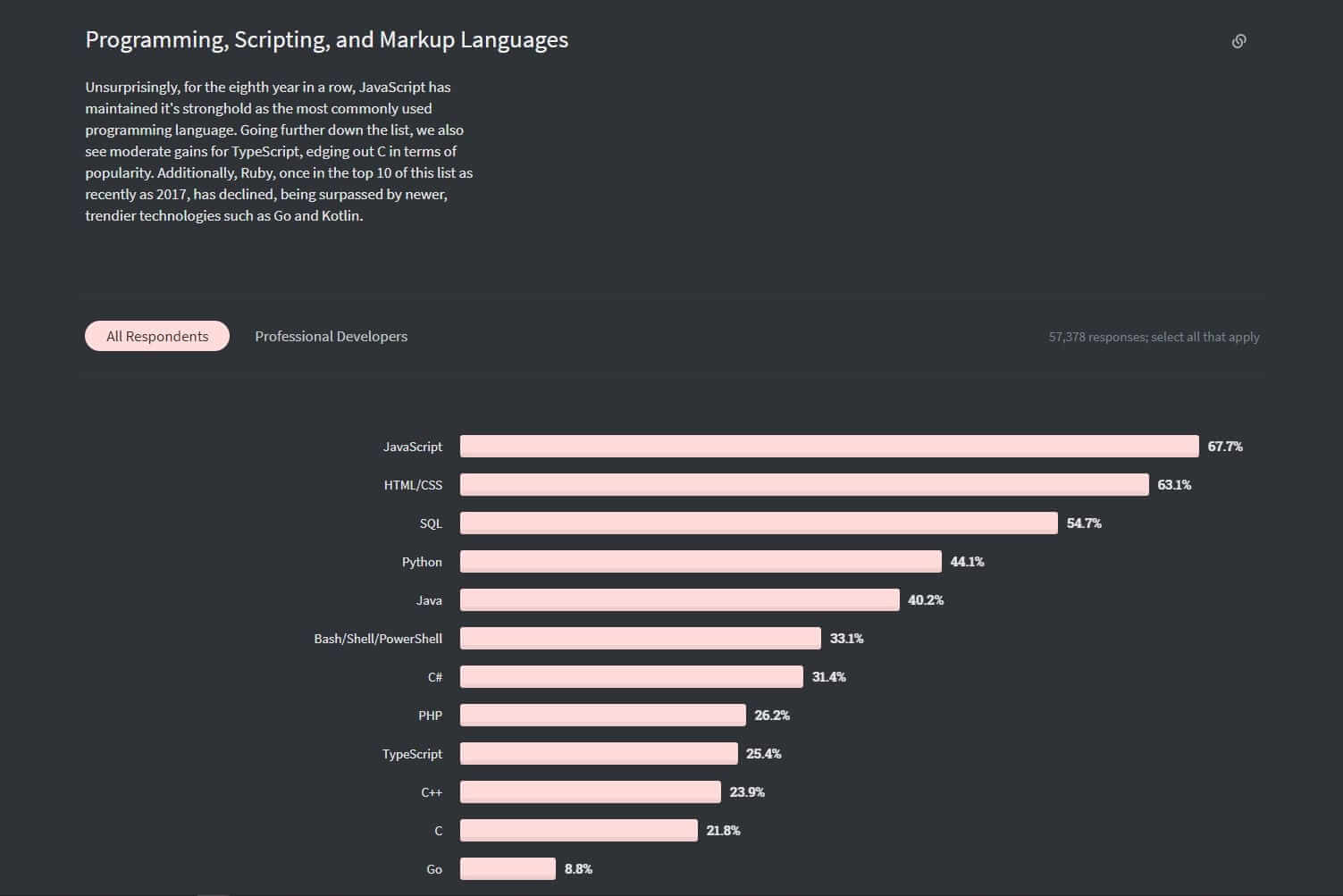
Ryan Dahl, the creator of Node.js, opted to use one of the most popular programming languages out there, JavaScript. Node.js increased the overall control developers had over applications. Developers can exercise a greater level of control over system calls, database calls, and network calls. Hence, we as developers can achieve better performing and feature-rich web applications. JavaScript is still one of the most preferred programming language across the world. As the StackOverflow survey results below can demonstrate. This feat achieved by JavaScript enables faster progress for all the libraries and frameworks associated with JS, including Node.js.
1. The Question: Frontend or Backend?
There is a massive number of libraries built for Node.js. The idea of using Node.js for frontend is a natural extension of the various features that it provides. Let us understand why the use of Node.js enhances the developer experience.
- JavaScript: The ability to use the same language for both frontend and backend makes it easier for developers.
- Availability of Packages and Libraries: There are many libraries available to use in the frontend. For example, the ‘moment’ is a library that processes dates in the specified format.
- The availability of the JS engine on the browser makes the integration of Node.js packages efficient.
Now that we have a better understanding whether frontend applications can be used with Node.js, we can answer with a huge YES. Yes, Node.js can be used in both the frontend and backend of applications. Let us now dive into a few of the applications that Node.js supports in the frontend and backend.
2. Frontend
- Code Processors: Code processors are required for displaying text in the browser. The HTML and CSS files that we receive are usually minimized in size by removing all the unnecessary characters for faster rendering and transmission. The pre-processors help the browser in rendering the files. Node.js enables us to code these processors in JS, thus allowing larger flexibility and customizability.
- Code Linters: A linter is a program that helps us identify and correct issues in our codebase. Issues related to syntax, certain custom standards specified by the development team, and programming errors can be identified using linters. Custom linters enhance the overall efficiency of the dev team at a company. One such example is the ESLint written in Node.js. Linters help out with interpreted languages, such as JavaScript, since the compilation step does not exist. For more information on Linting in Node.js using ESLint click on this article.
With the help of a linter, errors are caught while coding. The list of errors can be found at the official documentation for ESLint. Custom linters can be built on top of the ESLint. The Airbnb configuration, developed by Airbnb for internal software development, is open source. It is used by a majority of JS developers across the globe.
- Module Bundlers: Module bundlers are programs that take in various code files and bundles them into a single file. Such programs are usually included with Web frameworks like React. Webpack is another module bundler, it is a static module bundler built on top of Node.js.
- Styling: Styling of webpages is usually done with CSS. Packages such as styled-components have made styling very easy. Styled-components is a library written for React.js. It allows easier integration of styling with JS, resulting in more efficient styling code for user interaction.
- Packages: npm offers many packages to smoothen the process of development. For example, we can access components like text editors, color pickers, authentication components, etc. from npm. Building the frontend is as simple as collecting a bunch of required components and stitching them together to create a beautiful UI.
3. Backend
Since Node.js uses non-blocking IO, a significant reduction in the number of threads required for handling IO requests is possible. This results in making it a light-weight environment. Having looked at the various applications that seamlessly integrate and enhances our web experience, let’s consider the applications that Node.js was initially built for.
- Network and API calls: We looked at the various libraries available that allow us to make API calls. Have a look at it to get a better understanding into HTTP requests. Node.js gives us a greater degree of control over the HTTP requests made. We can specify the headers, set up proxies, and receive responses in formats suitable to our application.
- Database Integration: Node.js has libraries and interfaces that allow seamless integration with databases. CRUD (Create, Read, Update, and Delete) operations are done using JS. Database integrations allow us to handle database operations in JavaScript, making the learning curve for databases a lot easier to grasp.
- Operating System-Level Control over Application: System level programming, considers the computational resources a program will use and it can be controlled using Node.js. JavaScript provides features for concurrency and OS programming.
- Real-Time Applications: Let us look at some examples of real-time applications. They range from software solutions like live streaming, real-time logistics, tracking, social networking platforms, and hardware solutions such as Internet Of Things (IoT) applications. All the features discussed above help in designing systems that are scalable and feature-rich. The advantages of having the codebase predominantly in one language enable developers to debug errors easily and build systems that are easily integrable with each other.
4. Conclusion
We have considered the question of whether Node.js is an environment for frontend or backend. Node.js developed as a server-side runtime environment can be used extensively in the frontend as well. Node.js provides customizability, flexibility, and a large library of packages to help create feature-rich full-stack applications. Until the next article, be legendary.