Table of Contents
Today we are going to learn about a revolutionary technology that is being used to build great web applications: Node.js. You may have heard of it or worked with it; either way, join us as we further explore Node.js. We are going to talk about the history, some of the basics, and a few use case examples that use this revolutionary technology.
1. What is Node.js?
Node.js is a runtime server environment that uses JavaScript on the server side and asynchronous programming. It is a free and open source technology that runs on various platforms (Mac OS X, Unix, Windows, etc.).
Node.js can:
- Create, open, read, write, delete, and close files on the server
- Generate dynamic page content
- Collect form data
- Add, delete, change data in your database
Features
- Easy to learn
- Fast
- No buffering
- Consistent source code
- Massive library support
2. The Early Beginnings
Believe it or not, Node.js is 12 years old! In comparison, JavaScript is 26 years old and the Internet is 32 years old.
In 2009, Ryan Dahl wrote Node.js. At first, Node.js supported only Mac OS X and Linux. Dahl led the development and maintenance and later it was sponsored by Joyent.
The limited possibilities of the most popular web server at the time, Apache HTTP Server in 2009, was criticized by Dahl because it had to handle a lot of connections concurrently (up to 10,000 and more). When there was any blocked code in the entire process, or an implied multiple execution stack in cases of simultaneous connections, it would lead to issues, and this situation had to be resolved by creating code through sequential programming.
On November 8, 2009 at the inaugural European JSConf, the Node.js project was first demonstrated by Dahl. Node.js is a combination the V8 JavaScript Chrome engine, a low-level I/O API, and an event loop.
3. The Evolution
As many browsers competed to offer users the best performance, JavaScript engines also became considerably better. Major browsers worked hard on finding ways to make JavaScript run quicker and offer better support for it. Hence, Node.js was built at the right place and time. It introduced a lot of approaches for JavaScript server-side development and innovative thinking that has helped many developers.
One of the primary factors behind Node.js’ popularity among developers is its support for thousands of open-source libraries, a large majority of which are hosted on the npm website.
There is also a very active community surrounding Node.js with a lot of developer events and conferences, including Node.js Interactive, Node.js Summit, and NodeConf, as well as other regional events.
Web frameworks were developed by the Node.js open-source community to accelerate the development of applications. These frameworks include Connect, Sails.js, Koa.js, Express.js, Feathers.js, socket.io, Derby, Hapi.js, Meteor, and a lot more.
3.1. The journey so far:
2009
2010
- The beginning of Express
- The beginning of socket.io
2011
- Version 1.0 of npm was released
- Companies Uber, LinkedIn, etc. started adopting Node.js
- The beginning of hapi
2012
- Adoption continues and growing rapidly
2013
2014
- IO.js became a major fork of Node.js, “The Big Fork”, with the purpose of introducing ES6 support and moving faster
2015
- The Node.js Foundation began
- IO.js is merged back into Node.js
- npm introduces private modules
- Node.js 4 (versions 1, 2 and 3 never previously released)
2016
- The leftpad incident
- The beginning of Yarn
- The beginning of Node.js 6
2017
- npm focuses more on security
- The beginning of Node.js 8
- HTTP/2
- V8 introduces Node.js in its testing suite, officially making Node.js a target for the JS engine, in addition to Chrome
- Up to 3 billion npm downloads every week
2018
- The beginning of Node.js 10
- ES modules .mjs experimental support
2019
- The beginning of Node.js 12 – 13
- Work on Deno started to move server-side JS into the next decade with modern JavaScript support
2020
3.2. Setting up your first Node.js app
Installation instructions for Node.js can be found at the official Node.js website.
After you have downloaded and installed Node.js on your computer, we can now try to display our first “Hello World” program in a web browser.
Let’s create our first Node.js file named firstfile.js, and add the following code:
firstfile.js
const http = require('http');
const requestListener = function (req, res) {
res.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/html'});
res.end('Hello, World!');
}
const server = http.createServer(requestListener);
server.listen(8080);
This code tells the computer to display “Hello World!” when anyone with a web browser tries to access your computer on port 8080.
Using Command Line Interface
To be able to access the Node.js files, you must first initiate Node.js in the Command Line Interface (CLI) program of your computer. Depending on your operating system, accessing the CLI on your computer will vary. If your are a Windows user, click on the start button and look for “Command Prompt”, or you can simply write “cmd” in the search field for a quick search.
After opening the CLI, go to the folder containing the file myfirstfile.js.
Initiating Node.js File
Before any action can take place, the file created must be initiated by Node.js. To initiate your file, type node myfirstfile.js in your CLI and press Enter.
Hurray! Your computer is now a server. Your computer is accessible on port 8080. Open your internet browser, and type in: http://localhost:8080 to view your “Hello World!” application.
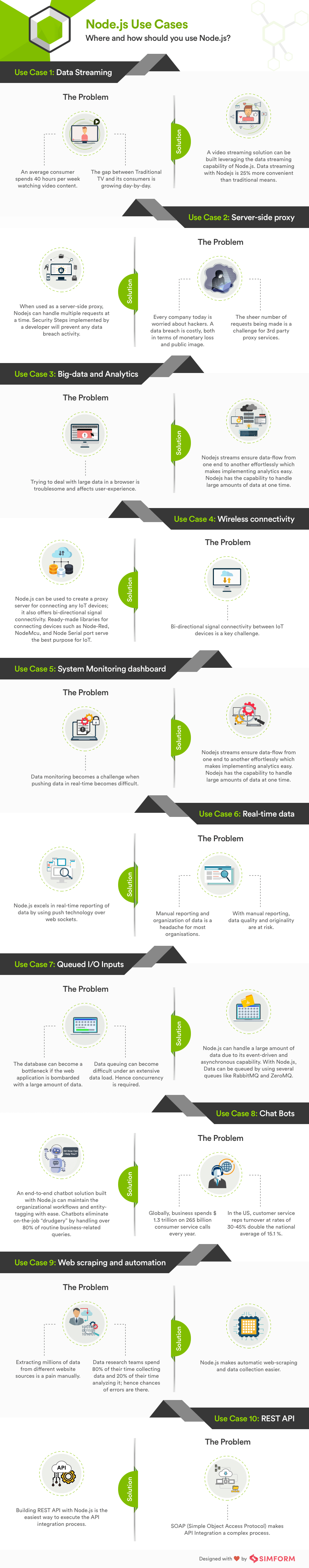
4. The Use Cases of Node.js
Node.js usage is not only limited to building web applications, but it can also be used for implementing various kinds of services such as:
- Backends and servers
- Frontends
- Developing APIs
- Microservices
- Scripting and automation
A few examples of enterprise users of Node.js software include GoDaddy, Groupon, IBM, LinkedIn, Microsoft, Netflix, PayPal, Rakuten, SAP, Voxer, Walmart, and Yahoo!.
Node.js use case Infographic